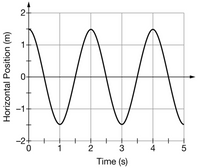
A block of mass .3 kg on a horizontal surface is attached to a horizontal spring of negligible mass. The other end of the spring is attached to a wall, and there is negligible friction between the block and the horizontal surface. The block-spring system is released from rest and undergoes
A.Determine the average velocity of the block from the slope of the curve between 0 s & 1 s then calculate KE using this average velocity.
B.Determine the average speed of the block from the slope of the curve between .2 s & .8 s then calculate KE using this average velocity.
C.Determine the average speed of the block from the slope of the curve between .4 s & .6 s then calculate KE using this average velocity.
D.Determine the average speed of the block from the slope of the curve between .45 s & .55 s then calculate KE using this average velocity.
Hello. Since your question has multiple sub-parts, we will solve the first three sub-parts for you. If you want the remaining sub-parts to be solved, then please resubmit the whole question and specify those sub-parts you want us to solve.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 10 steps

- The bumper cars at the state fair have identical 1.0-m-long horizontal springs protruding from the front of each car. A 250 kg car traveling at 1.5 m/s has a head-on collision with a 150 kg car traveling at 2.5 m/s in the opposite direction. The two springs are each compressed by 19 cm when the cars are instantaneously at rest, just before they rebound.What is the spring constant of the springs?arrow_forwarda 0.50 kg block attached to an ideal spring with a stiffness (spring) constant of 80.0 N/m oscillates on a horizontal frictionless surface. The total mechanical energy is 0.12 J. How fast is the block moving when it is 3.5 cm from the equilibrium point?arrow_forwardPlease type the work. Type the step by step explanationarrow_forward
- In a science museum, you may have seen a Foucault pendulum, which is used to demonstrate the rotation of the earth. In one museum's pendulum, the 110 kg bob swings from a 15.0-m-long cable with an amplitude of 5.0°. What is the pendulum's maximum kinetic energy?arrow_forwardA and B were a part of a potential energy topic: I kept getting a wrong answer. I would like some guidance on them. a. The potential energy of an object attached to a spring is 2.60 J at a location where the kinetic energy is 1.70 J. If the amplitude ? of the simple harmonic motion is 20.0 cm, calculate the spring constant ? (N/m) and the magnitude of the largest force ?spring,max (N) that the object experiences b. A 0.200-kg object attached to a spring oscillates on a frictionless horizontal table with a frequency of 3.00 Hz and an amplitude of 20.0 cm. What is the maximum potential energy ?max of the system? ?max=_J What is the displacement ? of the object when the potential energy is one‑half of the maximum? ?= _m What is the potential energy ? when the displacement of the object is 2.00 cm.arrow_forwardA horizontal springwith a spring constant of 25 N/mis lying on a frictionless surface. One end of the spring isattaches to a wall while the other end is connected to a 0.5 kgobject. The spring and object are compressed by0.07m, released from rest, and subsequently oscillate back and forth. a.Calculate the total energy of the system. b.Calculate the kinetic and potential energies of the system when the spring isstretchedby 0.03m. c.What is the speed of the object at the instant when the spring isstretchedby 0.03m relative to its unstrained length? d.What is the maximum speed of the object?arrow_forward
- Needs Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forwardA 14,000 N car starts from rest and rolls down a hill from a height of 10.0 m (see figure). It then moves across a level surface and collides with a light spring-loaded guardrail. (a) Neglecting any losses due to friction, and ignoring the rotational kinetic energy of the wheels, find the maximum distance the spring is compressed. Assume a spring constant of 1.6 x 106 N/m. ____m(b) Calculate the magnitude of the maximum acceleration of the car after contact with the spring, assuming no frictional losses. ____ m/s2(c) If the spring is compressed by only 0.30 m, find the change in the mechanical energy due to friction._____ Jarrow_forwardA 50.0 cm long spring with spring constant 237 N/m has a mass 1.8 kg attached to it, and it can oscillate on a horizontal table without any friction. The spring is pulled by a distance 5 cm from the resting position and released. What is the kinetic energy (in joules) of the mass at the instant when the length of the spring is 49 cm.arrow_forward
- A mass resting on a horizontal, frictionless surface is attached to one end of spring; the other end is fixed to a wall. It takes 3.5 J of work to compress the spring by 0.11 m. If the spring is compressed, and the mass is released from rest, it experiences a maximum acceleration of 15 m/s2. Find the value of the spring constant. Find the value of the mass.arrow_forwardA horizontal spring attached to a wall has a force constant of k = 780 N/m. A block of mass m = 1.90 kg is attached to the spring and rests on a horizontal, frictionless surface as in the figure below. www x=0 x = x;/2 m x = x₁ (a) The block is pulled to a position x; = 7.00 cm from equilibrium and released. Find the elastic potential energy stored in the spring when the block is 7.00 cm from equilibrium and when the block passes through equilibrium. x (cm) Elastic Potential Energy (J) 7.00 0 (b) Find the speed of the block as it passes through the equilibrium point. m/s (c) What is the speed of the block when it is at a position x;/2 = 3.5 cm? m/s (d) Why isn't the answer to part (c) half the answer to part (b)?arrow_forwardA block on a horizontal surface is attached to a horizontal spring of negligible mass. The other end of the spring is attached to a wall, and there is negligible friction between the block and the horizontal surface. The block-spring system is then placed into simple harmonic motion. The figure shows a graph of the velocity of the block as a function of time. At which of the following times does the block-spring system have maximum spring potential energy? A.1.5 s B.2.5 s C.2 s D.4.5 sarrow_forward