
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:References Mailings Review View Help Acrobat
Pictures
icture
cute
M
F3
F4
O B 2 r
Picture Tools
FO
Format
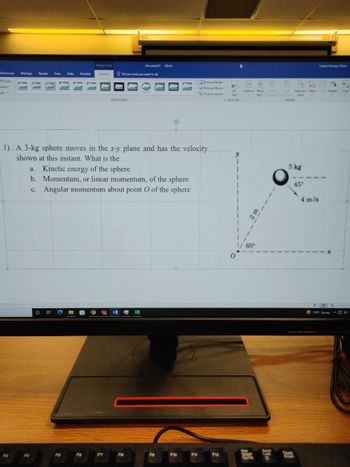
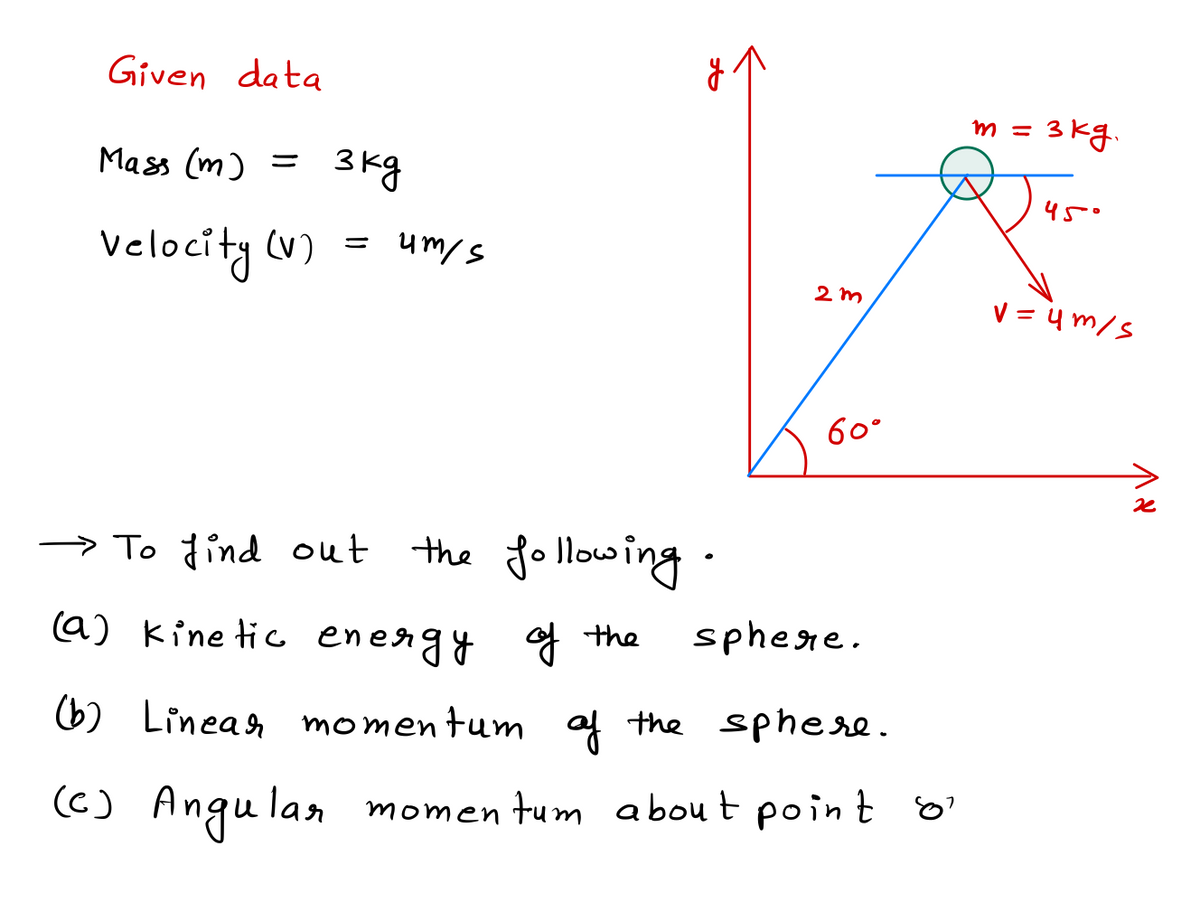
1) A 3-kg sphere moves in the x-y plane and has the velocity
shown at this instant. What is the
21
a. Kinetic energy of the sphere
b. Momentum, or linear momentum, of the sphere
c. Angular momentum about point O of the sphere
S.W.
Tell me what you want to do
Picture Styles
F7
Document1 Word
F8
XB
F9
F10
ZPicture Border-
Picture Effects
Picture Layout"
F11
F12
4
Alt
Text
& Accessibi..
y
1
I
I
I
0
OB
✔
Position Wrap Bring Send Selection Align Group Rotate
Text Forward Backward Pane
Arrange
E
1/ 60°
Print
Doreen
Sys Aq
Soroll
Look
B
3 kg
Puse
Break
45°
Castro Alvarez, Flavio
4 m/s
MR.
3
70°F Sunny
Crop
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Kinetic energy due to rotation of the body is defined as a. (1/2) m (v.)² b. (1/2) m (v.)² + (1/2) I ² c. (1/2) La co² d. I, 00²arrow_forwardGravitational Slingshot Often in designing orbits for satellites, people use what is termed a "gravitational slingshot effect." The idea is as follows: A satellite of mass m; and speed v,i circles around a planet of mass m, that is moving with speed v in the opposite direction. See the diagram below: Although the satellite never touches the planet, this interaction can still be treated as a collision because of the gravitational interaction between the planet and satellite during the slingshot. Since gravity is a conservative force, the collision is elastic. Use an x-axis with positive pointing to the right. Solve for the unknowns below algebraically first, then use the following values for the parameters. m, = 2.40E+24 kg m; = 880 kg Viz = 3.050E+3 m/s Vpiz = -6.10E+3 m/s Solve for the final velocity of the satellite after the collision.arrow_forwardTwo objects are moving in the x, y plane as shown. The magnitude of their total angular momentum (about the origin O) is: 2 m/s 3 m/s 6 kg 1 m 3 kg 2 m O1. 30 kg.ms-1 O 2.6 kg.m2s-1 O 3.21 kg.m2s-1 O 4.21 kg.ms-1 O 5.30 kg.m²s-1 O5.arrow_forward
- Velocity of C relative to D isn't 0 since block C slides along member DE, while member DE rotates, and you didn't use the formula for rotating axisarrow_forwardAs shown in the picture below, a 40-kg diver is positioned so that his radius of gyration is 0.4m as he leaves the board with an angular velocity of 5 rad/s (Position 1). What is the diver's angular velocity when he changes his pose to Position2, altering his radius of gyration to 0.2m? Position 1 Position 2 CARarrow_forwardI Suppose an autonomous surface vessel (ASV) traveling with velocity TvG/O= vi₁ begins to make a turn by adjusting the thrust of its left and right thrusters, TA and TB, respectively. The center of mass of the ASV is located at G and the ASV is symmetric about its vertical axis. The ASV also experiences a drag force that is proportional to its speed and opposes its velocity. At the instant shown, the drag force is D = -kvi₁ where k is a drag coefficient. 1. To model the mass moment of inertia, approximate the ASV as consisting of three rigid bodies: a flat plate as a center body of mass 6m and two slender rods housing the propulsion assemblies, each of mass m, at the outboard sides of the vehicle. Determine the mass moment of inertia, IG, about the vertical axis passing through the center of mass G. (Hint: Use the parallel axis theorem.) 2. At the instant shown, determine the inertial acceleration vector ac/o = axi₁ + ayi2 of the center of mass and the angular acceleration a of the…arrow_forward
- A weight of mass m is at rest at 0 when suspended from a spring, as shown. When it is pulled down and released, it oscillates between positions A and B. Which statement about the system consisting of the spring and the mass is correct? (Check ALL that apply) -B O The gravitational potential energy of the system is greatest at A. O The elastic potential energy of the system is greatest at O. O The kinetic energy of the system is greatest at 0. O The gravitational potential energy is smallest at O. O The elastic potential energy is smallest at 0.arrow_forwardA snooker ball x collides head-on with another snooker ball y moving in the opposite direction. Which of the following statement below is the correct statement of the conservation of momentum? The total momentum in the x and y 5. A. directions stay constant. The initial and final momenta of x is the B. same. The sum of the x and y components of C the momentum is zero. The final momentum of x is the same as D the final momentum of y.arrow_forward3/65 A pilot flies an airplane at a constant speed of 600 km/h in the vertical circle of radius 1000 m. Calcu- late the force exerted by the seat on the 90-kg pilot at point A and at point B. B 1000 m A 600 km/harrow_forward
- 3. Express the kinetic energy of each of the systems and determine the number of degrees of freedom of each system in terms of the specified generalized coordinates. Slender bar of mass m Slender bar of mass m To (a) (c)arrow_forward4. A loading car is at rest on a track forming an angle of 25° with the vertical when a force is applied to the cable attached at C. The gross weight of the car and its load is 5465 lb WG, and it acts at point G. Know the tension in the cable connected at C is 5000 Ib Tc. Neglect friction between the car and the track. Determine how far the car travels in 15 seconds. Model this as a particle at G. 24 in. B 25 in. 30 in. 25 in.arrow_forwardHi, how do you solve this question?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY