
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
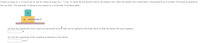
Transcribed Image Text:A block of mass m; = 4.0 kg is put on top of a block of mass mh = 7.0 kg. To cause the top block to slip on the bottom one, while the bottom one is held fixed, a horizontal force of at least 19 N must be applied to
the top block. The assembly of blocks is now placed on a horizontal, frictionless table.
(a) Find the magnitude of the maximum horizontal force F that can be applied to the lower block so that the blocks will move together.
N
(b) Find the magnitude of the resulting acceleration of the blocks.
m/s2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A loaded penguin sled weighing 71.0 N rests on a plane inclined at angle θ = 19.0° to the horizontal (see the figure). Between the sled and the plane, the coefficient of static friction is 0.250, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.160. (a) What is the minimum magnitude of the force ? parallel to the plane, that will prevent the sled from slipping down the plane? (b) What is the minimum magnitude F that will start the sled moving up the plane? (c) What value of F is required to move the sled up the plane at constant velocity?arrow_forwardAn initially stationary box of sand is to be pulled across a floor by means of a cable in which the tension should not exceed 1170 N. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the floor is 0.400. (a) What should be the angle between the cable and the horizontal in order to pull the greatest possible amount of sand, and (b) what is the weight of the sand and box in that situation?arrow_forwardA loaded penguin sled weighing 72.0 N rests on a plane inclined at angle 0 = 22.0° to the horizontal (see the figure). Between the sled and the plane, the coefficient of static friction is 0.270, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.140. (a) What is the minimum magnitude of the force , parallel to the plane, that will prevent the sled from slipping down the plane? (b) What is the minimum magnitude F that will start the sled moving up the plane? (c) What value of F is required to move the sled up the plane at constant velocity? (a) Number i (b) Number i (c) Number i Units Units Units +arrow_forward
- A hawser (a thick docking rope) thrown from a ship to a pier is wrapped two fullturns around a bollard. The tension in the hawser is 7500 N; by exerting a force of150 N on its free end, a dockworker can just keep the hawser from slipping. (a)Determine the coefficient of friction between the hawser and the bollard. (b)Determine the tension in the hawser that could be resisted by the 150-N force ifthe hawser were wrapped three full turns around the bollardarrow_forwardA 2.00 kg block is held in equilibrium on an incline of angle θ = 65° by a horizontal force applied in the direction shown in the figure below. If the coefficient of static friction between block and incline is μs = 0.300, determine the following. (a) the minimum value of N(b) the normal force exerted by the incline on the block Narrow_forwardTwo wooden blocks of masses m1 = 2.0 kg and m2 = 3.0 kg, are joined by an inextensible rope as shown in the figure. The coefficient of static and kinetic friction between the blocks and the surface are 0.60 and 0.35 respectively.If the acceleration of block 1 is 3 m / s2, calculate:(a) The value of the magnitude of the force F(b) The tension of the rope.arrow_forward
- A block is pushed across a horizontal surface by the force shown. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface is 0.39, F = 45 N, 0 = 19°, and M = 2.5 kg, F M (a) What is the magnitude of the normal force, applied by the contact surface on the block, in (N)? (b) What is the magnitude of the friction force on the block in (N)? (c) What is the magnitude of the acceleration (in m/s²) of the block?arrow_forward(a) What is the maximum frictional force in the knee joint of a person who supports 66.0 kg of her mass on that knee? (b) During strenuous exercise it is possible to exert forces to the joints that are easily ten times greater than the weight being supported. What is the maximum force of friction under such conditions? The frictional forces in joints are relatively small in all circumstances except when the joints deteriorate, such as from injury or arthritis. Increased frictional forces can cause further damage and pain.arrow_forwardA particle, of mass 6 kg, is in equilibrium on a rough horizontal plane under a force of magnitude T N, which acts at an angle 15 above the horizontal. Given the coefficient of friction between the particle and the rough horizontal plane is 0.35, what values could T take?arrow_forward
- The force P is applied to the 58-kg block when it is at rest. Determine the magnitude and direction of the friction force exerted by the surface on the block if (a) P = 0, (b) P = 180 N, and (c) P = 294 N. (d) What value of P is required to initiate motion up the incline? The static and kinetic coefficients of friction between the block and the incline are μs = 0.21 and Uk = 0.17, respectively. The friction force is positive if up the incline, negative if down the incline. Answers: (a) F= (b) F= (c) F= (d) P= 58 kg 13° i i i i 21° H₂=0.21 H = 0.17 Z z z N Narrow_forwardAn initially stationary box of sand is to be pulled across a floor by means of a cable in which the tension should not exceed 1090 N. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the floor is 0.330. (a) What should be the angle between the cable and the horizontal in order to pull the greatest possible amount of sand, and (b) what is the weight of the sand and box in that situation? (a) Number i (b) Number i Units Unitsarrow_forwardAn initially stationary box of sand is to be pulled across a floor by means of a cable in which the tension should not exceed 1070 N. The coefficient of static friction between the box and the floor is 0.480. (a) What should be the angle between the cable and the horizontal in order to pull the greatest possible amount of sand, and (b)what is the weight of the sand and box in that situation?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON