
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Calculate the mass of sand added to the bucket.
Calculate the acceleration of the system.
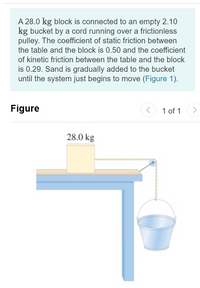
Transcribed Image Text:A 28.0 kg block is connected to an empty 2.10
kg bucket by a cord running over a frictionless
pulley. The coefficient of static friction between
the table and the block is 0.50 and the coefficient
of kinetic friction between the table and the block
is 0.29. Sand is gradually added to the bucket
until the system just begins to move (Figure 1).
Figure
1 of 1
<>
28.0 kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A tutor told me that the answer to 1b was 10N but I don't understand why it would be 10N for the tension. If that is correct could someone break it down for me?arrow_forwardThe following ramp has a slope of 14.0∘and a co-efficient of friction of μk=μk= 0.290. The mass of the box on the ramp, M, is unknown, but the mass hanging from down is given as 70.0 kg and the system accelerates to the right with an acceleration of a=a= 4.00 m/s2m/s2 (as shown below). Looking for: The force of tension in the rope will be: The mass, MM, of the box on the ramp is:arrow_forward2. Mass m₁ slides without friction on a plane inclined at 40° above horizontal plane. It is attached to a second mass m₂ by a light string. If m₁ = 5kg, m₂ = 4kg, determine the acceleration of each block and the tension of the string.arrow_forward
- The object shown below (length = 6 m) remains completely stationary, despite the fact that three forces act on it. Forces 1 and 3 act at either end, while force 2 acts 1/4 of the way from the left end. new-torque-prob If the size of force 3 is 4 N, then how large must the other two forces be? F1 F2 =arrow_forwardCreate a simple balance using a ruler as the balance beam and a pencil as the fulcrum. - Using a nickel as your standard, what are the ratios of the weights of a penny, dime, and quarter to that of a nickel? Explain how you determined these values.arrow_forwardLoad (L) = 5 kgs My: E - Elort E- Fulcrum Weight of forearm = 1.8 kgs L- Load Biceps brach musclo Distance of load from elbow joint = 35 cm Effort ) contraction of biceps brachi Distance of center of mass of forearm from elbow = 17 cm Distance of tendon from elbow = 4 cm A) Draw the free-body diagram to represent the forces and moments Load (Umeigtt of ond plus fosarm B) Write the torque equation for static equilibrium Fulcrum ( bon pintarrow_forward
- Question 5arrow_forward9) Consider the system below. In which direction will the heavier box slide? Which mass must increase, and by how much, to maintain the system in equilibrium? The angle at left is 28.1 degrees and the angle at right is 47.5 degrees. For the left, u = 0.405 and on the right 0.222. 4.65 kg 9.15 kgarrow_forward2. Take the example in class for when a fan attached to the sailboat fails to move the boat forward. The sail is removed but the fan keeps running. Will the boat move then? Why or why not? If so, which way will the boat move?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON