
Concept explainers
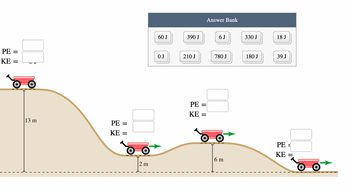
A 3 kg toy car sits at the highest point of a 13 m high hill. The car is gently pushed forward until it begins to roll down the slope. Assuming the car coasts freely, without any friction or air resistance, how much kinetic energy (KE) and potential energy (PE) will it have at each of the indicated points? Complete the diagram by placing the correct label in each bin. Use g = 10 m/s^2 for the acceleration due to gravity. The diagram is not drawn to scale.

We know that kinetic energy
potential energy
where, m = mass
g = gravitational acceleration
h = height
v = velocity
Now when an object is at its maximum height its potential energy is maximum but kinetic energy is zero.
Again, when the object is at minimum height its kinetic energy is maximum but potential energy is zero.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

- Look at the diagram below. 3.0 kg 10.0 m In the diagram, a 3.00 kg ball is dropped from a height of 10.0 m. What will its kinetic energy be just before it hits the ground? (Disregard air resistance; g= 9.81 m/s2) A 0.980 J B 29.4 J 98.0 J D 294 Jarrow_forwardA brick lies perilously close to the edge of the flat roof of a building. The roof edge is 50 ft above street level, and the brick has 260.0 J of potential energy with respect to street level. Someone edges the brick off the roof, and it begins to fall. What is the brick’s kinetic energy when it is 35 ft above street level? What is the brick’s kinetic energy the instant before it hits the street surface?arrow_forwardA ball is dropped from the top of a building. Person A choses the top of the building as a reference choice while person B choses the bottom. Explain whether the energy calculated using two differnt reference points are the same or different.arrow_forward
- In each situation shown in the figure below, a ball moves from point A to point B. For each case, find an algebraic expression for the change in potential energy in terms of the parameters given in the figure. You can assume that the radius of the ball is negligible. (Use any variable or symbol stated on each corresponding picture along with the following as necessary: g.) Δυ, Case 1 AU Case 2 %3D AU Case 3 m Case 1 R Case 2 B m m R 2R Case 3 1053 DMarrow_forwardThe block moves from point B at a velocity of 4,95 m:s1 up a rough inclined plane to point C. The speed of the block at point C is 2 m:s1. Point C is 0,5 m above the horizontal, as shown in the diagram below. During its motion from B to C a uniform frictional force acts on the block. 1.Use energy principles to calculate the work done by the frictional force when the 2 kg block moves from point B to point Carrow_forwardCalculate Kinetic Energy, Potential Energy, Rest Energy and Work using the following information. Force = 500,000 cN %3D Mass = 200,000 g Speed (velocity) = 5 m/s %D Height = 1500 mm %3D Distance = 3 miles (1 mile = 1.6 km) %3D %3D We also know that acceleration of gravity, g = 10 m/s^2 and %3D speed of light, c = 3 x 10^8 m/s. First do all necessary unit changes for all the above quantities and then show all work to calculate Work, KE, PE and RE. BIU A Paragraph + v II II II II II II II II II II II II II II II II II II II II lili II II II II II II II IIarrow_forward
- 1. A roller-coaster car with a mass of 1200 kg starts at rest from a point 20 m above the ground. At point B, it is 9 m above the ground. [Express your answers in kilojoules (kJ).] a. What is the initial potential energy of the car? b. What is the potential energy at point B? c. If the initial kinetic energy was zero and the work done against friction between the starting point and point B is 40 000 J (40 kJ), what is the kinetic energy of the car at point B 2. The time required for one complete cycle of a mass oscillating at the end of a spring is 0.80 s. What is the frequency of oscillation?arrow_forwardConsider a rope lowering a mass m=2.45kg at a constant speed v=8.73 m/s down a distance of d=5.72 m as shown in the figure below. c) What is the work done on the mass by the tension in the rope as it descends a distance d=5.72 m? d) What is the change in kinetic energy of the mass as it descends a distance d=5.72 m?arrow_forwardA woman runs up a flight of stairs. The gain in her gravitational potential energy is 1000 J. If she runs up the same stairs at half the speed, her gain in gravitational potential energy will be . . . Group of answer choices 500 J 2000 J 100 J 1000 Jarrow_forward
- Which of the following best describes the kinetic and potential energy of the skateboarder below? Group of answer choices They have the highest potential energy at point A and the highest kinetic energy at point C They have the highest potential energy at point B and the highest kinetic energy at point C They have the highest potential energy at point A and the highest kinetic energy at point B They have the highest potential energy at point C and the highest kinetic energy at point Aarrow_forwardAn object moves along the x axis, subject to the potential energy shown in the figure. (Figure 1) The object has a mass of 2.4 kg and starts at rest at point A. A) What is the object's speed at point B? B) What is the object's speed at point C? C) What is the object's speed at point D? D) What are the turning points for this object? Check all that apply. Point A Point B Point C Point D Point Earrow_forwardA cart is sliding along a frictionless track. It is moving with a speed of 10 m/s at position A on the track shown in the figure. What is the speed of the bead at point C?arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





