
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
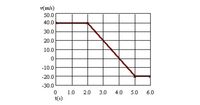
A 25 kg object and a 100 kg object collide. The graph below is for the 100 kg object. Assume momentum is conserved and find the impulse of the 25 kg object over the entire time shown.
Transcribed Image Text:v(m/s)
50.0
40.0
30.0
20.0
10.0
-10.0
-20.0
-30.0
1.0
2.0
3.0
4.0
5.0
6.0
t(s)
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
The change in momentum gives impulse.
......(1)
where f is the force
is the time interval
m is the mass of the body
is the change in velocity
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The force shown in the force-time diagram acts on a 2.5 kg object. Find the impulse of the force.Answer in units of N · s. Find the final velocity of the particle if it is initially at rest.Answer in units of m/s. Find the final velocity of the particle if it is initially moving along the x axis with a velocity of −3 m/s.Answer in units of m/s.arrow_forwardA 0.10 kg softball is traveling at 20.00 metres per second to the left. A batter strikes the ball and sends it traveling at 30.00 metres per second to the right. The bat and softball are in contact for 0.25 seconds. At the start of the problem you must state which direction you choose to be positive. What is the initial momentum and direction of the softball? What is the final momentum and direction of the softball? What was the impulse striking on the softball? What was the force of the bat striking the softball?arrow_forwardThe force shown in the force-time diagram acts on a 335 g object. Find the impulse of the force.Answer in units of N · s. Find the final velocity of the object if it is initially at rest.Answer in units of m/s. Find the final velocity of the object if it is initially moving along the x axis with average velocity of −21 m/s.Answer in units of m/s.arrow_forward
- A 160 g ball strikes a vertical wall and bounces off. The ball's initial velocity is a horizontal 5 m/s and the wall imparts an average normal force of 6.4 N for a time of 0.15 seconds during the bounce. What is the ball's final velocity (include magnitude and direction)? Use the impulse-momentum theorem to solve.arrow_forwardAn estimated force vs. time curve for a baseball struck by a bat is shown in the figure below. (a) From the curve, determine the impulse delivered to the ball. (b) From the curve, determine the average force exerted on the ball.arrow_forwardA golf ball m = 0.11 kg strikes a vertical concrete wall elastically with a horizontal velocity of v = 13 m/s. Write an expression for the magnitude of the impulse I experienced by the ball. If the ball was in contact with the wall for t = .1s, what is the magnitude of the force F the ball experienced in N? If the ball rebounds with only half the velocity it comes in with, what is the magnitude of the impulse in kg m/s? Determine the magnitude of the change in kinetic energy in the above situation. Give your answer in joules.arrow_forward
- In tae-kwon-do, a hand is slammed down onto a target at a speed of 15.4 m/s and comes to a stop during the 4.29 ms collision. Assume that during the impact the hand is independent of the arm and has a mass of 0.770 kg. (the magnitude of the impulse is 11.9 kg*m/s) What is the magnitude of the average force on the hand from the target? (PLEASE show how you get this answer )arrow_forwardA green pool ball (p = 30 kg x m/s) moves towards a yellow pool ball (p = -9 kg x m/s). Then, the two pool balls collide. After the collision, the green pool ball has a momentum of 3 kg x m/s. How much momentum does the yellow pool ball have after the collision? Explain your answer.arrow_forwardA car and a small truck traveling at right angles to one another with the same speed collide and stick together. The truck's mass is roughly twice the car's mass. Sketch the direction of their momentum vector immediately after the collision. Explain your result.arrow_forward
- A 0.350 kg lump of clay is dropped from a height of 1.15 monto the floor. It sticks to the floor and does not bounce. What is the magnitude of the impulse ? imparted to the clay by the floor during the impact? Assume that the acceleration due to gravity is ?=9.81 m/s2. The force exerted by the floor on the clay is plotted as a function of time in the figure. What must have been the maximum force ?max exerted by the floor on the clay?arrow_forwardProblem 3: An egg with a mass m is dropped from rest from a height h and falls to the ground and breaks. Part (a) Write an expression for the magnitude of the net impulse imparted to the egg as it is stopped by the floor. Your expression will be in terms of m, h, and g. Neglect air resistance. Expression : J = Select from the variables below to write your expression. Note that all variables may not be required. B, y, 0, b, c, d, e, g, h, j, k, m, n, P, S Part (b) What is the numeric value for the magnitude of the impulse if m = 0.045 kg and h = 1.6 m Numeric : A numeric value is expected and not an expression. J =arrow_forwardIn tae-kwon-do, a hand is slammed down onto a target at a speed of 13.2 m/s and comes to a stop during the 5.16 ms collision. Assume that during the impact the hand is independent of the arm and has a mass of 0.654 kg.What is the magnitude of the impulse?8.63 N*s What is the magnitude of the average force on the hand from the target? (Answer 2nd question)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON