
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Yerba Buena Island in a large rock outcrop in San Francisco Bay. Treasure Island is an artificial island formed by hydraulic filling on a shallow zone adjacent to Yerba Buena. The hydraulic fill basically consists of loose, fine to medium, silt and sand, with occasional clay zones. The islands are located roughly midway between the San Andreas Fault to the West and the Hayward fault to the East. During 1989 earthquake, ground acceleration was recorded at both islands.
Examine the seismographs image from 1989 earthquake and answer the following questions:
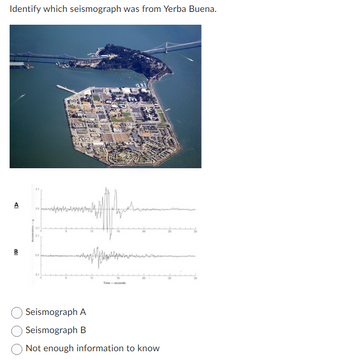
Transcribed Image Text:Identify which seismograph was from Yerba Buena.
A
100
Time-seconds
Seismograph A
Seismograph B
Not enough information to know
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Surveying with Construction Applications (8th Edition) Problem 6.3. Describe, in point form, how you can use a theodolite or a total station to prolong a straight line XY to a new point Z. (Assume the instrument is set up over point Y and is level.)arrow_forwardIn trying to minimise errors that come with using a tape in linear measurements, Mapalo suggested to the class that an EDM be used to compute the distance from BM1 to point A. A distance of 2122.241m was measured. Given that a frequency of 1.4985MHz was used, speed of light c = 299792458m/s, the refraction index of 1.0003 and that the effective wavelength measures to a centimetre, determine the phase measurement (i.e. Phase Distance and the corresponding Phase angle)arrow_forward4. Given the following set of stadia level notes: BACKSIGHT FORESIGHT STA STADIA VERTICAL ROD STADIA VERTICAL ROD ELEV INTERVAL INTERVAL READING INTERVAL INTERVAL READING A 1.75 -15°45' 2.10 425.15 ТР-1 2.15 -18°10' 1.92 1.55 +12°48' 1.58 В 3.20 -09°18' 1.65 The instrument used was a transit with an internal focusing telescope and a stadia interval factor of 98, and all linear measurements are in meters. FIND: A. The difference in elevation between station A and the turning point B. The elevation of TP-1 C. The elevation f B D. The difference in elevation between A and B.arrow_forward
- i need the answer quicklyarrow_forwardAdjust the angles of triangle ABC for the following angular values and weights: (Please check the data below) What is the correction (to the nearest seconds ) applied to angle A? O - 3" + 3" 6 + 6" What is the adjusted angle of Angle C? O 61 deg 10' 08' O 61 deg 08' 10 O 61 deg 08' 00' O 61 deg 10' 00" What is the value of the correction multiplier or "x" ? -1' 2" +2' What is the angle of Misclosure? +/- 11" O + 12" -13' - 0.11 Below are the observations for your reference 80°14'04" wt = 2 38°37'47" wt = 1 61°07'58" wt = 3 O O o O Oarrow_forwardA total station was setup on top of point A. The following observations have been recorded to point B in reflector-less mode: Оссиpied Point IH Target Azimuth Vertical SD (m) Point Angle (m) 2 2 A 1.39 D 261 34 49 -15 58 2 207.085 If the coordinates of point A is (E=1318.756, N= 1758.883, H= 252.975). What is the Elevation of point D? Round your answer to 3 decimal placesarrow_forward
- A total station was setup on top of point A. The following observations have been recorded to point B in reflector-less mode: Occupied Point IH Target (m) Point Azimuth 0 F " 0 Vertical Angle . 14 SD (m) A 1.36 C 214 29 37 -4 19 56 208.527 If the coordinates of point A is (E-1659.637, N-1161.376, H-310.472). What is the Northing of point C? Round your answer to 3 decimal places. Do not add units to your answer (e.g. 100.351 NOT 100.351m) Your Answer:arrow_forwardWhich of the following co-ordinates are not the same for all observers? options: Right Ascention Altitude Azimuth Declinationarrow_forwardQ12: A detailed survey was carried out using a number of radiations from a total station set up on Station A to a target placed on an area on interest. Station A has the following coordinates as shown in the Table 8 on a local plane datum. Table 8: Point Easting (m) Northing (m) Height (m) A 255.751 176.286 42.623 The instrument is set up at a height of 1.565 m (h) and the target pole is set at a height (h.) of 1.690 m. A radiation was made to a feature labelled B: Bearing (B) = 240°25'20" Slope Distance (SD) = 11.682 m Zenith Angle (ZA) = 93°22'30" Calculate the coordinates of B including its height. (PC 3.4, 4.3, RS 5, RK 3.1, 3.2, 6.2) A:arrow_forward
- شممبزSurvey engineeringarrow_forwardSurvey The stadia readings with a horizontal sight on a vertical staff held 40 m away from a tacheometer were 1.385 m and 1.780 m. The focal length of the object glass was 25 cm. The distance between object glass and trunnion axis of the tacheometer was 12 cm. Solve for the stadia interval.arrow_forwardThe length intercepted on the stadia rod is 3.6 m and the line of sight makes an angle of 3deg15’ with the horizontal. Find the distance, in meters, from the center of the instrument to the rod, if the stadia constant is 0.3 m and the stadia interval factor is 100.a. 172.43 b. 179.74 c. 196.87 d.187.36pls answer I need it asaparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning