
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
01: A 105cm Rod is suspended on a wall with a 5N force pulling upwards, 110 degrees away from the horizontal axis and 5cm from a 50kgm hanging object. Find the location of the C.G. away from the wall. Neglect the Mass of the rod and consider it a rigid body. Assume SSLC.
02: Considering a CCW movement is Positive, what is the total value of the Negative Moments at the point with the 50kgm object? Please answer in four decimal places, in Nm.
03: What is the value of C.G. away from the wall? (in meters, two decimal places)
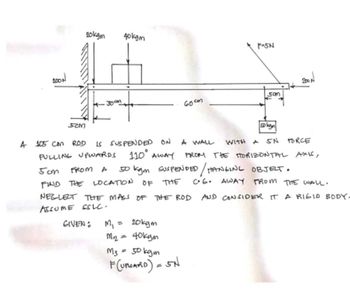
Transcribed Image Text:2001
52M
20kgm
30 am
40kgm
GIVEN: M₁ =
20kgm
M₂ = 40kgm
50 km
A 105 cm ROD IS SUSPENDED ON A WALL WITH A SN FORCE
PULLING UPWARDS 110° AWAY
FROM THE HORIZONTAL AXI6,
THE
San FROM A 50 kgm SUSPENDED / HANGING OBJECT.
FIND THE LOCATION OF
C.G. AWAY FROM THE WALL.
NEGLECT THE MASS OF THE ROD AND CONSIDER IT A RIGID BODY.
ASSUME SSLC.
M3
50 kgm
F(URDARD) = SN
60cm
P
F-5N
5am
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Torque Problem The diagram below shows the lower leg being held in a stationary. The torque acting to turn the leg in a clockwise direction is being generated by the weight of the leg and the weight of a barbel attached to the ankle. Using the information provided calculate the magnitude of the quadriceps force. LOWER LEG IN ANGULAR EQUILIBRIUM 15° Quadriceps muscle force 0.05m 0.14 m 50° 0.30m 90 Newtons 120 Newtons Show your calculations step by step here. Includes diagrams and short comments to explain your approach to solving the problem.arrow_forwardYou are sitting in a chair and you are ready to kick a soccer ball from a sitting position using only your quadriceps muscles to rotate your knee. Be sure you will not pivot your hips, as you are sitting in the chair; we want to simplify this problem to include only rotating your lower leg at the knee joint and keeping your thigh firmly fixed to the seat. For our purposes, your quadriceps muscles can be treated as a single string that exerts a tension on the knee at a right angle from a lever arm of 2.00 cm. The knee is connected to a plausible 50.0 cm lower leg as measured from the pivot point of the knee to the contact point where we will kick the ball.Before we kick it, we would like to balance the ball on our contact point (at our ankle, say) 50.0 cm away from the pivot point of the knee by extending the lower leg straight out (upper leg aligned with the lower leg). The soccer ball has a mass of 400 grams. We will neglect all mass of all parts of the leg here for brevity.a) Draw an…arrow_forwardA schematic diagram of the knee joint is shown in Fig, where Cdenotes the effective center of rotation of the knee and P is the point of insertion of the quadriceps tendon to the patella. The distance from C to P is 10 cm. The quadriceps, responsible for extension of the knee, are known to produce maximum isometric tetanic tension at an effective optimal length of 30 cm. This occurs when the knee flexion angle, θ, is 45◦. Obtaining muscle performance data from the appropriate figure in this chapter, determine the range of knee flexion angles for which the quadriceps produce an isometric tetanic tension at least 80% of maximal. Hint: be careful to use radians (rather than degrees) in this question when appropriate.arrow_forward
- The image below is of an arm in 90 degree elbow flexion holding an implement in the hand. SOLVE FOR THE TORQUE ABOUT THE ELBOW IN ORDER TO MAINTAIN EQUILIBRIUM. Here are the values. d1: 0.024m d2: 0.310m d3: 0.690m Fbarbell: 697N Farm: 74Narrow_forwardProblem 1: You have been hired to design a family-friendly see-saw. Your design will feature a uniform board (mass M=10 kg, length L = 3.7 m) that can be moved so that the pivot is a distance d from the center of the board. This will allow riders to achieve static equilibrium even if they are of different mass, as most people are. You have decided that each rider will be positioned so that his/her center of mass will be a distance xoffset ;= 17 cm from the end of the board when seated as shown. You have selected a child of mass m = 29 kg (shown on the right), and an adult of mass m2 = 62 kg (shown on the left) to test out your prototype. Xffset Xoffset Part (a) Determine the distance in meters. d = Part (b) Determine the magnitude of the force exerted on the pivot point by the see-saw while in use in newtons. EN = sin() cos() tan() 7 8 9 HOME cotan() asin() acos() E 4 atan() sinh() acotan() * 1 2 cosh() tanh() cotanh() + - END Degrees Radians BACKSPACE CLEAR DEL Submit Hint Feedback I…arrow_forwardsolve D and E onlyarrow_forward
- Four identical springs are attached to a surface as shown. Determine the spring force, spring constant and stretch length in each case. Also determine the length at which the last mass will hang at rest. Note: Drawing is not to scale. Fs k unit unit unit 0.16m case 1 case 2 0.19m case 3 0.27m 6kg case 2 What is mass 2 (m2)? unit case 1 What is length 3 (L3)? La 9kg unit case 3 cannot be determined check answers Unit 23: final review, springs and oscillations Desmos Scientific Online Calculator using g= 9,81m/s, vd 343m/s & 24 96 wwwarrow_forwardThe cable spool shown at the right has a weight of 50 lbs and has a moment of inertia of .28 slug-ft^2. Assume the spool rolls without slipping when we apply a 50-lb tension in the cable. Find: friction force between the spool and the ground.arrow_forwardAlert for not submit AI generated answer. I need unique and correct answer. Don't try to copy from anywhere. Do not give answer in image formet and hand writingarrow_forward
- Two blocks of equal massarrow_forwardneed help with Part D Pleasearrow_forwardThree springs are connected to a mass and to fixed supports. When the coordinate y is equal to zero, there is no spring force. Your tasks: Tw m k3 assume Staur C équilibrition Fload Figure 1: System schematic for Problem 1. A Draw the free body diagram for the mass m including all 3 spring forces and the load force Fload). B Draw the free body diagram for the mass m, but combine the springs into one equivalent spring with spring constant keq. Write the equivalent stiffness of the spring keq in terms of the other spring constants. (3 C Given that k₁ = 300 N/m, k₂ = 100 N/m, and k3 = 200 N/m, and Fload = 300 N, calculate the loaded deflection SA Yloaded- D Compute the amount of potential energy stored in each spring. E Compute the forces, in Newtons, in each spring and denote them as F₁, F2, and F3 when the load from Part D is applied. wwwarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY