
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
A cam is used to operate a platform that repeatedly lifts boxes for a height of 40 mm as shown. One cycle of the cam has the following motion requirements:
Rise to 40 mm in 1.5 s, Dwell for 0.25 s, Fall for 20 mm in 1 s; Dwell for 0.25 s; Fall a further 20 mm in 1 s and the cycle repeats after this.
The required speed of cam is.............rpm and the angle turned by cam during the Rise motion is...........degrees.
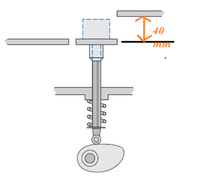
Transcribed Image Text:40
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw the cam clearlyarrow_forward1. A cam must rise in 3 seconds at constant velocity of 0.25 in/sec in the first segment. Then the follower must return to the zero position in 5 seconds with a full return cycloidal motion and then dwell for 3 seconds in segment 3. The final segment will be a full rise cycloidal motion. The total cycle time is 12 seconds, and the maximum height is in the first segment. Full return cycloidal motion 1 y = L + sin 2π Full rise cycloidal motion y = L sin Determine the following: The cam angular velocity. b. The cam rotation segment widths, B1 c. The lift (height) of the constant velocity segment. а. B4 , in degrees. Round off to nearest degree. d. The height at 0 = 180° е. The peak cam linear velocity V(t)peak with zero angular acceleration in segment 4.arrow_forwardA cam have the following specifications: Follower to move outward through 5 cm during 90° of cam rotation, it dwells for the next 60°. The follower then return to its original position through an angle 0R and then dwell for the rest of the cam rotation of 110°. The displacement of the follower is to take place with constant speed motion during both the outward and return strokes. The least radius of the cam is 4 cm. If the cam rotates at 300 r.p.m., construct the displacement, velocity and acceleration diagrams. Also determine The displacement, velocity, acceleration and the pressure angle for the following angles (40°, 75°, 145°, 200°).arrow_forward
- A cam is to give the following motion to a knife-edged follower: 1. Outstroke during 75° of cam rotation; 2. Dwell for the next 60° of cam rotation; 3. Return stroke during the next 80° of cam rotation, and 4. Dwell for the remaining 145° of cam rotation. The stroke of the follower is 30 mm and the minimum radius of the cam is 40 mm. The follower moves with uniform velocity during both the outstroke and return strokes. Draw the profile of the cam when (a) the axis of the follower passes through the axis of the camshaft, and (b) the axis of the follower is offset by 25 mm from the axis of the camshaft. Determine the maximum velocity and acceleration of the follower during its ascent and descent, if the cam rotates at 250 r.p.m. Draw the displacement, velocity and acceleration diagrams for one complete revolution of the camarrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ...arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY