Question

Transcribed Image Text:Solve the problem:
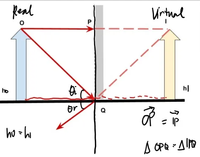
A 150 cm tall lady can just see her feet at the bottom edge
of the mirror, her eyes are 10cm below the top of her head.
a.) How high above the floor is the bottom edge of the
mirror?
b.) What is the minimum height of the top edge of the
mirror if she can see the top of her head?
Transcribed Image Text:Real
Urtunl
ho
h|
or
IP
ho -h
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2. Suppose that we have a glass rod (n, =1.50) surrounded by air with the left end ground to a convex hemisphere of 2 cm radius. If a point source is locaed 6 cm to the left of the hemisphere's vertex, where will its image appear? If the glass rod is immersed in water (nw= 1.33) determine the new location of the image of the point source. !!arrow_forwardA girl standing on the edge of a pond observes a fish that is 2 m deep as shown in the figure. If the girl is 1.32 m tall and looks at the fish at a 55 ° angle from the horizontal, how far is the fish from the girl? n air = 1 n water = 4/3 a) 6.93 m b) 1.87 m c) 4.85 m d) 3.44 marrow_forwardThe mirror equation relates the object distance, d0, the image distance, di, and the focal length, f, of a mirror as1 / d0 + 1 / di = 1 / fWhile in other topics, distance and length are strictly non-negative, in optics we introduce the following sign conventions: Object distance is positive for a real object and negative for a virtual object. Image distance is positive for a real image and negative for a virtual image. Focal length is positive for a converging mirror and negative for a diverging mirror (a) Select the best choice to complete this statement. A real object placed in front of a converging mirror creates a real image under all circumstances. under no circumstances. when the object is between the focal point and the mirror. when the object is farther than the focal length from the mirror. (b) Select the best choice to complete this statement. A real object placed in front of a diverging mirror creates a virtual image under all circumstances. under no circumstances.…arrow_forward
- 1. In a church choir loft, two parallel walls are 5.00 m apart. The singers stand against the north wall. The organist faces the south wall, sitting 0.900 m away from it. So that she can see the choir, a flat mirror 0.600 m wide is mounted on the south wall, straight in front of the organist. What width of the north wall can she see? __________ m 2. An object is placed 73 cm from a concave mirror of radius 45 cm. (a) Find the location of the image. (Enter in cm. Use a negative number if the image is behind the mirror) ______________ cmarrow_forward37 ... You are standing on the edge of a swimming pool and looking directly across at the opposite side. You notice that the bot- tom edge of the opposite side of the pool appears to be at an angle of 28° below the horizontal. However, when you sit on the pool edge, the bottom edge of the opposite side of the pool appears to be at an angle of only 14° below the horizontal. Use these observations to determine the width and depth of the pool. Hint: You will need to estimate the height of your eyes above the surface of the water when stand- ing and sitting.arrow_forwardThe apparent depth of an object submerged in water or other transparent liquid is A. closer to the surface than the actual objectB. deeper than the actual depth of the objectC. closer to the bottom of the material holding the liquidD. depends on the speed of light in waterarrow_forward
- 2arrow_forwardAt time t = 0, a ball is dropped (starting from rest) from a height of 3 m. The ball falls freely (i.e. without air resistance) toward a concave spherical mirror that has been laid horizontally on the ground directly below the ball. The mirror has a radius of curvature of magnitude 1 m. a) Calculate the position of the ball's image at t = 0. b) Calculate the position of the ball's image at an arbitrary time t. In other words, calculate the image position as a function of time. c) Calculate the position of the ball's image at t = 0.5 s. d) As the ball falls downward, its image moves upward. At what time do the ball and its image first coincide?arrow_forward3. The diagram shows a spherical surface which is silvered on both sides. Thus, the surface serves as double-sided mirror with one of the sides being concave and the other as convex. The principal axis, focal point, and center of curvature are shown. The region on both sides of the mirror is divided into eight sections labelled M, N, P, Q, R, S, T, and W. Five objects labelled as 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 are shown at various locations. Use the diagram to answer the following questions: R a. In what section would the image of object 1 be located? \. M P R b. In what section would the image of object 2 be located? M N Q R S c. In what section would the image of object 3 be located? (, N P Q R d. In what section would the image of object 4 be located? M P Q R e. In what section would the image of object 5 be located? M P Q R f. The double-sided mirror would produce virtual image to which objects? ( 1.2 and 3 1,2 and 4 3 and 5 4 and 5 g. The double-sided mirror would produce real image to which…arrow_forward
- A coin is placed at the bottom of an 80.0 cm deep aquarium filled with water. You are looking at the coin from above the aquarium. How deep will the coin appear to you in centimetres?arrow_forwardMCQ 4. A clown 2 m tall looks at himself in a full-length mirror (floor-to-ceiling). Where in the mirror must he look to see his feet? a. 1 m from the floor b. 50 cm from the floor c. 25 cm from the floor d. at the bottom of the mirror e. 1.5 m from the floorarrow_forwardAn olive is at the bottom of a glass of alcohol (n = 1.36). 6.78 cm beneath the surface. Above the alcohol is air. To a person in the air, who is directly above the olive, what is the apparent depth d' of the olive. d'= Number Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios