
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
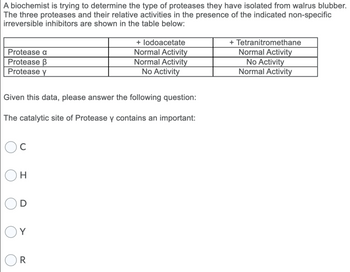
Transcribed Image Text:A biochemist is trying to determine the type of proteases they have isolated from walrus blubber.
The three proteases and their relative activities in the presence of the indicated non-specific
irreversible inhibitors are shown in the table below:
Protease a
Protease B
Protease y
Given this data, please answer the following question:
The catalytic site of Protease y contains an important:
с
H
Y
+ lodoacetate
Normal Activity
Normal Activity
No Activity
R
+ Tetranitromethane
Normal Activity
No Activity
Normal Activity
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Which of the following statements is not true about the catalytic triad in chymotrypsin? Group of answer choices the side chain of the serine 195 is hydrogen bonded to the imidazole ring of histidine the -NH group of the imidazole ring of histidine is hydrogen bonded to the carboxylate group of aspartate 102 the histidine residue serves to position the aspartate 102 side chain and to polarize its carboxylate group so that it is poised for deprotonation histidine acts as a general base catalyst none of thesearrow_forwardDuring the early stages of an enzyme purification protocol, when cells have been lysed but cytosolic components have not been separated, the reaction velocity-versus-substrate concentration is sigmoidal. As you continue to purify the enzyme, the curve shifts to the right. Explain your results. This is an allosteric enzyme and you must use a Lineweaver-Burk plot to determine KM and Vmax correctly. This is an enzyme that displays Michaelis-Menten kinetics and you purify away an inhibitor. This is an allosteric enzyme and during purification you purify away an activator. This is an allosteric enzyme displaying a double-displacement mechanism and during purification you purify away one of the substrates: This is an enzyme that displays Michaelis-Menten kinetics, and you must use a Lineweaver-Burk plot to determine KM and Vmax correctly.arrow_forwardIdris has successfully extracted enzymatic proteins from the fish viscera (intestines and stomach). After homogenization and centrifugation, he managed to pool the crude enzyme extract. He is characterizing the enzymes. Please help Idris by answering the followingquestions:(a). How do I determine the enzyme activity? Please give the unit. (b) How do I get the specific activity of this enzyme? Please give the unit.arrow_forward
- BIM-46187 is a protein inhibitor that binds to the a-subunit of the G. protein. It prevents the GDP/GTP exchange and prevents activity of the G protein. Which of the following would you expect to see lower levels of as a result? You can select more than or answer. S-S NH2 Mol. M: 795.11 Image: https://aobious.com/aobious/protein-inhibitors/1086-bim-46187.html Select one or more: O a. Cyclic AMP (CAMP) O b. Tyrosine kinase O . HSP O d. Adenylyl Cyclase (AC) O e. DAG O f. JAK O g. IP3arrow_forwardWhat is the importance in glycosylation in rtPA in terms of its activity as a protein therapeutic?arrow_forwardDescribe a common feature at the active site of serine proteases and acetyl cholinesterasearrow_forward
- The objective is to study a novel protease P isolated from the digestive tract of an Amazonian insect. This protease can exist into two forms Pi and Pa which have identical amino acid sequences (both of 80 kDa). However, only Pa shows proteolytic activity. To better understand the activation mode of Pi (inactive form) in Pa (active form), the following experiment was done using DIPF. DIPF (diisopropylphosphofluoridate) is a well-known irreversible inhibitor of serine proteases. It reacts with the catalytic serine residue of the active site of proteases as shown below: Enzyme -CH₂OH + CH(CH3)2 O F-P=0 O CH(CH3)2 Diisopropylphospho- fluoridate (DIPF) Enzyme -CH,—O CH(CH3)2 O <=0 O CH(CH3)2 DIP-Enzyme Both proteases Pa and P₁ were incubated with 32P-DIPF for 30 min at 37°C, and then dialysed to remove excess of unreacted radiolabelled reagent. The two proteases were then analyzed in Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE), with and without 2-mercaptoethanol.…arrow_forwardThe following data describe the catalysis of cleavage of peptide bonds in small peptides by a protease: Substrate K (1/s) K₁, (mM) k./K₁ (mM/s) A 0.1 10 B 1 1 10 0.1 100 0.02 8,000 0.05 10,000 0.5 Use this information to answer the next three questions. BODEF с D E F 0.01 1 100 5,000 160,000 20,000 4. Which substrate binds to the enzyme with the highest affinity? a. A b. B C. C d. D e. E f. Farrow_forwardDescribe type I, II, and III L-asparaginases. Mention characteristics and differences between them with respect to enzyme kinetics (rate, km, etc).arrow_forward
- Mechanistic probes often require the use of an electrophilic functional group to interact with an especially-reactive amino acid in the protein active site. For each of the follow functional groups that can be used in a mechanistic probe, provide a structure of the product. asaparrow_forwardWhen performing his experiments on protein refolding, Christian Anfinsen obtained a quite different result when reduced ribonuclease was reoxidized while it was still in 8 M urea and the preparation was then dialyzed to remove the urea. Ribonuclease reoxidized in this way had only 1% of the enzymatic activity of the native protein. Why were the outcomes so different when reduced ribonuclease was reoxidized in the presence and absence of urea?arrow_forwardPlease provide Typed solution in details, you can use only handwritten diagramarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON