
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A bullet of mass mb is fired horizontally with speed vi at a wooden block of mass mw resting on a frictionless table. The bullet hits the block and becomes completely embedded within it. After the bullet has come to rest within the block, the block, with the bullet in it, is traveling at speed vf.
What is the speed of the block/bullet system after the collision?
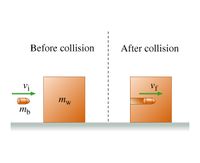
Transcribed Image Text:The diagram illustrates a collision scenario with two main parts: "Before collision" and "After collision."
**Before collision:**
- A bullet with mass \( m_b \) moves towards a wooden block with an initial velocity \( v_i \).
- The wooden block has a mass \( m_w \) and is stationary.
**After collision:**
- The bullet is embedded in the wooden block, and together they move with a final velocity \( v_f \).
**Explanation:**
- The diagram represents an example of an inelastic collision where the bullet and the block stick together after the collision.
- Before the collision, only the bullet has kinetic energy.
- After the collision, both the bullet and block move together with a new velocity.
This visual can help explain principles of momentum conservation and energy transfer in physics.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A hockey puck moving at 0.460 m/s collides with another puck that was at rest. The pucks have equal mass. The first puER is deflected 37.0° to the right and moves off at 0.360 m/s. What is the speed of the second puck after the collision? m/sarrow_forwardOne object is at rest, and another is moving. The two collide in a one-dimensional, completely inelastic collision. In other words, they stick together after the collision and move off with a common velocity. Momentum is conserved. The speed of the object that is moving initially is 29 m/s. The masses of the two objects are 2.8 and 8.8 kg. Determine the final speed of the two-object system after the collision for the case (a) when the large-mass object is the one moving initially and the case (b) when the small-mass object is the one moving initially.arrow_forwardA 5.3 kg sphere makes a perfectly inelastic collision with a second sphere initially at rest (they stick together after the collision). The composite system moves with a speed equal to one third the original speed of the 5.3 kg sphere. What is the mass of the second sphere?arrow_forward
- You release a 3-kg firecracker from rest. At t = 0.4 s, the firecracker is moving downward with speed 4 m/s. At this same instant, the firecracker begins to explode into two pieces with masses mtop = 1 kg and mbottom = 2 kg. At the end of the explosion (t = 0.8 s), the top piece is moving upward with speed 4 m/s.Determine the velocity of the bottom piece at t = 0.8 s.(Hints: Make a momentum vector diagram. Don’t forget to include impulse in your diagram!)arrow_forwardA 92 kg boulder , moving at 5.0 m/s attempts to pass directly across the adit of a mine. Just as the boulder reaches the end of the adit, it was met head-on in midair by two 75 kg miners, both moving in the direction opposite the boulder. One is moving 2.0 m/s, the other at 3.0 m/s . They all become entangled as one mass. What is their velocity after the collision? 18. What is the momentum of a 18 kg object traveling at a constant velocity that has 295 J of kinetic energy?arrow_forwardA 0.01 kg bullet traveling horizontally at the speed of sound (343 m/s) embeds itself into the Kevlar vest of a stationary 100 kg physics professor. The bullet and the professor then move as one. What is the speed of the bullet/professor system after the collision?arrow_forward
- A block with mass M = 5.60 kg is sliding in the positive x-direction at Vi = 8.00 m/s on a frictionless surface when it collides elastically in one dimension with a stationary block with mass m = 1.30 kg. Determine the velocities, Vf and vf, of the objects after the collision. Vf = ? vf = ?arrow_forwardBlocks A and B are moving toward each other on a horizontal, frictionless surface. Block A has a mass of 5 kg and a velocity of +40 m/s, while B has a mass of 10 kg and a velocity of -6 m/s. They suffer a head on, completely inelastic collision. What is the common speed of the blocks after the collision.arrow_forwardBlock A, with a mass of 0.410 kg, is traveling north on a frictionless surface with a speed of 5.00 m/s. Block B, with a mass of 0.480 kg, travels west on the same surface until it collides with A. After the collision, the blocks move off together with a velocity of 3.13 m/s at an angle of 42.5° to the north of west. What was B’s speed just before the collision?arrow_forward
- The drawing shows a collision between two small balls. Ball (1) has a mass of 140 g and is moving along the x-axis with a velocity of 4.60 m/s. It makes a collision with ball (2), which has a mass of 210 g and is initially at rest. After the 60°). What is the magnitude of %D collision, the two balls fly apart with angles as shown in the figure below (a = 58° and B the velocity of ball (2) after the collision? m/s +y m2 m1 +xarrow_forwardBox 1 is sitting at rest. Box 2 is moving to the left when it collides with Box 1 (see figure). This time the two boxes stick together after the collision. The surface is frictionless. Take the right to be the positive x-direction.The mass of Box 1 is 3.80 kg. The mass of Box 2 is 5.60 kg. The speed of Box 2 is 1.20 m/s before the collision. The speed of the boxes together is 0.715 m/s after the collision.What is the total kinetic energy (both boxes) after the collision?arrow_forwardA bullet of mass mb is fired horizontally with speed vi at a wooden block of mass mw resting on a frictionless table. The bullet hits the block and becomes completely embedded within it. After the bullet has come to rest relative to the block, the block, with the bullet in it, is traveling at speed vf.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON