
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
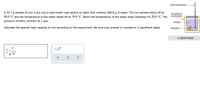
Transcribed Image Text:thermometer.
A 52.7 g sample of iron is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 300.0 g of water. The iron sample starts off at
insulated
container
94.0 °C and the temperature of the water starts off at 19.0 °C. When the temperature of the water stops changing it's 20.8 °C. The
pressure remains constant at 1 atm.
water
Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron according to this experiment. Be sure your answer is rounded to 2 significant digits.
sample -
a calorimeter
J
g.°C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 60.0 g sample of iron is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 300.0 g of water. The iron sample starts off at 98.3 °C and the temperature of the water starts off at 22.0 °C. When the temperature of the water stops changing it's 24.1 °C. The pressure remains constant at 1 atm. Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron according to this experiment. Be sure your answer is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. 0 J g. °C x10 X thermometer insulated container water sample. a calorimeterarrow_forwardA 55.1g sample of polystyrene, which has a specific heat capacity of 1.880·J·g−1°C−1, is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 200.0g of water. The temperature of the water starts off at 25.0°C. When the temperature of the water stops changing it's 31.9°C. The pressure remains constant at 1atm . Calculate the initial temperature of the polystyrene sample. Be sure your answer is rounded to the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardA 55.0 g sample of brass is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 100.0 g of water. The brass sample starts off at 86.7 °C and the temperature of the water starts off at 23.0 °C. When the temperature of the water stops changing it's 26.5 °C. The pressure remains constant at 1 atm. Calculate the specific heat capacity of brass according to this experiment. Be sure your answer is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. J 0- g-°C 0 x10 X thermometer. insulated container water sample a calorimeterarrow_forward
- A 57.0g sample of aluminum is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 250.0g of water. The aluminum sample starts off at 96.9°C and the temperature of the water starts off at 23.0°C. When the temperature of the water stops changing it's 26.2°C. The pressure remains constant at 1atm. Calculate the specific heat capacity of aluminum according to this experiment. Be sure your answer is rounded to 2 significant digits. Please type answer note write by hend.arrow_forwardA 56.2 g sample of aluminum, which has a specific heat capacity of 0.897 J-g¹C¹, is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 250.0 g of water. The temperature of the water starts off at 24.0 °C. When the temperature of the water stops changing it's 26.9 °C. The pressure remains constant at 1 atm. Calculate the initial temperature of the aluminum sample. Be sure your answer is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. °C X Ś thermometer- insulated. container water sample a calorimeterarrow_forwardA particular container holds 3.77 mol of neon gas. The volume of this container can be altered by sliding a piston in or out. The volume is changed from 8.60 L to 12.20 L while at the same time the temperature is changed from 303 K to 345 K. The molar heat capacity, Cym, for neon is 12.47 J/(mol · K). Assume that this value will not change over the given temperature range. What is the change in entropy for the gas? AS = J/K TOOLS x10 MacBook Proarrow_forward
- thermometer A 59.2 g sample of iron is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 200.0 g of water. The iron sample starts off at 95.8 °C and the temperature of the water starts off at 24.0 °C. When the temperature of the water stops changing it's 27.1 °C. insulated container The pressure remains constant at 1 atm. water Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron according to this experiment. Be sure your answer is rounded to 2 significant digits. sample a calorimeter g.°C Explanation Check O2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved Terms of Usse Privacy Accessibi MacBook Aiarrow_forwardthermometer A 58.2 g sample of polystyrene is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 300.0 g of water. The polystyrene insulated container sample starts off at 89.1 °C and the temperature of the water starts off at 19.0 °C. When the temperature of the water stops changing it's 23.0 °C. The pressure remains constant at 1 atm. water Calculate the specific heat capacity of polystyrene according to this experiment. Be sure your answer is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. sample a calorimeter J Ox10 g.°C ?arrow_forwardA 56.5 g sample of iron is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 300.0 g of water. The iron sample starts off at 86.7 °C and the temperature of the water starts off at 21.0 °C. When the temperature of the water stops changing it's 22.8 °C. The pressure remains constant at 1 atm. Calculate the specific heat capacity of iron according to this experiment. Be sure your answer is rounded to 2 significant digits. J 0₂-C x10 x thermometer insulated container water sample a calorimeterarrow_forward
- A 56.1 g sample of polystyrene, which has a specific heat capacity of 1.880 J-g °C-1 is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 250.0 g of water. The temperature of the water starts off at 24.0 °C. When the temperature of the water stops changing it's 29.8 °C. The pressure remains constant at 1 atm. Calculate the initial temperature of the polystyrene sample. Be sure your answer is rounded to the correct number of significant digits. °C thermometer. insulated container water sample. a calorimeter 區 OU Ararrow_forwardI don’t get thisarrow_forwardA 57.1 g sample of polystyrene, which has a specific heat capacity of 1.880 J-g¹C, is put into a calorimeter (see sketch at right) that contains 100.0 g of water. The temperature of the water starts off at 23.0 °C. When the temperature of the water stops changing it's 38.3 °C. The pressure remains constant at 1 atm. Calculate the initial temperature of the polystyrene sample. Be sure your answer is rounded to 3 significant digits. 0°C 0...º Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY