
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
For each compound, draw an akyl handle that can be used to produce it by the indicated mechanism. Show the organic starting material and reagens needed.
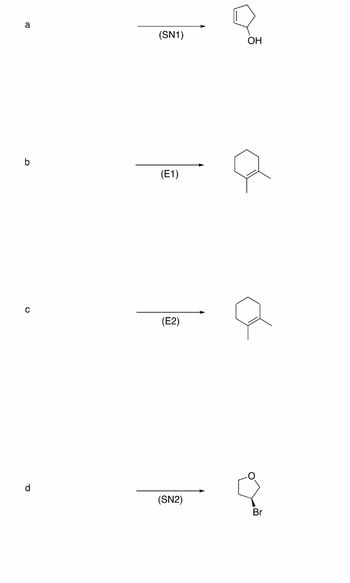
Transcribed Image Text:The image illustrates four different organic reactions, each labeled with a letter (a, b, c, d) and showcasing different mechanistic pathways.
**a. SN1 Reaction:**
- The diagram shows a secondary alkyl halide undergoing an SN1 reaction to form an alcohol.
- The starting material is a cyclohexane ring with an iodine substituent (I) and a reaction arrow indicating the formation of a cyclohexanol.
**b. E1 Reaction:**
- The diagram depicts an E1 elimination reaction.
- The starting material is a secondary alkyl halide, with the reaction resulting in the formation of an alkene.
- It shows a cyclohexane ring with a single methyl substituent added through elimination.
**c. E2 Reaction:**
- The diagram represents an E2 elimination reaction.
- The starting material is similar to the E1 example, but in this mechanism, the elimination occurs in one concerted step.
- The product is again an alkene on a cyclohexane ring, similar to the one in part b.
**d. SN2 Reaction:**
- The diagram depicts an SN2 substitution reaction.
- The starting material is a bromocyclopentane with a reaction arrow leading to the formation of another cyclohexane derivative.
- The change involves the substitution of the bromine substituent by another group through the backside attack characteristic of SN2 reactions.
These diagrams provide visual representations of common reaction mechanisms in organic chemistry, all involving changes in the cycloalkane substrates.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Draw a curved arrow mechanism for the reaction. You can assume that all reactants and products are shown.arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this SN1 reaction. Ignore any inorganic byproducts.arrow_forwarddraw by hand the complete mechanism for the saponification reaction of the given acetate when treated with sodium hydroxide in water, followed by an acid workup. include all relevant arrows and electrons and put a box around your final product.arrow_forward
- Draw the mechanism for this reaction.arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps.arrow_forwardDraw tautomerization mechanism in (a) acid and (b) base. (From enol form to keto form)arrow_forward
- 4. Propose a synthesis of each of the following compounds using the indicated starting material. You may use any organic compounds and any inorganic compounds or solvents of your choice. Do not show any reactive intermediates, mechanisms, or transition states, but be sure to show each isolable compound along your synthetic route. a. b. C. CH3 Ph steps Ph CI steps ACHO -CH3 CN steps Ph Ph -OH (racemic)arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting structure, draw the curved electron- pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic steps. Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Then draw any missing organic intermediates or products for this reaction. Include all lone pairs in the structures. Ignore inorganic byproducts, counterions, and solvents. Select to Add Arrows Br2 Please select a drawing or reagent from the question areaarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY