
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
13
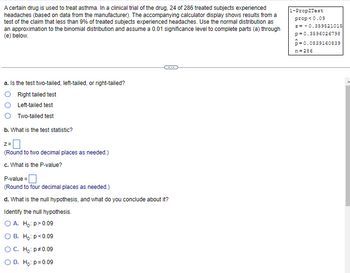
Transcribed Image Text:A certain drug is used to treat asthma. In a clinical trial of the drug, 24 of 286 treated subjects experienced
headaches (based on data from the manufacturer). The accompanying calculator display shows results from a
test of the claim that less than 9% of treated subjects experienced headaches. Use the normal distribution as
an approximation to the binomial distribution and assume a 0.01 significance level to complete parts (a) through
(e) below.
a. Is the test two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed?
Right tailed test
Left-tailed test
Two-tailed test
b. What is the test statistic?
Z=
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
c. What is the P-value?
P-value=
(Round to four decimal places as needed.)
d. What is the null hypothesis, and what do you conclude about it?
Identify the null hypothesis.
O A. Ho: p>0.09
B. Ho: p<0.09
O C. Ho: p *0.09
O D. Ho: p=0.09
1-PropZTest
prop<0.09
z = -0.359521015
p=0.3596026798
p=0.0839160839
n=286

Transcribed Image Text:Decide whether to reject the null hypothesis. Choose the correct answer below.
O A. Reject the null hypothesis because the P-value is greater than the significance level, c.
B. Fail to reject the null hypothesis because the P-value is less than or equal to the significance level, c.
O C. Fail to reject the null hypothesis because the P-value is greater than the significance level, c.
O D. Reject the null hypothesis because the P-value is less than or equal to the significance level, c.
e. What is the final conclusion?
O A.
There is not sufficient evidence to support the claim that less than 9% of treated subjects experienced headaches.
B. There is not sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that less than 9% of treated subjects experienced headaches.
O C. There is sufficient evidence to support the claim that less than 9% of treated subjects experienced headaches.
D. There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that less than 9% of treated subjects experienced headaches.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman