
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
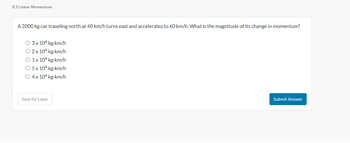
Transcribed Image Text:9.3 Linear Momentum
A 2000 kg car traveling north at 40 km/h turns east and accelerates to 60 km/h. What is the magnitude of its change in momentum?
O 3x 104 kg.km/h
O 2x 104 kg-km/h
O 1x 104 kg-km/h
O 5 x 104 kg-km/h
O 4 x 104 kg-km/h
Save for Later
Submit Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7. A 1.000 kg particle moves at a speed of 0.500 m/s, as shown in Figure 2a. It collides with a 2,000 kg particle at rest at origin. What is the system's total momentum of the system in the x and y direction before the collision? +y m2) V4 30 m m2 +X +X 45° (a) (b) Fig. 2: Collision of mass m, and m, 8. Figure 2b shows that, after a collision, m, travels at a speed v3 at an angle e, = 315.0° with respect to the horizontal axis, while m, moves at a speed v, at an angle O, = 30.0° with respect to the horizontal axis. Write an equation for the system's total momentum in the x and y direction after the collision. 9. Using the equations produced in question 8, solve the value of v3 and v4.arrow_forwardWhat is the momentum of a garbage truck that is 14500 kg and is moving at 10.0 m/s ? momentum: kg⋅m/s At what speed would a 9.35 kg trash can have the same momentum as the truck? speed: m/sarrow_forwardA pitcher throws a baseball of mass m = 0.150m=0.150 kg with a velocity of 43.7 m/s. The momentum of the baseball is a numerical answer below. Accepted formats are numbers or "e" based scientific notation e.g. 0.23, -2, 1e6, 5.23e-8 ..... k x xg /sarrow_forward
- Table 1a: Elastic Collisions and Change in Momentum Trial vf (m/s) vi (m/s) Dv (m/s) Dp (kg•m/s) cart 0.89 -0.97 1.86 0.5022 cart with one mass 0.65 -0.80 1.45 0.754 cart with two masses 0.51 -0.63 1.14 0.878 Table 1b: Elastic Collisions and Impulse Trial I (N•s) cart 0.632 cart with one mass 0.959 cart with two masses 1.066 Table 1c: Elastic Collisions and Impulse Trial % difference between I and Dp (I -Dp)/ ((Dp+ I)/2) * 100 cart 22.89 % cart with one mass 23.93 % cart with two masses 19.34 % Q1. What can you conclude about Table 1c (Impulse I and change in Momentum Dp) for Elastic Collisions?arrow_forward1. What is the change in momentum of a 26.3 g bird flying with the speed of 9.25 m/s due east then due north?arrow_forwardQuestions 1.-4. refer to a head-on collision between two balls with the following initial values: Before Collision m2 V Ix 3.5 kg 4.5 kg 5.0 m/s -2.0 m/s 1. What is the total momentum (in kg m/s) of the system? 2. If the two balls stick together, what is their common speed (in m/s) after they collide? 3. How much kinetic energy (in joules, positive number) was lost in this collision? 4. If the two balls do not stick together, and the first ball moves at vịx = -1 m/s after they collide, what is the speed (in m/s) of the second ball?arrow_forward
- I. A lump of clay (m = 3.01 kg) is thrown towards a wall at speed v = 3.15 m/s. The lump sticks to the wall. (a) What kind of collision is it? Is momentum conserved during this collision? Why or why not? (b) Calculate the impulse imparted on the lump by the wall. (c) Calculate percent of initial kinetic energy lost during this collision. II. Same lump is thrown towards the same wall, but this time it bounces off the wall at speed of 3.15 m/s. (a) What kind of collision is it? Is momentum conserved during this collision? Why or why not? (b) Calculate the impulse imparted on the lump by the wall. (c) Calculate percent of initial kinetic energy lost during this collision. III. Same lump is thrown towards the same wall, but this time it bounces off the wall at speed of 2.24 m/s. (a) What kind of collision is it? Is momentum conserved during this collision? Why or why not? (b) Calculate the impulse imparted on the lump by the wall. (c) Calculate percent of initial kinetic…arrow_forwardmeteor moving through the Earth's atmosphere has a momentum of 1.15 x 104 kgm/s. As it falls, friction with the atmosphere slows it to 1/4 its original speed, as its mass shrinks to 2/9 of its original mass. Determine its new momentum. A. 320 kgm/s B. 639 kgm/s C. 10350 kgm/s D. 207000 kgm/sarrow_forwardPhysics: Unit: Momentum and collisions Consider a collision in one dimensional that involves two objects of masses 4.5 kg and 6.2 kg. The larger mass is initially at rest, and the smaller mass has an initial velocity of 16 m/s (E). The final velocity of the larger object is 10.0 m/s (E). Calculate the final velocity of the smaller object after the collision.(Hint: = m1Vi1 + m2Vi2 = m1Vf1 + m2Vf2)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON