
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
A bag of cement with a mass of 100kg hangs in equilibrium from three wires as shown in the figure . Two of the wires make angles θ1=40 and θ2=30 with the horizontal. Assuming the system is in equilibrium,
a. What is the magnitude of tension in string 1
b. What is the magnitude of tension in string 2
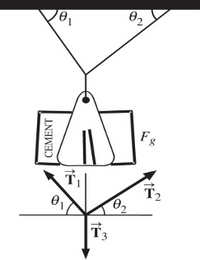
Transcribed Image Text:Fg
T2
T3
CEMENT
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Helparrow_forward1 This loudspeaker has a weight of 70 Newtons and is being held up by two cables. Both cables are at an angle of 25 degrees. This means that they both have the same tension, T. What is the vertical component of the tension in each cable? Ty %D unit What is the horizontal component of the tension in each cable? Tx unit What is the total tension in each cable? T = unit %3Darrow_forwardA crate hangs from a rope that is attached to a metal ring. The metal ring is suspended by a second rope that is attached overhead at two points, as shown. What is the angle 0 if the tension in rope 1 is 1.63 times the tension in rope 2? Rope 2 = Rope 1arrow_forward
- 2. A bag of cement of Mass 45 kg hangs from three wires as shown in figure. Two of the wires make angles 01=60° and 02=30° with the horizontal. If the system is in equilibrium, find the tensions T1, T2 in the wires. CEMENTarrow_forwardFnet = ma, x = xo + Voxt += axt², Vx = Vox + axt, (v₂)² = (vox)² + 2axAx, g = 9.8 m/sec² Problem 1: The three ropes in the Figure are tied to a small, very light ring. Two of the ropes are anchored to walls at right angles, and the third rope pulls as shown. a) What is T₁, the tension from Rope 1 for the Figure below on the left? Answer: 86.6 N b) What is T₂, the tension from Rope 2 for the Figure below on the left? Answer: 50.0 N c) What is T3x, the x-component of the tension from Rope 3 for the Figure below on the right? Answer: 50 N. d) What is T3y, the y-component of the tension from Rope 3 for the Figure below on the right? Answer: 80 N. e) What is T3, the tension from Rope 3 for the Figure below on the right? Answer: T3 = √(T3x)² + (T3y)² = 94.3 N Rope 1 Rope 2 √30° 100 N 0.60 m 0.80 m T₁ = 50 N T₂ = 80 N T₁ w 34arrow_forwardYou hang a light in front of your house using an elaborate system to keep the 12-kg object in static equilibrium (Figure 1). What are the magnitudes of the forces that the ropes must exert on the knot connecting the three ropes if θ2 = 63∘ and θ3 = 45∘?arrow_forward
- There is a 31.5 kg box sitting on the shelf. 1 lb=4.448 N a) What is the box's weight in N? b) What is the box's mass in the US (English) system?arrow_forward1. A 160kg utility pole extends 12.0m above the ground. A horizontal force of 250N acts at its top and the pole is held in the vertical position by a cable. a. Draw a free-body (or force) diagram for the pole. b. Determine the tension in the cable. c. What are the reaction forces exerted at the lower end of the pole by the ground? 2. A 40.0kg uniform platform is suspended by two cables, 2.00m apart, where the centre of the platform lies midway between the cables. A 5.00kg paint bucket is placed on the platform, 24.0cm to the right of the right cable. Determine the tension in each cable.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON