
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
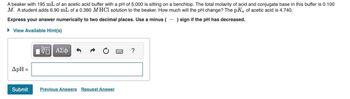
Transcribed Image Text:A beaker with 195 mL of an acetic acid buffer with a pH of 5.000 is sitting on a benchtop. The total molarity of acid and conjugate base in this buffer is 0.100
M. A student adds 6.90 mL of a 0.360 M HCl solution to the beaker. How much will the pH change? The pKa of acetic acid is 4.740.
Express your answer numerically to two decimal places. Use a minus (-) sign if the pH has decreased.
► View Available Hint(s)
ApH =
Submit
VE ΑΣΦ
Previous Answers Request Answer
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Defining buffer solution!
VIEW Step 2: Calculation for moles of acid and base!
VIEW Step 3: Calculation for moles of acetic acid and acetate ion!
VIEW Step 4: Calculation for moles of HCl added!
VIEW Step 5: Formation of BCA table!
VIEW Step 6: Calculation for pH of buffer solution after the addition of HCl!
VIEW Step 7: Calculation for change in pH!
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 8 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A chemistry graduate student is given 450. mL of a 1.50M propanoic acid (HC₂HCO₂) solution. Propanoic acid is a weak acid with K=1.3 × 10¯. mass of NaC₂H₂CO₂ should the student dissolve in the HC₂H5CO₂ solution to turn it into a buffer with pH = 4.72? 2 You may assume that the volume of the solution doesn't change when the NaC₂H-CO₂ is dissolved in it. Be sure your answer has a unit symbol, and round it to 2 significant digits. 0 x10 X What 5arrow_forwardPlease help!arrow_forwardA beaker with 1.50×102 mL of an acetic acid buffer with a pH of 5.000 is sitting on a benchtop. The total molarity of acid and conjugate base in this buffer is 0.100 M. A student adds 6.70 mL of a 0.390 M HCl solution to the beaker. How much will the pH change? The pKa of acetic acid is 4.740.arrow_forward
- Payliarrow_forwardA beaker with 195 mLmL of an acetic acid buffer with a pH of 5.000 is sitting on a benchtop. The total molarity of acid and conjugate base in this buffer is 0.100 MM. A student adds 7.70 mLmL of a 0.440 MM HClHCl solution to the beaker. How much will the pH change? The pKapKa of acetic acid is 4.740. Express your answer numerically to two decimal places. Use a minus ( −− ) sign if the pH has decreased.arrow_forwardA buffer with pH = 8.96 must be created. 8.90 g of the acid component of the best buffer system will be used, and the volume of the solution will be 1 L. Choose which is the best buffer system, then compute the mass of the salt or base component of the chosen system. Choices: HClO (Ka = 2.9 x 10-8 , 52.46 g/mol)& KClO (90.55 g/mol) NH3 (Ka = 5.65 x 10-10 , 17.031g/mol) &NH4Cl (53.491 gmol) CH3COOH (Ka = 1.77 x 10-5 , 60.052 g/mol) & CH3COOK (98.15 g/mol) HClO2 (Ka = 1.1 x 10-2 , 68.46 g/mol)) & KClO2 (106.55 g/mol)arrow_forward
- Acetic acid has a Ka of 1.8 x 10¬º. Three acetic acid/acetate buffer solutions, A, B, and C, were made using varying concentrations: A. [acetic acid] ten times greater than [acetate], B. [acetate] ten times greater than [acetic acid], and C. [acetate] = [acetic acid]. Match each buffer to the expected pH. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. • View Available Hint(s) Reset Help [acetate] ten times greater than [acetic acid] [acetate] = [acetic acid] [acetic acid] ten times greater than [acetate] pH = 3.74 pH = 4.74 pH = 5.74arrow_forwardA beaker with 1.20×102 mL of an acetic acid buffer with a pH of 5.000 is sitting on a benchtop. The total molarity of acid and conjugate base in this buffer is 0.100 M. A student adds 8.00 mL of a 0.330 M HCl solution to the beaker. How much will the pH change? The pKa of acetic acid is 4.740.arrow_forwardA beaker with 1.0 x 10^2 mL of an acetic acid buffer with a pH of 5.000 is sitting on a benchtop. The total molarity of acid and conjugate base in this buffer is 0.100 M. A student adds 8.80 mL of a 0.360 M HCl solution to the beaker. How much will the pH change? The pKa of acetic acid is 4.740.arrow_forward
- A buffer is made with 0.50 M weak acid and 0.50 M sodium salt of the conjugate base. The pKa of the weak acid is 9.30 After the addition of a small amount of strong concentrated acid, the new equilibrium concentrations are 0.6 M weak acid and 0.4 M base. Calculate the new pH. Enter result with 2 decimal places, digits only.arrow_forwardHow many grams of ammonium chloride must be added to 0.53 L of 1.7 M ammonia to prepare a pH = 10.01 buffer? (See the Acid-Base Table.)arrow_forward9 If the dissociation constant of a weak acid is 1.4 x 10-5, at what ratio should you adjust the concentration of the weak acid and its conjugate base in order to prepare a buffer that has a pH of 4.85? a) 0.100 M weak acid with 0.0100 M conjugate base b) 0.0100 M weak acid with 0.100 M conjugate base c) 0.100 M weak acid with 0.200 M conjugate base d) 0.300 M weak acid with 0.300 M conjugate base e) 0.500 M weak acid with 0.250 M conjugate basearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY