
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
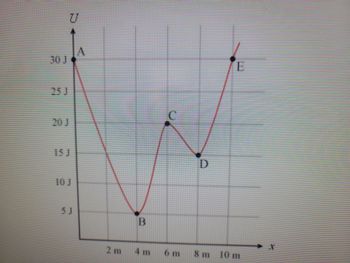
A 2.2kg mass starts from rest at point A and moves along the x-axis subject to potential energy shown in the figure.
Determine the speed of the mass at points B,C and D.
Transcribed Image Text:25J
77
20 J
15J
2 m
4 m
C
6 m
E
8 m 10 m
Y
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 222 kg weather rocket reaches its maximum height 32 km above the Earth's surface. Determine a)The amount of gravitational potential energy at its maximum height. b) Its speed when it hits the ground (neglect frictional effects).arrow_forwardNeeds Complete typed solution with 100 % accuracy.arrow_forwardHi there!! My question is bolded below :) It is a multiple choice question, so I have also listed every possible answer. A person with a mass of 42kg starts from rest at position A, as shown, and then slides down to positions B, C, and D. Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the person at A. 412 J 672 J 4.2 kJ 6.6 kJ Thanks!arrow_forward
- A child of mass m = 27 kg slides down a slide of height h = 2.1 m without friction. Let gravitational potential energy be zero at ground level. Write an expression for the child's total mechanical energy, E, at the top of the slide, in terms of the variables in the problem and the acceleration due to gravity g. Calculate the change in the child's potential energy, ΔU in joules, from the top to the bottom of the slide at ground level (i.e. ΔU = Uground- Utop). What is the child's final speed, vf in m/s?arrow_forwardA 8.67 kg8.67 kg particle is subjected to only conservative forces, and its potential energy diagram is shown. Between points G and K, at what location is the particle moving the fastest? J G K The particle is moving at the same speed at all of the points listed here. I H At point D, the particle has a speed of 14.1 m/s.14.1 m/s. What is the maximum speed ?maxvmax achieved by the particle between points G and K? Assume the points on the graph can be determined to three significant digits. Therefore, the calculated value for maximum speed should contain three significant digits.arrow_forwardOn board the starship Serenity, Captain Mal has two boxes connected together by a cord that passes over a massless, frictionless pulley mounted on the ceiling of the storage bay. The first box has a mass of 252.0kg and the second box has a mass of 278.0kg. If the 278.0kg box starts off at rest 2.60m above the ground, find the speed of the box when it reaches the ground. Assume the gravity on Serenity is 9.80m/s2.arrow_forward
- Problem 6: A 0.25 kg ball is suspended from a light 1.2 m string as shown. The string makes an angle of 35° with the vertical. Let U=0 when the ball is at its lowest point (0 = 0). What is the gravitational potential energy, in joules, of the ball before it is released? What will be the speed of the ball, in meters per second, when it reaches the bottom? (from Problem 9) Does replacing the ball by a steel sphere of mass 0.75 kg at the end increase the maximum speed? L Otheexpertta.comarrow_forwardAt NASA's Zero Gravity Research Facility in Cleveland, Ohio, experimental payloads fall freely from rest in an evacuated vertical shaft through a distance of 132 m. (a) If a particular payload has a mass of 28 kg, what is its potential energy relative to the bottom of the shaft? (b) How fast will the payload be traveling when it reaches the bottom of the shaft? Convert your answer to mph for a comparison to highway speeds.arrow_forwardOn Earth with a gravational acceleration g, the potential energy stored in an object varies directly with its mass m and its vertical height h. What is the equations of the potential energy of a 2kg skateboard that is sliding down a ramp?arrow_forward
- What is the energy E required to accelerate a 1635 kg car from rest to 25 m/s? E = J Compared to the amount of energy required to accelerate a car from rest to 25 m/s, how much energy is required to accelerate the car from 25 m/s to twice that speed, 5.0 × 10' m/s? the same three times as much twice as much four times as much O O Oarrow_forwardA 2.3 kg mass starts from rest at point A and moves along the x-axis subject to the potential energy shown in the figure below. PE 30 J 25 J 20 J 15 J D 10 J 5 J 2 m 4 m 6 m 8 m 10 m (a) Determine the speed (in m/s) of the mass at points B, C, D. (For each answer, enter a number.) point 4.7 m/s В X Is energy conserved? If so, how do you know it is conserved? How does the total energy at A compare to the total point energy at any other point. m/s X Is energy conserved? If so, how do you know it is conserved? How does the total energy at A compare to the total point energy at any other point. m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON