
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
What is the equivalent resistance between points a and b as shown?
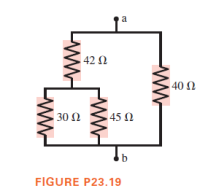
Transcribed Image Text:a
42 N
40 N
30 Ω
45 N
b
FIGURE P23.19
ww
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For the circuit shown, find the (a) total resistance (b) total current (c) current through each resistor and the (d) potential drop across each resistor. 100 ka 3 ka 25 kn 60 kn 10 ka 225 V 30 knarrow_forwardTwo steel conductors are bent into rectangular prisms with square bases of lengths a and, where /-2s. If the thin prism has a length of L-10s and the thick prism has a length of Ladda; compare the resistances of the two conductors: Select one: II a. The thicker conductor has smaller resistance b. The thinner conductor has smaller resistance c. They have equal resistances d. We cannot answer the question with the information providedarrow_forwardConsider the combination of resistors shown in the figure below. (a)Calculate the equivalent resistance (in Ω) between points a and b. 11.7 is the answer I got can't seem to get the rest help, please. (b)If a voltage of 21.7 V is applied between points a and b, find the current (in A) in each resistor. 12 Ω 6.0 Ω 5.0 Ω 4.0 Ω 8.0 Ωarrow_forward
- you are trying to reduce the resistance in a branch of a circuit from 110 omega to 80 omega. You add a resistor to this branch of the circuit to make this change. What value of resistance should you use, and how should you connect this resistor ?arrow_forwardWhat is the equivalent resistance (in ohm) between points a and b in the diagram above if R1 = 80.0 Ω, R2 = 25.0 Ω, R3 = 65.0 Ω, and R4 = 40.0 Ω ?arrow_forwardUse mesh analysis to determine the three mesh currents in the circuit ? iz 3 0 7 V + 6 V izarrow_forward
- A 5 V battery of negligible internal resistance is connected across a 200 V battery and a resistance of 39 Q as shown in the figure. Find the value of the current 5 V 39 2 200 Varrow_forwardThe figure below shows five resistors and two batteries connected in a circuit. What are the currents I,, I2, and I3? (Consider the following values: R, = 1.08 0, R2 = 2.20 0, R3 = 3.18 0, R4 = 4.04 0, R5 = 6.06 0. Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values in your calculations-including answers submitted in WebAssign. Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) A A I3 = A Rs R3 12.0 V R2 9.00 V R1arrow_forwardA Wheatstone Bridge is used to determine the value of an unknown resistance R4 as shown in the diagram. The value of R2 is fixed at 22 Ω. The resistors shown as R1 and R3 are two parts of a uniform resistance wire. The bridge is balanced (i.e. no current flows through the voltmeter, V) when the length of wire corresponding to resistance R1 is 40 cm and the length of wire corresponding to resistance R3 is 60 cm. Calculate the value of the unknown resistance R4.arrow_forward
- Consider the circuit shown in the figure below. (Assume R, = 15.5 N and R, = 3.50 N.) b 25.0 V R2 R2 R 20.0 N (a) Find the potential difference between points a and b. (b) Find the current in the 20.0-N resistor. Aarrow_forwardWhat are the largest and smallest resistances you can obtain by connecting a 36 , a 55 , and a 2902 resistor together? Hint: How should you connect resistances so that the equilvalent resistance is larger than the indivudual resistances? Hint: How should you connect resistances so that the equilvalent resistance is smaller than each indivudual resistance? Rmax Rmin = = Ω Ωarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON