Question
A bead of mass m = 6.20 kg is released from point A and slides on the frictionless track shown in Figure P5.30. The height of A is ha = 5.90 m.
Figure P5.30
(a) Determine the bead's speed at points B and C.
(b) Determine the net work done by the force of gravity in moving the bead from A to C
| point B | m/s |
| point C | m/s |
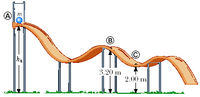
Transcribed Image Text:### Physics of a Roller Coaster Track
This diagram illustrates a section of a roller coaster track with significant points marked as A, B, and C:
- **Point A**: This is the starting point, where a ball with mass \( m \) is placed at a height \( h_a \). The height of point A indicates the potential energy at the start of the track.
- **Point B**: The track descends and then ascends to point B, which is located 3.20 meters above the ground. As the ball moves to this point, it converts some of its initial potential energy to kinetic energy and then back to potential energy.
- **Point C**: The next valley in the track, with point C at a height of 2.00 meters above the ground. At this point, the ball would have less potential energy than at point B but more kinetic energy after descending.
The track design showcases energy transformation principles, where potential energy is highest at point A and varies as the ball travels along the path, changing to kinetic energy as it moves. This demonstrates the conservation of mechanical energy in a frictionless system.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- During a rockslide, a 390 kg rock slides from rest down a hillside that is 460 m long and 300 m high. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the rock and the hill surface is 0.24. If the gravitational potential energy U of the rock-Earth system is set to zero at the bottom of the hill, what is the value of U just before the slide?1.15×106 J How much mechanical energy is dissipated by frictional forces during the slide? What is its speed then? What is the kinetic energy of the rock as it reaches the bottom of the hill?arrow_forwardYou may have noticed runaway truck lanes while driving in the mountains. These gravel-filled lanes are designed to stop trucks that have lost their brakes on mountain grades. Typically, such a lane is horizontal (if possible) and about 40.0 m long. Think of the ground as exerting a frictional drag force on the truck. A truck enters a typical runaway lane with a speed of 59.0 mph ( 26.4 m/s ). Use the work-energy theorem to find the minimum coefficient of kinetic friction between the truck and the lane to be able to stop the truck.arrow_forwardIn the figure, a constant force F a of magnitude 84.0 N is applied to a 3.0 kg shoe box at angle = 57.0°, causing the box to move up a frictionless ramp at constant speed. How much work is done on the box by F awhen the box has moved through vertical distance h = 0.35 m? Number i Unitsarrow_forward
- A 10.0-kg particle, starting at point A at a height of 5.00 m above the ground with an initial velocity of 8.00 m/s, is moving down the curved runway. Upon leaving the runway, the particle shoots straight upwards to a height of 7.00 m above the ground before falling back down. What is the work done by nonconservative forces on the ball?arrow_forwardM PAMP7 ** F20 A student pulls a crate of mass M up the inclined surface the distance d. The surface rises 0 degrees above the horizontal, as shown in the figure How much work does gravity do on the crate? Please use the following values: M = 11.9 kg, 0 = 26.9°, d = 5.88 m, g 9.80 m/s (PAMP716F20) a) 0612 J b) О310J c) O-612 J d) 0 686 J e) O-310 Jarrow_forwardA block of mass m = 4.20 kg is released from rest from point and slides on the frictionless track shown in the figure below. (Assume h = 6.00 m.) h₂ m 3.20 m 2.00 m (a) Determine the block's speed at points and Ⓒ. point Ⓡ point Ⓒ m/s m/s (b) Determine the net work done by the gravitational force on the block as it moves from point J to point Ⓒarrow_forward
- Problem1. A block slides on a rough horizontal surface from point A to point B. A force (magnitude P = 2.0 N) acts on the block between A and B, as shown. Points A and B are 1.5 m apart. (a) How much work is done on the block by the force P? (b) If the kinetic energies of the block at A and B are 6.0 J and 4.0 J, respectively, how much work is done on the block by the net force as the block moves from A to B? (c) What is the work done by the friction force? 40° Barrow_forwardStarting from rest, a 6.2-kg block slides 3.2 m down a rough 37-degree incline. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the incline is μk = 0.55. a) Determine the work done by the friction force between block and incline. b) Determine the work done by the normal force. c) Determine the net work done on the block.arrow_forwardplease help.arrow_forward
- D & E PLEASEarrow_forwardA 69.0-kg athlete leaps straight up into the air from a trampoline with an initial speed of 8.9 m/s. The goal of this problem is to find the maximum height she attains and her speed at half maximum height. What is the gravitational potential energy associated with the athlete? Write a general equation for energy conservation in this case and solve for the maximum height. Substitute and obtain a numerical answer. Write the general equation for energy conservation and solve for the velocity at half the maximum height. Substitute and obtain a numerical answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios