Question
thumb_up100%
The answer to the question is on the internet but I could not access it.
https://www.chegg.com/homework-help/questions-and-answers/exercise-5-figure-4-face-centred-cubic-crystal-crystal-face-centred-cubic-structure-basic--q31292651
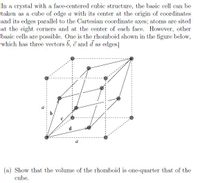
Transcribed Image Text:In a crystal with a face-centered cubic structure, the basic cell can be
taken as a cube of edge a with its center at the origin of coordinates
and its edges parallel to the Cartesian coordinate axes; atoms are sited
at the eight corners and at the center of each face. However, other
basic cells are possible. One is the rhomboid shown in the figure below,
which has three vectors b, c and d as edges.
b
a
(a) Show that the volume of the rhomboid is one-quarter that of the
cube.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2- Assuming that the oscillating ionic compound is cesium chloride, if you know the atomic weight of chlorine is 35.5 gm/mol and the atomic weight of cesium is 133 gm/mol, and assuming that Hooke's constant is y=4N/m²? NA = 6.02 x 1023 mol-¹ 1. Calculate the maximum frequency of the optical branch? 2. Calculate the frequency of the optical and acoustic branch at the boundary? 3. Determine the range of the forbidden frequency region? 4. Determine the Debye Temperature? 5. If you know that the lattice constant a = 3.14 Å, draw the first Brillion zone curve with its optical and acoustic branches. 6. If you know that the two atoms have the same mass equal to the mass of the smaller atom, then repeat the previous calculations and redraw the differentiation curve?arrow_forward. How are we able to determine the chemical composition and temperature of any visible object? ite often advertisements appear for telescopes that extol their aluating telescopes? enifviarrow_forward2. The emission spectrum for sodium below shows two bright lines at frequency 1(f ) and frequency 2(f ). The difference in energy between Frequency 1 and Frequency 2 can be determined with what formula using the frequencies (f and f ) and Planck’s constant (h)? answer choices are in the images attached!!arrow_forward