
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
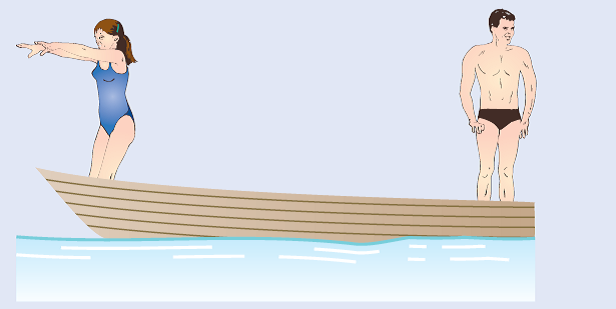
A 180-lb man and a 120-lb woman stand at opposite ends of a 300-lb boat, ready to dive, each with a 16-ft/s velocity relative to the boat. Determine the velocity of the boat after they have both dived, if (a) the woman dives first, (b) the man dives first.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In order to avoid the extra energy and time required in starting and stopping, whenever possible trains are loaded through a vertical chute which drops heavy loads directly into the moving train car beneath. The modern average locomotive and a single empty train car have a mass of approximately 23000 kg. If the train passes beneath shoot with a velocity of 6 meters per second when a 5200 kg load of gravel and stone is dropped into the empty train car beneath determine b) the final velocity of the train after the load has been delivered. 5 pts Question 15arrow_forwardQ2. As shown in the image below, the freight cars A and B are approaching each other, and they have a mass of mA = 23 Mg and mg = 14 Mg, respectively. The directions of their initial velocities are shown in the image, and the speeds are VA,1 4.3 m/s and v³,1 = 2.9 m/s. Determine the velocity of A after collision if the cars collide and rebound, such that B moves to the right with a speed of 1.8 m/s. Right is considered the positive direction and negative sign must be included if A moves to the left after the collision. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 3 places after the decimal point, and proper Sl unit. A Your Answer: VA,1 Answer units B VB.1 =arrow_forwardA railroad car having a mass of 15000 kg is coasting at 1.5 m/s on a horizontal track. At the same time another car having a mass of 12000 kg is coasting at 0.75 m/s in the opposite direction. If the cars meet and couple together, determine the speed of both cars just after the coupling.arrow_forward
- (2) A 5 lb ball is attached to a 3 ft long rope and it rotates in a vertical circular path at a constant tangent velocity of 30 ft/s. (a) Determine the tension in the rope when the ball is at point A. (b) Determine the tension in the rope when the ball is at point B. B 3 ft Aarrow_forwardIn order to avoid the extra energy and time required in starting and stopping, whenever possible trains are loaded through a vertical chute which drops heavy loads directly into the moving train car beneath. The modern average locomotive and a single empty train car have a mass of approximately 23000 kg. If the train passes beneath shoot with a velocity of 6 meters per second when a 5200 kg load of gravel and stone is dropped into the empty train car beneath determine b) the final velocity of the train after the load has been delivered. Antakarrow_forwardFreight car A with a gross weight of 138000 lb is moving along the horizontal track in a switching yard at 3.0 mi/hr. Freight car B with a gross weight of 166000 lb and moving at 3.9 mi/hr overtakes car A and is coupled to it. Determine (a) the common velocity V of the two cars as they move together after being coupled and (b) the loss of energy |AE| due to the impact. 3.9 mi/hr Answers: (a) V = B i (b) |AE| = i 3.0 mi/hr mi/hr ft-lbarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY