
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A bag of cement weighing 325 N hangs in equilibrium from 3 wires as suggested in the figure. Two of the wires make angles 1 = 60 deg. and angle 2 = 4o deg with the horizontal. Assuming the system is in equilibrium, find the forces (tensions) T1, T2, and T3 in the wires.
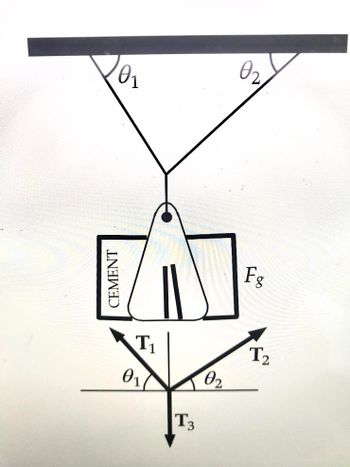
Transcribed Image Text:CEMENT
0₁
T3
02
Fg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A manager walks d = 3.4 m along a uniform plank supported by the floor at one end and by a vertical rope at the other, as in the figure. Find the tension in the rope if the plank's mass and length are M = 11 kg and L = 6 m, the manager's mass is m = 56 kg, and the angle = 21°. LL T = d— 0 N m 1 Report your numerical answer below, assuming three significant figures. Remember to include a "-" as necessary. HP Search M LDCEarrow_forwardA uniform plank of length 2.00 m and mass 29.5 kg is supported by three ropes, as indicated by the blue vectors in the figure below. Find the tension in each rope when a 685–N person is d = 0.500 m from the left end. magnitude of T1 = magnitude of T2 = magnitude of T3 =arrow_forwardA bag of cement weighing 525 N hangs in equilibrium from three wires as suggested in the figure below. Two of the wires make 62.0⁰ and 02 = 43.0° with the horizontal. Assuming the system is in equilibrium, find the tensions T₁, T2, and T3 angles 0₁ 1' in the wires. T₁ = 0 = Consider the net force at the point where the three wires come together. What is the acceleration of this point? N 0.53 X T₂ = The horizontal component of your T₁ is not equal to the horizontal component of your T₂, so the object would be accelerating horizontally. N T3 = 525 N 201 T₁ CEMENT T3 0₂ T₂ Fgarrow_forward
- Current Attempt in Progress In a two-dimensional tug-of-war, Alex, Betty, and Charles pull horizontally on an automobile tire at the angles shown in the picture. The tire remains stationary in spite of the three pulls. Alex pulls with force FA of magnitude 218 N, and Charles pulls with force Fcc magnitude 175 N. Note that the direction of Fc is not given. What is the magnitude of Betty's force FB if Charles pulls in (a) the direction drawn in the picture or (b) the other possible direction for equilibrium? 150° Alex (a) Number (b) Number Charles Betty Units Units 2arrow_forwardA uniform plank of length 2.00 m and mass 29.0 kg is supported by three ropes, as indicated by the blue vectors in the figure below. Find the tension in each rope when a 685-N person is d = 0.500 m from the left end. magnitude of Í magnitude of Í N magnitude of Í N 40.0° « d =| 2.00 marrow_forwardIn the figure, a 499 kg construction bucket is suspended by a cable A that is attached at O to two other cables B and C, making angles 0₁ = 51.0° and 9₂ = 54.0° with the horizontal. Find the tensions in (a) cable A, (b) cable B, and (c) cable C. (Hint: To avoid solving two equations in two unknowns, position the axes as shown in the figure.) B C 0₂arrow_forward
- Write the solution on a paper and round to 4 decimal placesarrow_forwardA bag of cement weighing 525 N hangs in equilibrium from three wires as suggested in the figure below. Two of the wires make angles ?1 = 61.0° and ?2 = 42.0° with the horizontal. Assuming the system is in equilibrium, find the tensions T1, T2, and T3 in the wires. T1 = N T2 = N T3 =.arrow_forwardA mass M1 = 4.1 kg mass is suspended from the ceiling and a mass M2 = 4.3 kg is suspended under it, as shown. The tensions in the strings are labeled and . A hand exerts an upward force of 22 N on the lower mass mass. Calculate the magnitude of the tension T1arrow_forward
- Three main forces that act on the patella, and are shown on the diagram below. These forces are the quadriceps muscle force (FQ), the patella ligament force (FPL), and the patellofemoral joint reaction force (FPF). The angles a and ẞ are with respect to a line that is perpendicular to FPF. Assuming a = 10°, ẞ = 30°, and FQ = 4000 N, use the equations for static equilibrium to calculate the FPL in Newtons. Round to an integer, such there is no need for a decimal. FQ FPF FP Barrow_forwardThree rugby players are pulling horizontally on ropes attached to a box, which remains stationary. Player 1 exerts a force F equal to 200 N at an angle 0, equal to –60.0° with respect to the +x-direction, as shown in the figure. Player 2 exerts a force F2 equal to 300 N at an angle 02 equal to 37.0° with respect to the +x-direction. The view in the figure is from above. Ignore friction and note that gravity can be ignored in this problem. Determine the force F3 exerted by player 3. State your answer by giving the x- and y-components, F3, and Fay, respectively. F, F3x -339.59 N F3y N Player 3's rope breaks, and player 2 adjusts by pulling with a force of magnitude F; equal to 250 N at the same angle as before. Defining angles above the x-axis as positive and those below as negative, at what angle 0 is the acceleration of the box relative to the +x-direction? The magnitude of the acceleration is measured to be 10.0 m/s?. What is the mass m of the box? kg m = F TOOLS x10arrow_forwardA bag of cement whose weight is Eg hangs in equilibrium from three wires as shown in Figure. Two of the wires make angles 01 and 02 with the horizontal. Assuming the system is in equilibrium. What is the tension in the left-hand wire? Fg cos 02 a) T1 sin(8,+82) Fg sin 02 sin(e,+82) b) T1 2Fg cos 02 c) T1 sin(e,+02) 2Fg sin 82 d) T = cos(e,+02) 3Fg sin 02 e) T1 cos(e,+02) CEMENTarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON