
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
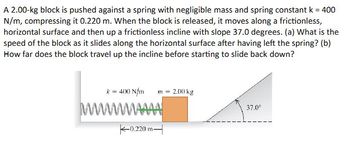
Transcribed Image Text:A 2.00-kg block is pushed against a spring with negligible mass and spring constant k = 400
N/m, compressing it 0.220 m. When the block is released, it moves along a frictionless,
horizontal surface and then up a frictionless incline with slope 37.0 degrees. (a) What is the
speed of the block as it slides along the horizontal surface after having left the spring? (b)
How far does the block travel up the incline before starting to slide back down?
k = 400 N/m }}}=
wwwwwwww
0.220 m
2.00 kg
37.0°
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 6.00 ✕ 105 kg subway train is brought to a stop from a speed of 0.500 m/s in 0.700 m by a large spring bumper at the end of its track. What is the force constant k of the spring?............N/marrow_forwardA bungee jumper has an elastic cord attached to her feet. The cord, whose unstretched length is nine meters, behaves just like a spring and is attached at the other end to the top of a platform high above the ground. After the bungee jumper steps off the platform, when is her speed the greatest? a)nine meters below the platform, when the cord first begins to stretch. b)when the upward force from the cord balances the downward force of gravity c)at the lowest point, when the gravitational potential energy is smallest d)when the kinetic energy equals the elastic potential energy in the cordarrow_forwardA block of 5 kg is pushed up against a platform that is attached to a spring of 1200 N/m. The spring is compressed 25 cm. The block starts out 5 m from point P and is released from rest. To the left of point P the surface is frictionless. To the right of point P the surface is frictional with coefficients of static and kinetic friction of 0.5 and 0.25, respectively. All parts of this problem must be solved using energy methods with the exception of cases discussed in lecture. a) Calculate the energy stored in the spring. b) What is velocity of the block once it leaves the platform? c) What is the work done by friction once the block is 2 m to the right of point P? d) How far from point P does the block stop?arrow_forward
- As shown in the figure, a 0.570 kg object is pushed against a horizontal spring of negligible mass until the spring is compressed a distance x. The force constant of the spring is 450 N/m. When it is released, the object travels along a frictionless, horizontal surface to point A, the bottom of a vertical circular track of radius R = 1.00 m, and continues to move up the track. The speed of the object at the bottom of the track is vA = 13.0 m/s, and the object experiences an average frictional force of 7.00 N while sliding up the track. (a) What is x? __ m (b) If the object were to reach the top of the track, what would be its speed (in m/s) at that point? __ m/s (c) Does the object actually reach the top of the track, or does it fall off before reaching the top? reaches the top of the trackfalls off before reaching the top not enough information to tellarrow_forwardProblem 2. A 4.0 kg object moving with an initial velocity of 8.0 m/s on a horizontal surface comes torest due to friction after it travels a distance of 10.0 m.(a) What is the increase of thermal energy caused by friction? Take g = 9.8 m/s2.(b)What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the object and the surface?arrow_forwardA block with mass 2.0 kg is pressed against a spring with spring constant 500 N/m, compressing the spring a distance of 0.1 m. It is then released from rest, moves across a frictionless horizontal surface, down a frictionless hill (vertical height 3.5 m), and onto a horizontal surface with friction (coefficient of kinetic friction 0.4). How far will the block slide across the horizontal frictional surface before coming to rest?arrow_forward
- A block with mass m = 12 kg rests on a frictionless table and is accelerated by a spring with spring constant k = 4696 N/m after being compressed a distance x1 = 0.469 m from the spring’s unstretched length. The floor is frictionless except for a rough patch a distance d = 2.8 m long. For this rough path, the coefficient of friction is μk = 0.42. 1) How much work is done by the spring as it accelerates the block? J 2) What is the speed of the block right after it leaves the spring? m/s 3) How much work is done by friction as the block crosses the rough spot? J 4) What is the speed of the block after it passes the rough spot? m/s 5) Instead, the spring is only compressed a distance x2 = 0.129 m before being released. How far into the rough path does the block slide before coming to rest? m 6) What distance does the spring need to be compressed so that the block will just barely make it past the rough patch when released? m 7) If…arrow_forwardA small block is sent through point A with a speed of 11 m/s, as shown in the figure. Its pathis without friction until it reaches the section of length L, where the coefficient of kinetic friction is0.5. The indicated heights are h1 = 6 m and h2 = 2 m. L = 10m.(a) Find the speed of the block when it reaches point C.(b) Find the speed of the block when it reaches point D.arrow_forward7. A 2.5kg block slides along a frictionless surface with a speed of 4 m/s. The blocks slides along until itmakes contact with a spring, compressing the spring 15 cm from its rest length at which point the block ismomentarily at rest. (a) how much energy is stored in the spring? (b) what is the spring constant?arrow_forward
- A single conservative force F = ( 6.0x - 11) i N, where x is in meters, acts on a particle moving along an x axis. The potential energy U associated with this force is assigned a value of 24 J at x = 0. (a) What is the maximum positive potential energy? At what (b) negative value and (c) positive value of x is the potential energy equal to zero?arrow_forward10. A 4.0 kg block is pushed against a spring with negligible mass and force constant k = 700 N/m, compressing it 0.20 m. When the block is released, it moves along a frictionless, horizontal surface and then up a frictionless incline with slope 40°. (a) What is the speed of the block as it slides along the horizontal surface after having left the spring? (b) How far does the block travel up the incline before starting to slide back down? (c) Redo part b. if there is a non-zero coefficient of kinetic friction k = 0.10 on the incline (but not on the horizontal surface). k m 30ºarrow_forwardA conservative force F is in +x-direction and has a magnitude F(x)=2.00/(x+0.070)3 N. Let U(x) approach 0 when x approaches infinity. An object with mass 1.00 kg is released from rest at x = 0 and moves in the +x-direction. If F is the only force action on the object, what is the object's speed when it reaches x = 0.500 m?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON