
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Balance the reactions
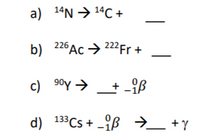
Transcribed Image Text:a) 14N → 14C +
b) 226Ac → 222Fr +
26 Ac → 222Fr +
22F +
c) 90y → + -iß
d) 133CS + -ß →_ +y
+ _{ß
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Analysis
Given : Different type of reactions
To find : missing part in the reactions
Solution : As we know that, Generally three types of radioactive decay are possible.
1 = alpha decay, 2 = beta decay, 3= gamma decay
In alpha decay alpha particle is removed
In beta decay two type of particles are removed one is beta particle and another one is positron
In Gamma decay, gamma rays are obtained that doesn't have any mass and charge.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the reaction when aqueous solutions of lead(II) nitrate and copper(II) sulfate are combined. The net ionic equation for this reaction is: Be sure to specify states such as (aq) or (s).arrow_forwardAqueous iron (III) nitrate and aqueous strontium chloride combine to produce solid iron (III) chloride and aqueous strontium nitratearrow_forward1) Group 1 metals react almost instantly and violently with water, as a single replacement reaction to produce an aqueous solution of metal hydroxide and hydrogen gas. A sample of solid lithium weighing 84.25 mg is dropped into a beaker containing 50.0 mL of water. Assume the density of water is 0.9988 g/mL. a) Write the balanced equation. b) Calculate the theoretical yield (in grams) of lithium hydroxide. c) Assuming the reaction is complete, and that there is no volume change, what is the concentration (in M) of lithium hydroxide in the solution that results?arrow_forward
- A 2.000-g piece of copper wire was used to precipitate silver ions as silver from a solution. When the copper metal reacts, Cu?* ions are formed, which are soluble in water. If 0.750 g of Ag(s) were produced in this process, what should the final mass of the copper wire be?arrow_forwardBalance the following reaction by choosing the correct coefficient that goes with each compound * Y, → _ XY,arrow_forwardWrite a balanced chemical equation based on the following description: aqueous iron(III) chloride reacts with aqueous ammonium sulfide to make aqueous ammonium chloride and solid iron(III) sulfide a) Write a balanced chemical reaction equation for the above reaction. b) Determine the type of reaction (decomposition, single-displacement, etc.) for the above reaction.arrow_forward
- Barium chloride solution is mixed with potassium sulfate solution to produce solid barium sulfate andpotassium chloride solution. For this reaction, write: (a) a balanced chemical equation, including all states of matter(b) a total ionic equation(c) a net ionic equationarrow_forwardConsider the reaction when aqueous solutions of barium hydroxide and iron(III) acetate are combined. The net ionic equation for this reaction is:arrow_forwardC. Single Replacement reactions Reactants Products Stramhaqx irdt 1ot 16ow noy bloe AgNO,+ Cu Copper (II) nitrate (aq) + Silver (s) Balanced equation:arrow_forward
- When aqueous solutions of potassium phosphate and calcium chloride are combined, solid calcium phosphate and a solution of potassium chloride are formed. The net ionic equation for this reaction is?arrow_forwardConsider the reaction when aqueous solutions of calcium acetate and cobalt(II) sulfate are combined. The net ionic equation for this reaction is:arrow_forward19. Sodium Hydroxide, when mixed with hydrochloric acid, will produce Sodium Chloride and Water. a) Write the balanced equation for the reaction. b) What mass of sodium hydrocide can be prepared by the reactio of 225 g of calcium hydroxide withexcess sodium carbonate. (154 g)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY