
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
i got this question wrong, could you please give me the correct answer so i can use it to study?
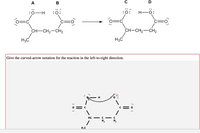
Transcribed Image Text:### Reaction Mechanism and Curved-Arrow Notation
#### Initial Reaction Structures (Reactants)
- **Molecule A**:
- Structure: A carboxylic acid group with an additional single bonded hydrogen.
- Atoms: Contains a carbon with a double-bonded oxygen (C=O) and an OH group.
- Additional Groups: The carbon is bonded to a propyl group (CH2-CH2-CH3).
- **Molecule B**:
- Structure: A carbonyl group with no additional hydrogens bonded to the carbon.
- Atoms: Contains a carbon double-bonded to oxygen (C=O) with a single lone pair.
#### Final Reaction Structures (Products)
- **Molecule C**:
- Structure: Similar to Molecule B with a carboxylic acid structure.
- Atoms: Has a carbon doubly bonded to an oxygen (C=O).
- Additional Groups: Remains bonded to the same propyl group (CH2-CH2-CH3).
- **Molecule D**:
- Structure: Similar to an alcohol with no charge.
- Atoms: Contains an OH group with a hydrogen atom bonded.
#### Curved-Arrow Notation
- **Description**: The diagram below the reaction equation illustrates the electron flow using curved-arrow notation.
- **Electron Flow**:
- A curved arrow starts from the lone pair of electrons on the oxygen of Molecule A's OH group.
- The arrow points towards the hydrogen atom, indicating that the lone pair is forming a bond with the hydrogen.
- Another curved arrow starts from the bond between the hydrogen and oxygen in the OH group, pointing towards the oxygen in Molecule B, indicating the transfer of the hydrogen atom.
This notation shows the movement of electrons during the reaction, facilitating the conversion of reactants to products. Understanding this visual representation is crucial for deciphering reaction mechanisms in organic chemistry.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
The curved arrow notation has to be given.
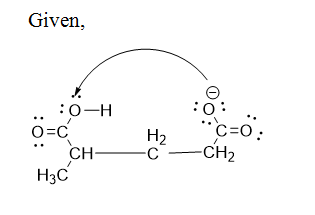
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you please help me with number 3arrow_forwardI tried both suggestions and they were both incorrect. Not sure what else to tryarrow_forwardM Apple Google Disney ESPN Yahoo! Biomedical Careers Program Apple iCloud Yahoo Images Bing Google Wikipedia COWLv2 |... b D2L ☆ & G For the reaction r r Submit Answer prod03-cnow-owl.cengagenow.com Fe(s) + 2HCI(aq)→→→FeCl₂(s) + H₂(g) AH° = -7.4 kJ and AS° = 107.9 J/K D2L D2L D2L Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. The Weather Channel Yelp TripAdvisor b D2L M G C The maximum amount of work that could be done when 2.08 moles of Fe(s) react at 286 K, 1 atm is Assume that AH° and ASº are independent of temperature. Retry Entire Group 4 more group attempts remaining kj. +88 Marrow_forward
- Catra wanted to determine the concentration of copper(II) chloride at an unknown concentration .She began by trying to determine the value of epsilon (ε) using beers law for copper(II) chloride. Catra remembered in lab when they wanted to solve for epsilon they would test the absorbance for three different concentrations of a known solution and then graph it. Catra got frustrated and asked Shera what to do next to determine epsilon. What should Shera tell Catra?arrow_forwardis this a Z or E? and why is it.arrow_forwardI don't know this questionarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY