
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
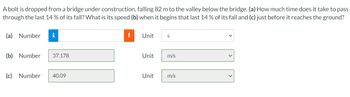
Transcribed Image Text:A bolt is dropped from a bridge under construction, falling 82 m to the valley below the bridge. (a) How much time does it take to pass
through the last 14% of its fall? What is its speed (b) when it begins that last 14% of its fall and (c) just before it reaches the ground?
(a) Number
i
(b) Number 37.178
(c) Number 40.09
!
Unit
Unit
S
m/s
Unit m/s
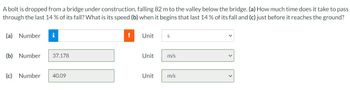
Transcribed Image Text:A bolt is dropped from a bridge under construction, falling 82 m to the valley below the bridge. (a) How much time does it take to pass
through the last 14% of its fall? What is its speed (b) when it begins that last 14% of its fall and (c) just before it reaches the ground?
(a) Number
i
(b) Number 37.178
(c) Number 40.09
!
Unit
Unit
S
m/s
Unit m/s
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Falls resulting in hip fractures are a major cause of injury and even death to the elderly. Typically, the hip's speed at impact is about 2.0m/s. If this can be reduced to 1.3 m/s or less, the hip will usually not fracture. One way to do this is by wearing elastic hip pads. A) if a typical pad is 5.0 cm thick and compresses by 2.0 cm during the impact of a fall, what constant acceleration (in m/s^2 and in g's) does the hip under go to reduce its speed from 2.0 m/s to 1.3 m/s? The acceleration that you found in part "a" may seem very large, but to fully understand its effects on the hip, calculate how long it lasts.arrow_forwardVector A can be expressed in (i,j,k) notation as 5.0i - 4.0j, and vector B as -7.0i + 2.0j. Determine the value of 3A + 2B in terms of magnitude and angle. The angle can be specified either as a value between 0 and 360 degrees counter- clockwise with respect to the positive x-axis, or as a value between 0 and 90 degrees in the appropriate Cartesian quadrant. Paragraph I + v ... 96% 75°F lılıarrow_forwardThe acceleration of an object due to air resistance is a = -bư/m, where v is the %3D speed of the object and m is its mass. What are the SI units of b? O kg/s O kg/s? O kg/m kg/m? O kg - m/s? none of thesearrow_forward
- Your answer is partially correct. A bolt is dropped from a bridge under construction, falling 82 m to the valley below the bridge. (a) How much time does it take to pass through the last 14% of its fall? What is its speed (b) when it begins that last 14% of its fall and (c) just before it reaches the ground? (a) Number i (b) Number 37.178 (c) Number 40.09 eTextbook and Media Hint GO Tutorial Unit Unit Unit S m/s m/sarrow_forward2 Dante plays basketball. After 3 games, he had scored 25 points and after 7 games he had scored 60 points. If Dante continues to score points at this pace, what is a reasonable projection for his total points scored after 24 games? F 115 points G 180 points H 204 points J 260 pointsarrow_forwardHere are three vectors in meters: d1 = -6.60î + 8.70ĵ + 3.50k d 2 = - 2.00î – 4.00ĵ + 2.00k d 3 = 2.00î + 3.00ĵ + 1.00k What results from (a) đ1· ( đ 2 + đ 3 ), (b) đ 1 · ( đ 2 × đ 3), and d 1 x ( d 2 + d 3 ) (c), (d) and (e) for i,j and k components respectively)? (a) Number i Units (b) Number Units (c) Number i Units (d) Number Units (e) Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- You go watch your friend as she runs at a cross country meet. The first time she passes you, your friend runs by going due north at a speed of 4.40 m/s. You move to a different place on the course and twelve minutes after you saw her the first time, your friend runs past you again. This time she is traveling at a speed of 3.80 m/s in the direction 30.0◦ W of S. What is the direction of her average acceleration between those same two times?arrow_forwardAn object's velocity as a function of time in one dimension is given by the expression; v(t) = 3.8t + 6.68 where are constants have proper SI Units. At what time is the object's velocity 61.2 m/s?arrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle is given by v = 29t²-88t - 196, where v is in feet per second and t is in seconds. Plot the velocity v and acceleration a versus time for the first 4 seconds of motion. After you have the plots, answer the questions as a check on your work. -1 Questions: + 0 + 1 When t = 0.5 sec, V = 2 i When t = 3.3 sec, V = i + 3 +s, ft or m When the acceleration is zero, the velocity is i ft/sec, a = ft/sec, a = i i ft/sec. ft/sec² ft/sec²arrow_forward
- A particle of mass m has a time-dependent position vector r(t) = (Rcos(ωt),Rsin(ωt),αt) in Cartesian coordinates, where R, ω and α are positive constants. What are the physical dimensions of R, ω and α? Show that the speed of the particle is constant. Does it mean that the acceleration is zero? Justify.arrow_forwardThe velocity of a particle as a function of time is given by v(t)=(3t-t )i-4 j all in S.I. units. a) What are the dimensions of the "-1 " in the – ti term? What are the units of the "3 " in the 3t i term? b) Find the position vector of the particle, r(t), if r(0) = -5 i- 2j :) Find the time ti > 0 when the position in the i direction is a maximum. d) Find a 1 -> 3 the average acceleration vector in the time interval 1 to 3 seconds.arrow_forwardPart (a) Do this for the range r > R. E = _____ Part (b) Do this for the range r < R. E = _____arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON