
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
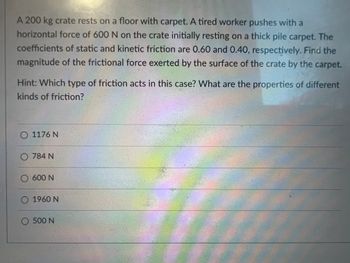
Transcribed Image Text:A 200 kg crate rests on a floor with carpet. A tired worker pushes with a
horizontal force of 600 N on the crate initially resting on a thick pile carpet. The
coefficients of static and kinetic friction are 0.60 and 0.40, respectively. Find the
magnitude of the frictional force exerted by the surface of the crate by the carpet.
Hint: Which type of friction acts in this case? What are the properties of different
kinds of friction?
O 1176 N
O 784 N
O 600 N
O 1960 N
O 500 N
TEALING
knong
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A block is being pulled up an inclined plane by a force with magnitude F=45.0 N as shown In the figure above. The block has a mass of m =1.35 kg. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block an the surface of the incline plane is µ = 0.287. The inclined plane makes an angle \theta= 31.7 degrees with respect to the horizontal. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the mass?arrow_forwardWhich of the following best describes the directions of friction and normal force? Your answer: Friction is always horizontal and normal force is always vertical. Friction is always horizontal and normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. Friction is always parallel to the surface and normal force is always vertical. Friction is always parallel to the surface and normal force is always perpendicular to the surface. There is no consistent pattern.arrow_forwardIf the coefficient of kinetic friction between an object with mass M = 3.00 kg and a flat surface is 4 =0.410, what force will cause the object to accelerate at 2.50 m/s? The force is applied at an angle of 0 = 30.0* (see the figure below). M Hk F = ? 1) Calculate the force. N Submitarrow_forward
- A physics major is cooking breakfast when he notices that the frictional force between the steel spatula and the Oiled Steel frying pan is only 0.150 N. Knowing the coefficient of kinetic friction between the two materials (0.03), he quickly calculates the normal force. What is it? Narrow_forwardA box of mass mb is being blown by a strong steady wind across the level surface of a picnic table. The wind exerts a constant horizontal force of magnitude Fwb. As the block slides it accelerates with a magnitude ab. Assuming that kinetic friction is acting, develop an expression for the coefficient of kinetic friction µk between the box and table. Your final answer should be in terms of mb, Fwb, ab and g.arrow_forwardThe coefficient μ of kinetic frictions depends on the surfaces in contact and their conditions, while the coefficient μ of static frictions does not depend on the surfaces conditions. a) Trueb) Falsearrow_forward
- Calculate the magnitude of a normal force on a 22.7 kg block in the following circumstances. a. the block is resting on a level surface. b. the block is resting on a surface tilted up at 40.8 degrees with respect to the horizontal. c. the block is resting on the floor of an elevator that is accelerating upward at 2.53 m.s^2 d. the block is on the level surface and a force of 115 N is exerted on it at an angle of 40.8 degrees below the horizontal.arrow_forwardYou are lowering two boxes, one on top of the other, down a ramp by pulling on a rope parallel to the surface of the ramp as shown below. Both boxes move together at a constant speed of 13.1 cm/s. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ramp and the lower box is 0.374, and the coefficient of static friction between the two boxes is 0.793. a. What force do you need to exert to accomplish this? b. What are the magnitude and direction of the friction force on the upper box? 32.0 kg 48.0 kg 2.50 m 4.75 m e on tearrow_forwardA 20 kg box is released from rest from the top of a 15 m long inclined plane, which is angles 30 degrees above the horizontal. Assuming there is friction between the ramp and the wagon, how is this frictional force affected if the angle of the inclined plane is increased? O The frictional force increases. O The frictional force stays the same. O The frictional force decreases. O The frictional force cannot be determined with the given information.arrow_forward
- A 18kg crate is pushed across the floor, using a force that makes an angle of 21 degrees with the horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between crate and floor is µs=0.45. The coefficient of kinetic friction between crate and floor is µk=0.20. a) What magnitude of pushing force is required to just start the crate sliding? b) Once it has started sliding, if you continue to push the crate with the same amount of force found in “a”, what will its acceleration be?arrow_forwardA 620 kg packing crate is being pulled up a 16 degrees-inclined plane by a rope. The rope is parallel to the incline. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.3. (a) What is the size of the normal force acting on the crate? N (b) What is the size of the kinetic friction force acting on the crate? N (c) What is the size of the tension force if the crate is moving with constant velocity?arrow_forwardYou are trying to slide a heavy trunk across a horizontal floor. The mass of the trunk is 85kg, and you need to exert a force of 3.3*10^2 N to make it just begin to move. a)Determine the coefficient of static friction between the floor and the trunk.b)After the trunk starts moving, you continue to push with this force. The trunk reaches a speed of 2.0m/s after 5.0s. Calculate the acceleration of the trunk if the coefficient of kinetic friction between the trunk and the floor is 0.32.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON