
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: Statics, 4th Edition
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781305501607
Author: Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher: CENGAGE L
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
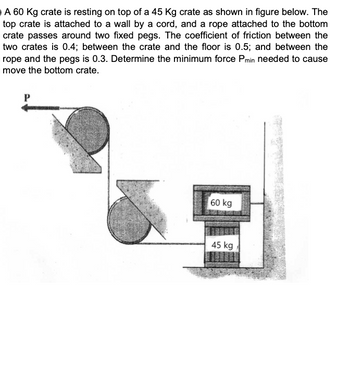
Transcribed Image Text:A 60 Kg crate is resting on top of a 45 Kg crate as shown in figure below. The
top crate is attached to a wall by a cord, and a rope attached to the bottom
crate passes around two fixed pegs. The coefficient of friction between the
two crates is 0.4; between the crate and the floor is 0.5; and between the
rope and the pegs is 0.3. Determine the minimum force Pmin needed to cause
move the bottom crate.
60 kg
45 kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The coeffient of static friction between the uniform bar AB of weight W and the ground is 0.45. Find the smallest angle and the corresponding force P that would initiate simultaneous tipping and sliding of the bar.arrow_forwardThe block of weight W is pulled by the force P inclined at the angle to the horizontal. Find the smallest force P and the corresponding angle that would cause impending sliding of the block. The angle of static friction between the block and the ground is s.arrow_forwardTwo identical chairs, each weighing 14 lb, are stacked as shown. The center of gravity of each chair is denoted by G. The coefficient of static friction is 0.2 at B (the contact point between the chairs) and 0.35 at A, C, and D. Determine the smallest force P that would cause sliding.arrow_forward
- A 1.1-kg disk A is placed on the inclined surface. The coefficient of static friction between the disk and the surface is 0.35. Is the disk in equilibrium if P=5.5N and =30?arrow_forwardThe figure shows a steel bar being processed by a rolling mill. Given that P=80kN and r =0.016, determine the force F required to advance the bar at a constant speed.arrow_forwardThe 40-lb spool is suspended from the hanger GA and rests against a vertical wall. The center of gravity of the spool is at G and the weight of the hanger is negligible. The wire wound around the hub of the spool is extracted by pulling its end with the force P. If the coefficient of static friction between the spool and the wall is 0.25, determine the smallest P that will extract the wire.arrow_forward
- The uniform ladder of weight W is raised slowly by applying a vertical force P to the rope at A. Show that P is independent of the angle .arrow_forwardA pair of wedges is used to lift a crate as shown in The crate weighs 4000 lb, the wedge angle e is Fig. 18°, and the coefficient of friction is 0.15 at all surfaces. The weight of the wedges is negligible. Determine The force P necessary to insert the wedge. Warrow_forwardThe 250 lb uniform crate (center of gravity at G) shown in the figure must be moved without tipping. The applied force P is horizontal. 1.5 ft 1.5 ft Determine: a. The largest coefficient of static friction between the crate and the floor that allows the crate to slide and 2.5 ft P. not tip 4.5 ft b. The corresponding magnitude of P 3.5 ft Include all needed FBD's to solve, and put units on your answers.arrow_forward
- Inclined Ramp A box sitting on a horizontal surface isattached to a second box sitting on an inclined ramp by a ropethat passes over an ideal pulley. The rope exerts a tensionforce T on both weights along the direction of the rope, andthe coefficient of friction between the surface and boxes is0.6 (see Problems 91 and 92). If the box on the right weighs100 pounds and the angle of the ramp is 35°, how much must thebox on the left weigh for the system to be in static equilibrium?Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardAn arrangement of three boxes is shown in figure below. Box A weighs 25 N and rests on an inclined plane, while box B weighs 50 N and rests on a horizontal plane. The coefficient of friction between box A and the inclined plane is 0.3, and between box B and the horizontal plane is 0.4. The pulleys are all frictionless. Determine the range of weight of box C for which no motion will occur. Consider both sliding and tipping of boxes A and B. 0.6 m 0.75 m 25 N 5 A 4 C pome 0.8 m 0.6 m 50 N B 1.2 marrow_forwardAn arrangement of three boxes is shown in figure below. Box A weighs 25 N and rests on an inclined plane, while box B weighs 50 N and rests on a horizontal plane. The coefficient of friction between box A and the inclined plane is 0.3, and between box B and the horizontal plane is 0.4. The pulleys are all frictionless. Determine the range of weight of box C for which no motion will occur. Consider both sliding and tipping of boxes A and B. 0.6 m 0.75 m 25 N A 5 4 C 0.8 m -0.6 m 50 N B 1.2 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L