
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
5.46 (a) and (b)
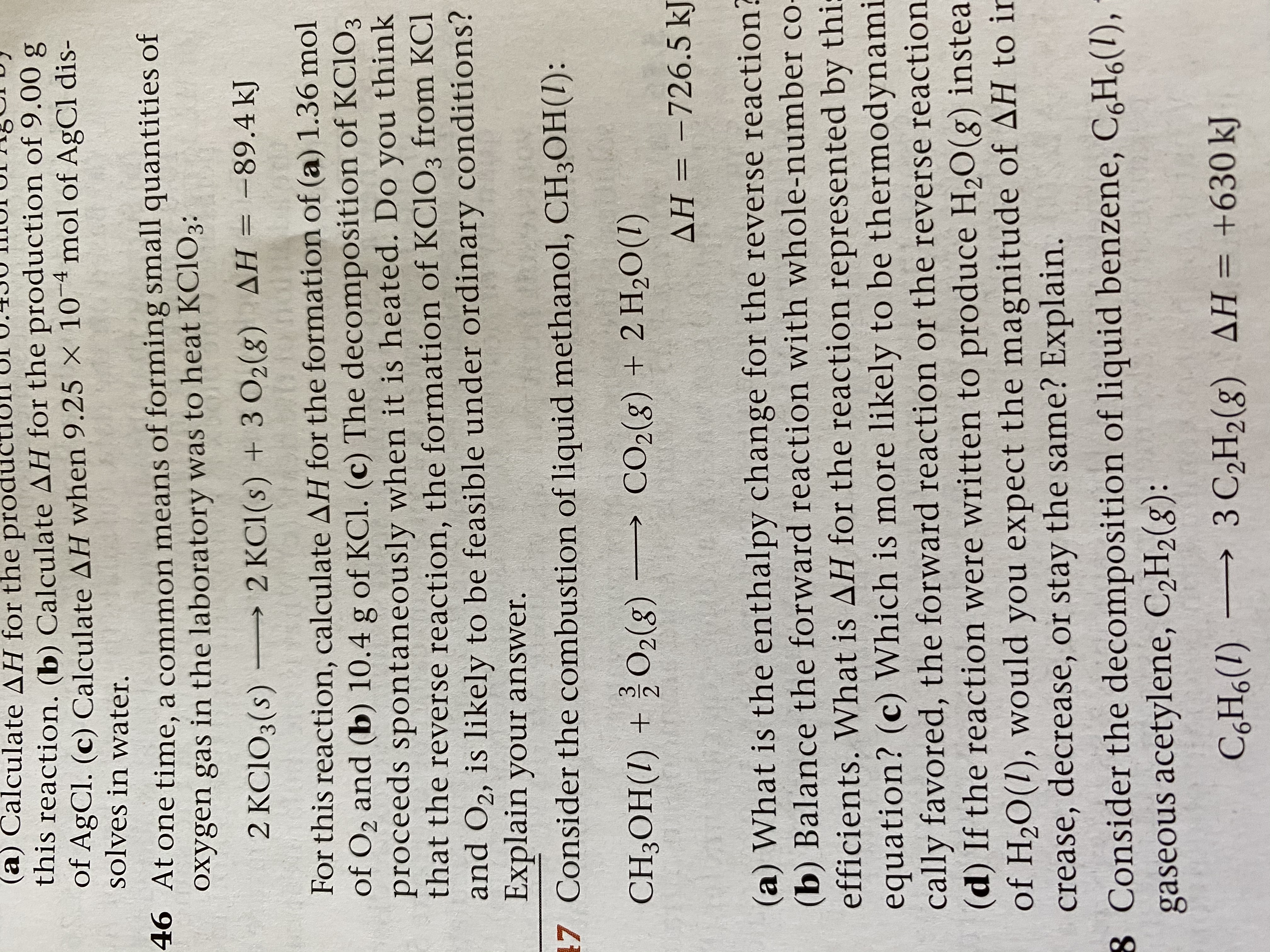
Transcribed Image Text:(a) Calculate AH for the producti
this reaction. (b) Calculate AH for the production of 9.00 g
of AgCl. (c) Calculate AH when 9.25 × 10¯4 mol of AgCl dis-
solves in water.
46 At one time, a common means of forming small quantities of
oxygen gas in the laboratory was to heat KCIO3:
2 KCIO3(s) –→ 2 KC1(s) + 3 O2(8) AH = -89.4 kJ
For this reaction, calculate AH for the formation of (a) 1.36 mol
of O2 and (b) 10.4 g of KCl. (c) The decomposition of KC1O3
proceeds spontaneously when it is heated. Do you think
that the reverse reaction, the formation of KC1O3 from KCl
and O2, is likely to be feasible under ordinary conditions?
Explain your answer.
7 Consider the combustion of liquid methanol, CH3OH(1):
CH3OH(1) + ¿O2(g)
→ CO2(g) + 2 H2O(1)
AH = -726.5 kJ
%3D
(a) What is the enthalpy change for the reverse reaction?
(b) Balance the forward reaction with whole-number co-
efficients. What is AH for the reaction represented by thi:
equation? (c) Which is more likely to be thermodynami
cally favored, the forward reaction or the reverse reaction
(d) If the reaction were written to produce H,O(g) instea
of H20(1), would you expect the magnitude of AH to ir
crease, decrease, or stay the same? Explain.
8 Consider the decomposition of liquid benzene, C,H6(1),
gaseous acetylene, C2H2(8):
C,H6(1) → 3 C2H2(g) AH = +630 kJ
%3D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When the following equation is completed and balanced, what is/are the product(s)? MgO(s) + HCl(aq) --> ? (A) MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l) (B) MgOH2(aq) + Cl2(g) (C) MgOCl2(aq) + H2(g) (D) Mg(s) + Cl2(g) + H2O(l)arrow_forwardo) Silver chloride is soluble in ammonia because the silver ion is reduced True False into its elemental form with ammonia.arrow_forward(Q95) Given the hypothetical reaction A (g) 3 B (g), that has an equilibrium constant of Keg = 0.173. If the current concentration of A = 0.442 M and that of B = 0.395 M, the reaction will proceed forward (favoring %3D products). True Falsearrow_forward
- (a) 1.23 M sugar (C₁₂H₂O₁) solution (density of solution 1.12 g/mL) 1.09 201 (b) 0.849 M NaOH solution (density of solution 1.04 g/mL) m (c) 5.21 M NaHCO, solution (density of solution 1.19 g/mL) m Guided Sarrow_forward35.00 mL of a solution of KIO3 reacted with exactly 35.00 mL of a 0.1000 M solution of KI in acid medium according to the equation I03 + I + H* » I2 + H2O (a) Balance the equation and calculate the molarity of the KIO3 solution. (b) 59.00 mL of this KIO3 is treated with excess pure KI in acid solution and the liberated I, is itrated with 0.1000 N Na2S2O3. What volume of titrant is required?arrow_forward(a) Iz(s) + 5 Cu²* (aq) + 6 H;O(I) –→ 2 103"(aq) + 5 Cu(s) + 12 H*(aq) (b) Hg²*(aq) + 21 (aq) → Hg(1) + Iz(s) (c) H2SO3(aq) + 2 Mn(s) + 4 H¯ (aq) · S(s) + 2 Mn²*(aq) + 3 H2O(I)arrow_forward
- (2) 8. Write the balanced equation for the neutralization reaction between HI and Ba(OH)2 in aqueous solution. Include phases (physical states) in your equation. Use the arrow, not "=".arrow_forward(a) You are about to prepare three solutions of 0.5 M KI, 0.01 M K2S2O8, and 0.01 M Na2S2O3*5H2O in 250 mL volumetric flasks. - Describe how you will go about this, i,e, explain all steps of weighing of solutes, volumetric measurements (filling up with deionised water) ect. Calculate what mass of solute you will need in each of solutions mentioned above that you need to prepare. Show all calculations steps. (b) You are also tasked to fill burettes with the above-mentioned solutions, however, after filling up the solutions, you realised that there is a bubble towards the bottom tip inside the burette. Is it wise to continue with the experiment, while there is a bubble, if NOT explain why. (c) According to the manual's Experimental procedure, one conical flask (flask 1) contains a mixture of 20 mL of the KI solution plus 10 mL of the Na2S2O3 solution, while in the second flask (flask 2) there is 20 mL of the K2S2O8 solution with added five drops of starch solution. Why can't you add…arrow_forward4 help use sig figsarrow_forward
- Write the expression Kc for the following reactions. (a) Fe2+(aq) + Ce4+(aq) ⇋ Fe3+(aq) + Ce3+(aq) (b) CaCO3(s) ⇋ CaO(s) + CO3(g)arrow_forwardPLEASE PROVIDE DETAILED SOLUTION AND GIVE THE EXPLANATION OF CORRECT AND INCORRECT OPTIONS....arrow_forwardIn the following reaction in aqueous solution, the acid reactant is base reactant is HONH2 (aq) + HCO3(aq) = CO32- (aq) + HONH3+ (aq) HONH2; HCO3 HONH3; HONH2 HCO3; HONH2 HCO3; CO3²- HONH2; CO32- and thearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY