
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
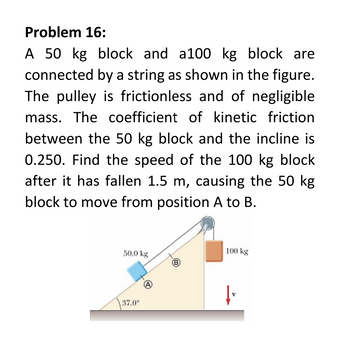
Transcribed Image Text:Problem 16:
A 50 kg block and a100 kg block are
connected by a string as shown in the figure.
The pulley is frictionless and of negligible
mass. The coefficient of kinetic friction
between the 50 kg block and the incline is
0.250. Find the speed of the 100 kg block
after it has fallen 1.5 m, causing the 50 kg
block to move from position A to B.
50.0 kg
37.0⁰
A
100 kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 6.0-kg rock is subject to a variable force given by the equation. F(x) = 4.0 N - (2.0 N/m)x + (6.0 N/m²)x² If the rock initially is at rest at the origin, find its speed when it has moved 6.0 m. 3 m/s 15 m/s 18 m/s 33 m/sarrow_forwardTwo objects are connected by a light string passing over a light, frictionless pulley. The 5.00-kg object is released from rest at a point 4.00 m above the floor. Find the speed of the 5.00-kg object when it is 1 meter above the floor. m, = 5.00 kg h = 4.00 m m, = 3.00 kg 4.756 m/s 3.834 m/s 4.475 m/s 3.942 m/s 4.135 m/s 3.384 m/s А. D. В. Е. С. F.arrow_forwardIn the figure, a small, initially stationary block is released on a frictionless ramp at a height of 3.0 m. Hill heights along the ramp are as shown in the figure. The hills have identical circular tops, and the block does not fly off any hill. Which hill is the first the block cannot cross? What does the block do after failing to cross that hill? The normal force on the block least? * 3.5 m (4) 2.5 m 1.5 m (3) 3.0 m (2) 0.5 m O 3, Moves backwards, at the top of 1 O 3, oscillates between 2 an 3, at the bottom of 2 and 3 O 4, Moves backwards, at the top of 3 O 3, Moves backwards, at the top of 3arrow_forward
- Part A A net force along the x-axis that has x-component F = -12.0 N+(0.300 N/m² )x² is applied to a 4.90 kg object that is initially at the origin and moving in I-direction with a speed of 8.60 m/s. What is the speed of the object when it reaches the point x = 7.80 m? the Express your answer with the appropriate units. HA ? m v = 8.3 Submit Previous Answers Request Answerarrow_forwardm2 m1 Two unequal masses are hung by a massless cord over a pulley in an Atwood machine. After the masses are released from rest, which of the following statements is true about the total gravitational potential energy UG and the total kinetic energy K of the system? Ug increases and K increases O UG decreases and K increases UG decreases and K decreases UG increases and K decreasesarrow_forwardQUESTION 7 From the diagram below, what is the speed of the block when it reaches point A at the lowest point on the surface? 2.00-kg block with an initial velocity of 5.00 m/s down the track Frictionless track В 9.00 m 5.00 m A a. 11.2 m/s b. 9.70 m/s C. 14.2 m/s d. 15.7 m/s е. 12.7 m/sarrow_forward
- Sam, whose mass is 73 kg, takes off across level snow on his jet-powered skis. The skis have a thrust of 240 N and a coefficient of kinetic friction on snow of 0.1. Unfortunately, the skis run out of fue after only 12 s. V= 28 Submit m ▾ Part B Previous Answers ✓ Correct Correct answer is shown. Your answer 27.52 was either rounded differently How far has Sam traveled when he finally coasts to a stop? Express your answer with the appropriate units.arrow_forwardAssume that the force of a bow on an arrow behaves like the spring force. In aiming the arrow, an archer pulls the bow back 48 cm and holds it in position with a force of 163 N. If the mass of the arrow is 51 g and the "spring" is massless, what is the speed of the arrow immediately after it leaves the bow? v=v= m/s A boy throws a ball of mass 0.2 kg straight upward with an initial speed of 22 m/s When the ball returns to the boy, its speed is 17 m/s How much work does air resistance do on the ball during its flight? W=W= J (give the absolute value, rounded to one decimal place)arrow_forwardAn arrow of mass 0.0348 kilograms is placed on a bow, and the string is drawn back 0.533 meters with an average force of 143 newtons. a. With what speed does the arrow leave the bow? b. If the arrow is shot straight up, how high does it rise? Solve using the law of conservation of energy, not a constant acceleration equation.arrow_forward
- A 13.0kg stone slides down an icy, essentially frictionless, hill that is shown in the figure. At the top of the hill, the stone is moving at 1.75m/s down the hill. While the hill is frictionless, the stone experiences friction along the level, rough ground (beyond the base of the hill) all the way to a wall. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction are 0.800 and 0.300 respectively. The stone slides along the ground for 9.15m before making contact with a long spring, which has a spring constant of 25.0N/m. (“Long” in this case means that the spring is sufficiently long to stop the stone before it hits the wall.) Will the stone move again after it has been stopped by the spring?arrow_forwardRank these four objects in increasing order of kinetic energy, beginning with the smallest. Object A Object B Object C Object D m = 5.0 kg v = 4.0 m/s h = 2.0 m m = 10.0 kg v = 2.0 m/s h = 3.00 m m = 1.0 kg v = 5.0 m/s h = 5.0 m m = 5.0 kg v = 2.0 m/s h = 4.0 marrow_forwardm = 325 kg h1 = 19.5 m h2 = 4.7 m A roller coaster car of mass m is rolling down the track, starting from rest, as shown in the figure. The initial height from the ground is h1 (Position-1), while the final height is h2 (Position-3). The system has no friction. What is the speed of the car when it reaches its final height (Position-3).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON