
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
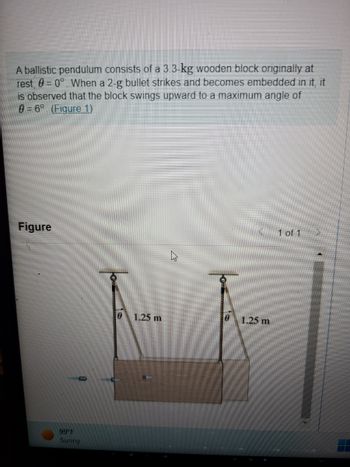
Transcribed Image Text:A ballistic pendulum consists of a 3.3-kg wooden block originally at
rest, 0 = 0°. When a 2-g bullet strikes and becomes embedded in it, it
is observed that the block swings upward to a maximum angle of
0 = 6°. (Figure 1)
Figure
99 F
Sunny
0 1.25 m
0
1.25 m
1 of 1
Transcribed Image Text:▼
Part A
Estimate the speed of the bullet.
Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units.
UB=
Submit
μÅ
Value
Provide Feedback
Request Answer
Units
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 5 A solid sphere of radius R = 0.15 m and mass m = 0.9 kg purely rolls with velocity v = 1.1 m/s along a horizontal surface before striking a low curb of height h = 0.05 m. The impact with the kerb can be assumed to involve no rebound so that the ball pivots about contact point P. The moment of inertia of the sphere is IG = (2/5) mR². Ө Calculate the following: (a) the angular velocity of the ball before impact; (b) the kinetic energy of the ball before impact; g G (c) the angular momentum of the ball around contact point P just before impact (CW +ve); hint: account for both linear and angular motion in the calculation A Moving to another question will save this response. (d) the angular velocity of the ball just after impact (CW +ve). hint: calculate the moment of inertia of the ball around point P using parallel axis theorem h T >>arrow_forwardA solid sphere of mass M and radius R rolls without slipping along a table at speed v. What is its kinetic energy? Mv2/5 Mv2/2 Mv2 3Mv2/2 7Mv2/10arrow_forwardThose data are for questions 15 to 20 The 5-lb rod AB with a length of l=2 ft is hanging in the vertical position. A 2-lb block , sliding on a smooth horizontal surface with a velocity of 10 ft/s, strikes the rod at its end B. e = 0.8. The goal is to find the linear velocity of the block and the angular velocity of the bar just after collision. Step 5: Find the linear velocity of the block after impact. Give your answer in ft/s with 1 decimal.arrow_forward
- applied mechanics 2arrow_forwardThe 46-kg rod is released from rest when 0 = 45° . (Figure 1) Figure B 1.5 m 0 k = 300 N/m 1 of 1 Part A Determine the angular velocity of the rod when 0 = 0°. The spring is unstretched when 0 = 45°. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. W2 = Submit 19 Value μA Provide Feedback X Incorrect; Try Again Units Previous Answers Request Answer ?arrow_forwardRod OA rotates counterclockwise with an angular position - 2t rad, where t is in seconds. The double collar B is pin-connected together such that one collar slides over the rotating rod and the other collar slides over the circular hoop rod described by the equation r = 1.6cose m. If the total mass of both collars is 0.5 kg and of the rod and hoop are negligible, when = 30° which takes t = ()(180) sec, determine the circumferential acceleration of the collars, ag. [m/s2] (sign sensitive) 6=ki 16 cos 8.arrow_forward
- A bullet (W₁ = 3.5 oz) with a is fired horizontally with a velocity v₁ = 1675 ft/sec into the block (W₂ = 5.7 lb) of soft wood initially at rest on the horizontal surface. The bullet emerges from the block with the velocity v₂ = 1280 ft/sec, and the block is observed to slide a distance of d = 7.3 ft before coming to rest. Determine the coefficient of kinetic friction μk between the block and the supporting surface. Answer: Uk= i W₁ W₂arrow_forwardConsider a slender rod AB with a length l and a mass m. The ends are connected to blocks of negligible mass sliding along horizontal and vertical tracks. If the rod is released with no initial velocity from a horizontal position as shown in Fig.A, determine its angular velocity after it has rotated through an angle of θ (see Fig B) using the conservation of energy method. (Hint: Moment of inertia of rod about G = (1/12)ml2 The kinetic energy of a rigid body in plane motion isarrow_forwardB7arrow_forward
- A 74 g ball B dropped from a height ho=1.9 m reaches a height h₂= 0.25 m after bouncing twice from identical 250-g plates. Plate A rests directly on hard ground, while plate Crests on a foam-rubber mat. ho B hy Determine the height h1 of the ball's first bounce. The height h1 of the ball's first bounce is m.arrow_forwardThe 2-1b collar is released from rest at A and slides down along the smooth rod as shown in (Figure 1). Figure 2 ft 1 of 1 Part A If the attached spring has a stiffness 4 lb/ft, determine its unstretched length so that it does not allow the collar to leave contact with the top surface of the rod until 0 = 60°. Express your answer in feet to three significant figures. [ΨΕ ΑΣΦ1 lo = Submit Provide Feedback Request Answer vec ? ftarrow_forwardQuestion 3: Objects A and B are connected by a rope with fixed length of 7 ft. They start moving from rest at x = 0, being pulled by the constant 20-lb force. If the coefficient of kinetic friction 4 is 0.2 between both objects A, B and the contacting surface, what is the speed of object B when x = 4 ft? Neglect the friction at the pulley. WB= 20 lb B 3 ft x = 4 ft 20 lb W 12 lbarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY