
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
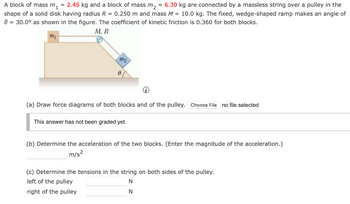
Transcribed Image Text:A block of mass m₁
=
2.45 kg and a block of mass m₂
=
6.30 kg are connected by a massless string over a pulley in the
shape of a solid disk having radius R = 0.250 m and mass M = 10.0 kg. The fixed, wedge-shaped ramp makes an angle of
0 = 30.0° as shown in the figure. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.360 for both blocks.
m₁
M, R
m2
(a) Draw force diagrams of both blocks and of the pulley. Choose File no file selected
This answer has not been graded yet.
(b) Determine the acceleration of the two blocks. (Enter the magnitude of the acceleration.)
m/s²
(c) Determine the tensions in the string on both sides of the pulley.
left of the pulley
right of the pulley
N
N
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 1 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 4.00 kg mass is attached to a vertical rod by the means of two 1.25 m strings which are 2.00 m apart. The mass rotates about the vertical shaft producing a tension of 80.0 N in the top string. (a) What is the tension on the lower string? (b) How many revolutions per minute does the system make?arrow_forwardThe diagram shows two masses connected by a massless, stetchless string. The block on the inclined surface has a mass of 1.58 kg and the surface is frictionless. The hanging mass is 0.322 kg. The incline makes an angle of 18.1° relative to horizontal. The pulley is MASSLESS and free to rotate. The arrangement is released from rest. How fast will the hanging mass be traveling once it has descended a distance of 0.606 m?arrow_forwardThe figure shows a conical pendulum, in which the bob (the small object at the lower end of the cord) moves in a horizontal circle at constant speed. (The cord sweeps out a cone as the bob rotates.) The bob has a mass of 0.025 kg, the string has length L = 1.2 m and negligible mass, and the bob follows a circular path of circumference 0.69 m. What are (a) the tension in the string and (b) the period of the motion? Сord L. Bob (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- I'm struggling to understand how to do this: A block of mass m1 = 1.55 kg and a block of mass m2 = 6.05 kg are connected by a massless string over a pulley in the shape of a solid disk having radius R = 0.250 m and mass M = 10.0 kg. The fixed, wedge-shaped ramp makes an angle of θ= 30.0°. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.360 for both blocks. Use g=9.8 m/s2. (a) Determine the acceleration of the two blocks. (Enter the magnitude of the acceleration.) (b) Determine the tensions in the string on both sides of the pulley (left side and right side).arrow_forward1.0m 3.0m 0.5m mi m, PA N, 5. The drawing above shows two objects on a board supported at two locations. The m; = 40 kg (centered over P), m2=20 kg and m3=10 kg. a. Show the forces acting on the board below with arrows with labels beginning at their approximate point of application (see example for the force exerted by m;). (Don't forget the gravitational forces acting on the board.) P F1arrow_forwardHand written solutions are strictly prohibited.arrow_forward
- The two blocks are connected by a massless rope that passes through a pulley. Mass of first block is m1 = 1 kg, mass of the second block is m2= 5 kg. Mass of the pulley is M = 2 kg. Radius of the pulley is R= 10 cm. First block is placed on the 30 incline and the second block is hanging above the table at the height of 40 cm. Then, the system is released and the first block starts sliding up the incline and the second block starts falling toward the table. a) forces that apply to the pulley. b) pulley. Consider the pulley to be a disc and use disc's moment of inertia(/ = MR?/2) c) acceleration of the blocks. Draw the FBD for both blocks and draw separately the Write down equations of motion for the blocks and Using the equations from part (b) to calculate the Finally, find the velocity that the second block will d) acquire just before hitting the table using energy. m1 m2arrow_forwardChildren playing pirates have suspended a uniform wooden plank with mass M = 13.4 kg, length ℓ = 2.40 m, and angle θ = 35.0°, as shown in the figure. Sophia, with a mass of m = 21.6 kg, is made to "walk the plank" and is d = 1.5 m from reaching the end of the plank. What is the tension acting on the rope at the end (i.e value of F3)?arrow_forwardIn the figure, block 1 has mass m, = 440 g, block 2 has mass m2 = 590 g, and the pulley is on a frictionless horizontal axle and has radius R= 5.4 cm. When released from rest, block 2 falls 78 cm in 5.3 s without the cord slipping on the pulley. (a) What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the blocks? What are (b) tension T2 (the tension force on the block 2) and (c) tension T1 (the tension force on the block 1)? (d) What is the magnitude of the pulley's angular acceleration? (e) What is its rotational inertia? Caution: Try to avoid rounding off answers along the way to the solution. Use g = 9.81 m/s?. m, m2 (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Units (c) Number i Units (d) Number i Units (e) Number Units > > > >arrow_forward
- One end of a string is wrapped several times around a pulley of mass 0.92 kgkg that is oriented vertically. The other end of the string is connected to a block of mass 0.35 kg, which is then slowly lowered until the string becomes taut. After which the person lets go of the block completely, thus allowing the block to descend and the pulley to rotate in unison. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the block after the person has let go?arrow_forwardA system comprised blocks, a light frictionless pulley, and connecting ropes is shown in the figure. The B block has a mass of 9.3 kg and is on a perfectly smooth horizontal table. The surfaces of the A block, which has a mass of 8.2 kg, are rough, with μk=μk= 0.25 between the block and the table. If the C block with mass 9.9 kg accelerates downward when it is released, find its acceleration.arrow_forwardConsider two boxes initially at rest as shown, each of mass 5.0 kg, that are connected by a massless string over a pulley of radius 5.0 cm and rotational inertia equal to 4.0 x 10-3 kg·m². The coefficient of kinetic friction between the inclined surface and the box is 0.15. Find the speed of the boxes just after they have moved 1.0 m. Justify approach taken as you begin your solution. 30° m marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON