
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
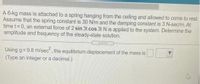
Transcribed Image Text:A 6-kg mass is attached to a spring hanging from the ceiling and allowed to come to rest.
Assume that the spring constant is 30 N/m and the damping constant is 3 N-sec/m. At
time t=0, an external force of 2 sin 3t cos 3t N is applied to the system. Determine the
amplitude and frequency of the steady-state solution.
**..*.
Using g= 9.8 m/sec", the equilibrium displacement of the mass is
(Type an integer or a decimal.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A system with 100g_mass and a spring constant of k=150N/m has a damping constant y=1.1. ASsume the mass was pulled to the right 30 cm at t=0and released. a)Estimate the time at which the amplitude has decayed to ¼ of its initial value. b)Assume the system is connected to a forcing function given by(in Newtons)F(t)=3coswtEstimate the value of the amplitude at resonance.arrow_forwardCL ANO A pendulum with a length of 1.00 m is released from an initial angle of 14.0°. After 1 000 s, its amplitude has been reduced by friction to 6.50°. What is the value of b/2m? Need Help? Watch Itarrow_forwardSuppose a mass- Spring System has spring Constant 4l6l6 N/m and mass 7 kg. The mass is displaced in the positive x-dirėctión by 0.3 m and set in motion at 2.66 m/s in the negative x- direction. Calculate the phase shift as a positive angle in radiáns, assum ing a cosine solutiónarrow_forward
- need help with darrow_forwardAn object executing simple harmonic motion has a maximumspeed vmax and a maximum acceleration amax. Find (a) the amplitude and (b) the period of this motion. Express your answers interms of vmax and amaxarrow_forwardA 2.0-kg ball executing a simple harmonic motion has the following velocity as a function of time: v=-A w sin w t, where A= 1.0 m and @ = 20 rad/s. At what time (first time after the ball started) will the kinetic energy of the ball be 100 J?arrow_forward
- The potential energy of an object attached to a spring is 2.50 J at a location where the kinetic energy is 1.40 J. If the amplitude ? of the simple harmonic motion is 22.0 cm, calculate the spring constant ? and the magnitude of the largest force ?spring, max that the object experiences.arrow_forwardTwo massless springs with spring constants 610 N/m and 116 N/m are hung from a hor- izontal support. A block of mass 6 kg is suspended from the pair of springs, as shown. When the block is in equilibrium, each spring is stretched an additional Ar. Then the block oscillates with an amplitude of 49 m and it passes through its equilibrium point with a speed of 539 m/s. 610 N/m -oooo² 6 kg -0000² 116 N/m What is the angular velocity of this system? The acceleration due to gravity is 9.8 m/s. 1. w = 15 2. w = 2 3. w = 11 rad/s 4. w = 13 5. w = 21 6. w = 16 7. w = 8 X 8. w = 4 9. w = 6 10. = 18arrow_forwardThe suspension system of a 2200 kg car is made of springs that are compresses by 8 cm when the mass of the car is placed on it. Also, the collision amplitude decreases by 50% each cycle. Find the damping constant 6 (in units of kg/s) for the spring and shock absorber system of one wheel, assuming each wheel supports 550 kg. 134arrow_forward
- The potential energy of an object attached to a spring is 2.60 J at a location where the kinetic energy is 1.30 J. If the amplitude ?of the simple harmonic motion is 19.0 cm, calculate the spring constant ? and the magnitude of the largest force ?spring, max that the object experiences.arrow_forwardO Macmillan Learning A small bolt with a mass of 27.0 g sits on top of a piston. The piston is undergoing simple harmonic motion in the vertical direction with a frequency of 1.45 Hz. Use g = 9.81 m/s² for the acceleration due to gravity. What is the maximum amplitude Amax with which the piston can oscillate without the bolt losing contact with the piston's surface? Amax = marrow_forwardA0.366 kg body undergoes simple harmonic motion of amplitude 6.08 cm and period 0.500 s. (a) What is the magnitude of the maximum force acting on it? (b) If the oscillations are produced by a spring, what is the spring constant? (a) Number i Units (b) Number i Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON