
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
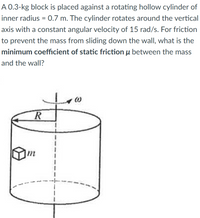
Transcribed Image Text:A 0.3-kg block is placed against a rotating hollow cylinder of
inner radius = 0.7 m. The cylinder rotates around the vertical
axis with a constant angular velocity of 15 rad/s. For friction
to prevent the mass from sliding down the wall, what is the
minimum coefficient of static friction u between the mass
and the wall?
m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A block of mass m:=4 kg is placed on an inclined plane with angle a-35°, connected to a second hanging block of mass m_2 by a cord passing over a small frictionless pulley. The static and kinetic friction coefficients are \mu_s=0.5 and \mu_k=0.3, respectively. a.- Determine the mass m_2 such that the block m_1 rises along the plane with constant speed once set in motion. 1.35 kg B: 1.31 kg 1.52 kg B: C: 0.65 kg 1.17 kg b.- Determine the mass m1 such that the block mi moves down the plane with constant speed once set in motion. D: 0.92 kg 1.61 kg D: E: 1.54 kg E: 3.28 kg 2.15 kg c. In what range of values of m2 do the blocks remain at rest, if they are released from rest? A 0.25 kgs my s1.36 B: 0.65 kg smis 3.93 C 0.13 kgs mas 1.87 D: 0.43 kg smis 2.23 E: 0.35 kg s mis 3.87 kg kg kg kgarrow_forwardThere is a box with height 1.2 m, width 0.8 m and mass 50 kg. It contains a very expensive equipment, which cannot be tilted while moving. There is a rope connected to the top-right corner of the box that you can pull with. The static friction coefficient between the floor and the box is 0.4. Assuming the rope angle θ is 30 degrees and m/s2. a) Is it possible to move the box using the rope without tilting the box? (need to show details) b) What is the minimum force required to move the box on the floor?arrow_forwardTwo blocks with masses M1 and M2 are connected by a massless string that passes over a pulley as shown. M1 is on an incline of 49.5° with coefficient of kinetic friction μ1 = 0.205. M2 has a mass of 4.84 kg and is on an incline of 35.5° with coefficient of kinetic friction μ2 = 0.105. The pulley can be modeled as a disk with a mass of 305 g and radius of 15 cm. When the system is released, Block M2 accelerates down the incline at rate of 0.52 m/s2. (a) Determine mass of block 1 and the tension forces in the string connecting the blocks and the pulley. Draw accurate free body diagrams of both blocks and pulley, label each force correctly and show the steps in derivation of equations. (b) How much energy will be dissipated by friction 2 second after the blocks are released?arrow_forward
- A 24 kg box is being pushed across the floor by a constant force <111, 0, 0> N. The coefficient of kinetic friction for the table and box is 0.18. At t= 8 s the box is at location <16, 5, -6> m, traveling with velocity <3, 0, 0> m/s. What is its position and velocity at t= 9.2 s? What is the new velocity and new position?arrow_forwardConsider the system shown below. The incline plane is fixed and the coefficient kinetic friction between M and 2M is ?1, and coefficient kinetic friction between the plane and 2M is ?2. Let M=2.0kg, ?=22o, ?1=0.14, and ?2=0.25. (a) What is the magnitude of the frictional force on mass M? (b) What is the magnitude of the total frictional force on mass 2M? (c) What is the acceleration of mass M? (d) What is the acceleration of mass 2M?arrow_forwardA box of mass m = 0.7 kg is attached to a rope which is wrapped around a physical pulley with a radius of R = 10.2 cm and a rotational inertia of I = 0.075 kg·m2. When the box is released it starts to fall down with a constant acceleration and, at the same time, the pulley starts to spin up, see the picture below. Assuming that the pulley is frictionless, what is the magnitude of the box's acceleration and what is the tension in the rope? The acceleration of the box, a ? The tension in the rope, T? If the box starts from rest and traveled downwards a distance of h = 28 cm, what is the speed of the box and what is the angular velocity of the pulley? The speed of the box, v =? The angular velocity of the pulley, ω? -------------------------------------------------------------- A Merry Go Round carousel has a radius of R = 2.4 m and a rotational inertia of I = 695 kg·m2. A 75‑kg student is on the carousel at the midpoint between the carousel's center and the rim (at R/2 distance from…arrow_forward
- 1:E1 A docs.google.com/for Untitled Section Determine the force P required to lower the 40-kg cylinder at a slow steady speed. The coefficient or friction between the cord and its supporting surface is 0.30. (g-10 m/s³). 40 kg Your answer If (4, =0.4) then the o between the normal force N and the friction force F will be Your answer العربية الإنجليزية IIIarrow_forward4) This Atwood's machine includes two blocks connected by a cable, going over a pulley without slipping. Block 1 (30.0 kg) is connected to a spring (70.0 N/m), and slides on a horizontal surface with a coefficient of kinetic friction of 0.0100. Block 2 is 50.0 kg, and hangs vertically from the cable. The pulley is a disk with a radius of 0.500 m, and its moment of inertia about the center of mass is 10. 0 kg-m“. a) Draw the three free body diagrams, and write out Newton's 2nd Law for each. b) Derive the equation of motion (inhomogeneous 2nd order ODE) for this system. c) Use u-substitution to rewrite this as a homogeneous 2nd order ODE. d) Assume the position x as a function of time t is of the form x(t) = A cos (wt + p) I disk for undamped natural frequency w, phase angle P, and amplitude A. The initial conditions are: x(0) v(0) = -3. 00 m/s. Solve for the position of the mass as a function of time (you need to solve for w, 4, and A). = 2. 00 m and Mzarrow_forwardYou pick up a boiled egg using kitchen tongs as shown. The egg is 60 g and it hasa static friction coefficient of 1.4 with the tongs. Determine the minimum magnitude of force Fyou need to apply so the egg does not fall. Assume you won’t break/crack the egg.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY