
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
Transcribed Image Text:A 4.45 g sample of an ideal gas occupies 0.860 L at 23.1°C and 1.025 atm. What will be its volume at 6.5°C and 2.0 atm?
This discussion is closed.
-
Submit Answer Tries 0/99
0-
CI
00
::
OCT
21
90
tv A
Timer
Notes
Evaluate
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
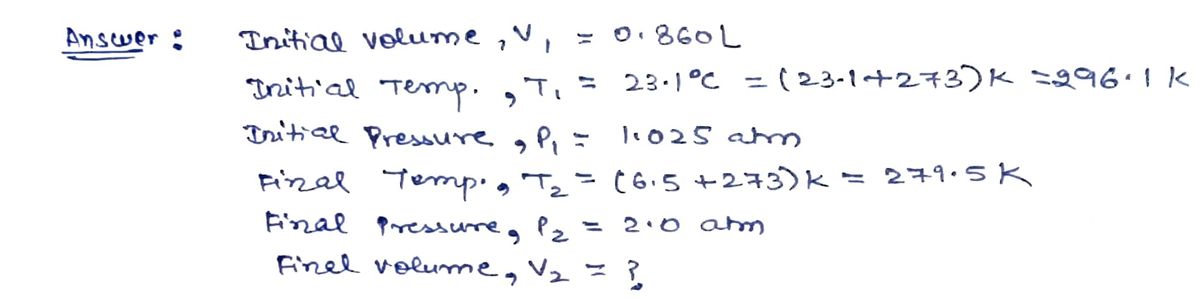
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider equimolar samples of different ideal gases at the same volume and temperature. Gas A has a higher molar mass than gas B. Compare the pressures. A>B A=B A<B Compare the rms speeds. A>B A=B A<B Compare the average kinetic energies. A>B A=B A<B Consider equimolar samples of the same ideal gas at the same volume, but different temperatures. Sample C is at a higher temperature than sample D. Compare the pressures. C>D C=D C<D Compare the rms speeds. C>D C=D C<D Compare the average kinetic energies. C>D C=D C<D Consider equimolar samples of the same ideal gas at the same temperature, but different volumes. Sample E has a larger volume than sample F. Compare the pressures. E>F E=F E<F Compare the rms speeds. E>F E=F E<F Compare the average kinetic energies. E>F E=F E<Farrow_forward#10 for the hw please show workarrow_forward[References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. How many grams of carbon disulfide are needed to completely consume 91.1 L of chlorine gas according to the following reaction at 25 °C and 1 atm? carbon disulfide ( s ) + chlorine ( g ) → carbon tetrachloride (I) + sulfur dichloride (s) grams carbon disulfide Submit Answer Try Another Version 1 item attempt remaining EGO Not Visited ot Previous Next Show Hint 10 四图t 10 tv 27 MAR 34 280 MacBook Airarrow_forward
- I need help with part A and B in chemistryarrow_forwardO Macmillan Learning Under identical conditions, separate samples of O₂ and an unknown gas were allowed to effuse through identical membranes simultaneously. After a certain amount of time, it was found that 7.24 mL of O₂ had passed through the membrane, but only 3.39 mL of of the unknown gas had passed through. What is the molar mass of the unknown gas? # 3 __a E unknown molar mass: D C $ 4 R F V do L % T G B MacBook Pro Y H & 7 N U g/mol J * 8 M | 1+ K ( 9 (>)) I command option { [ ? | + 11 } 1 delete retarrow_forwardSince volume and pressure are inversely related, we can make some assumptions about initial and final states using the data provided. We can also identify initial and final states by finding trigger words in the language of the problem. Look for words like “first,” “initially,” or “originally” to describe initial states and “result” or “after” for final states. What volume would a sample of helium occupy at 6.0 atm if the helium was initially compressed in a 1.0 L tank at 20. atm at constant temperature? Organize your data into the table to help analyze the problem. Leave blank any boxes for which you do not have information. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.arrow_forward
- A tire in your car is filled with air with an internal volume of 30.0 L. Determine the number of moles of air in the tire when the temperature outside is 20 °C and the pressure inside the tire is 3.50 atm. moles Accessibility: Investigate MacBook Pro Focusarrow_forwardA sample of ideal gas gas a volume of 3.15L at 11.60C and 1.60atm. What is the volume of the gas at 23.60C and 0.994atm?arrow_forward(References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. A sample of xenon gas at a pressure of 0.949 atm and a temperature of 26.9 °C, occupies a volume of 11.0 liters. If the gas is compressed at constant temperature to a volume of 3.30 liters, the pressure of the gas sample will be Submit Answer Try Another Version 3 item attempts remaining Previous Next Email Inst Cengage Learning | Cengage Technical Support AP DELLarrow_forward
- A 8.00 L tank at 24.8 °C is filled with 19.2 g of boron trifluoride gas and 13.4 g of carbon monoxide gas. You can assume both gases behave as ideal gases under these conditions. Calculate the mole fraction of each gas. Round each of your answers to 3 significant digits. mole fraction gas boron trifluoride carbon monoxide Check Explanation Prive Terms of Use O 2019 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved. 11 4X 12/ 99+ OType here to search hp ins prt sc delete f1o f6 backspace & $ vaing eyLevng eSEO ON ARES ON Battery IC 6499 Rarrow_forwardA 1.00-L sample of an unknown gas weighs 0.785 g and is at 0.965 atm and 29.2°C. What is the identity of the gas? Neon Methane Argon Chlorine gas O Carbon Dioxidearrow_forwardRank the samples of gas described in the table below in order of increasing average speed of the atoms or molecules in them. That is, select "1" next to the sample in which the atoms or molecules have the slowest average speed. Select "2" next to the sample in which the atoms or molecules have the next slowest average speed, and so on. average speed of atoms or molecules gas sample 1.3 mol of krypton gas at 2.5 atm and -28. °C (Choose one) v 2.3 mol of xenon gas at 2.9 atm and – 28. °C |(Choose one) v 1.9 mol of krypton gas at 1.7 atm and 30. °C (Choose one) v 1.0 mol of krypton gas at 3.0 atm and 1. °C |(Choose one)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY