
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
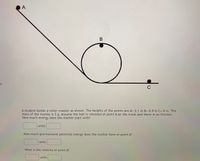
Transcribed Image Text:A
C
A student builds a roller coaster as shown. The heights of the points are A= 2.1 m B= 0.9 m C= 0 m. The
mass of the marble is 5 g. Assume the ball is released at point A on the track and there is no friction.
How much energy does the marble start with?
units
How much gravitational potential energy does the marble have at point A?
units
What is the velocity at point A?
units
B
SI
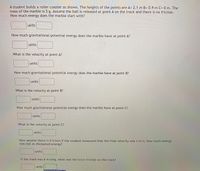
Transcribed Image Text:A student builds a roller coaster as shown. The heights of the points are A= 2.1 m B= 0.9 m C= 0 m. The
mass of the marble is 5 g. Assume the ball is released at point A on the track and there is no friction.
How much energy does the marble start with?
units
How much gravitational potential energy does the marble have at point A?
units
What is the velocity at point A?
units
How much gravitational potential energy does the marble have at point B?
units
What is the velocity at point B?
units
How much gravitational potential energy does the marble have at point C?
units
What is the velocity at point C?
units
Now assume there is friction.If the student measured that the final velocity was 1 m/s, how much energy
was lost as dissipated energy?
units
If the track was 6 m long, what was the force friction on the track?
units |
Enter text [more
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A force acts on a particle that moves along the X axis and varies with position according to the graph shown. if the mobile starts from the origin. a. calculate the work done by the force when it moves from position x=8m to position x= 13m. b. find the average power that force develops if it takes 0.5 seconds to reach the position x= 2marrow_forwardA baseball hits the catcher’s glove with a horizontal velocity of 55m/s. The mass of the baseball is 0.15kg. The displacement of the ball due to the deformation of the catcher’s glove and the movement of the catcher’s hand is 23cm from the instant the ball makes contact with the glove until it stops. a. How much kinetic energy does the baseball have just before it strikes the glove? b. How much work does the catcher have to do to the ball during the catch and is it positive or negative? c. What is the average impact force exerted by the glove on the baseball? Answer parts a-c. Include units and direction.arrow_forwardConstructed Response 1 Jim is lying on his back on the ground throwing a ball in the air and catching it. There is a balcony 10 meters above his head onto which he is trying to land the ball. On his last throw the ball lands on the balcony. The graph below shows the potential and kinetic energy of the ball from when it left Jim's hand to when it landed on the balcony. ★ Graivational Potential energy A Kinetic energy 200 180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0. 0. 4 9. 10 Height (m) 8. 2. Energy (J)arrow_forward
- Part A A child pulls a sled with constant speed pulling the rope at an angle of 30° to the horizontal and drags the sled for 100 m. The friction coefficient is 0.40. What work did the friction force do if the sled's mass is 5.1 kg? Express your answer with the appropriate units. W = 1624.2 J Ć ?arrow_forwardA 23.3-kg child descends a slide 3.4 m high and reaches the bottom with a speed of 1.9 m/s. Part A How much thermal energy due to friction was generated in this process? Express your answer using two significant figures.arrow_forwardYou take a 13kg bag of lead pellets and drop it from 2m above the ground.a. How much gravitational potential energy does the bag have when held 2m above the ground?b. The bag is dropped. Just before it hits the ground, how much kinetic energy does it have?c. How fast is the bag moving just before it hits the ground?d. When it hits the ground, the kinetic energy will be transformed mostly into thermal energy. If 40%of this energy goes into the lead pellets as heat, what will be the increase in temperature of thelead? Assume led has a specific heat capacity of 160J/kg·K.arrow_forward
- 1.) A 15 kg mass is dropped from rest a distance of 18 m above the ground. Make certain you show all your work: a. Draw a picture. b. Indicate on your drawing where KE = 0 and where PE = 0 c. Using Conservation of Energy determine the final speed of the object just before it strikes the ground. d. Next, again showing all your work, use 1-dimensional Kinematics to solve the same problem. e. Which method, in your opinion is easier?arrow_forwardi just need help with C and D A big ship with a mass of 5.95 x 10 7 kg has a speed of 11.0 m/s at some instant. A. What is the ship’s kinetic energy? B. How much work is required to stop it? C. How is work related to the mechanical energy? D. What is the magnitude of the constant force required to stop it as it undergoes a displacement of 2.75 km?arrow_forwardPart A With what minimum speed must you toss a 180 g ball straight up to just touch the 13-m-high roof of the gymnasium if you release the ball 1.2 m above the ground? Solve this problem using energy. Express your answer with the appropriate units. HA Umin = Value Units Submit Request Answer Part B With what speed does the ball hit the ground? Express your answer with the appropriate units. μΑ Value Unitsarrow_forward
- at a glance S Add-ons Help Last edit was 16 minutes ago Arial BIUA CD 国 12 LE2 2. At the Yankee stadium Alex Rodiguez scores a home run against the Miami Dolphins ,by hitting the 0.015kg baseball with a bat causing the ball to increase its velocity from 0m/s to 50m/s. a Is the work done on the baseball positive or negative ? b. How would you determine the work done by Alex on the baseball 2arrow_forwardA 100gram ball thrown vertically downward stricken the ground with a speed of 20m/s. It then bounces, and reaches a final height of 5.0 meters. a.what is the ball's kinetic energy b. What is the ball's potential energy at the 5.0-m height c. What is the ball's kinetic energy immediately after it rebounds from the surface d. What is the ball's speed immediately after it rebounds from the surfacearrow_forwardA body moves with increasing speed. Which of the following statements is true? A. The net work done on the body is positive, and the kinetic energy is increasing. B. The net work done on the body is positive, and the kinetic energy is decreasing. C. The net work done on the body is zero, and the kinetic energy is decreasing. D. The net work done on the body is negative, and the kinetic energy is increasing. E. The net work done on the body is negative, and the kinetic energy is decreasing.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON