
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
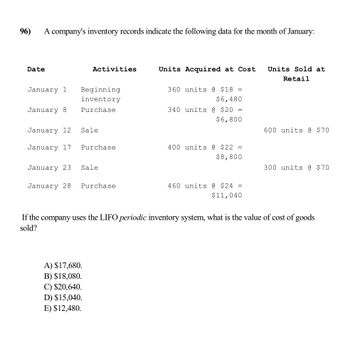
Transcribed Image Text:96)
A company's inventory records indicate the following data for the month of January:
Date
January 1
Beginning
inventory
January 8 Purchase
Activities
January 12
January 17 Purchase
Sale
January 23
January 28 Purchase
Sale
A) $17,680.
B) $18,080.
C) $20,640.
D) $15,040.
E) $12,480.
Units Acquired at Cost
360 units @ $18 =
$6,480
340 units @ $20 =
$6,800
400 units @ $22 =
$8,800
460 units @ $24 =
$11,040
Units Sold at
Retail
600 units @ $70
300 units @ $70
If the company uses the LIFO periodic inventory system, what is the value of cost of goods
sold?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Date April 1 April 7 A company's inventory records indicate the following data for the month of April: Activities Beginning inventory Purchase Units Acquired at Cost 880 units @ $36 = $31,680 760 units @ $40 Units Sold at Retail = $30,400 April 11 Sale 1,360 units @ $110 April 16. April 22 Purchase Sale 680 units @ $44 = : $29,920 400 units @ $110 The company uses a periodic inventory system. Determine the cost assigned to ending inventory using the specific identification method. Ending inventory consists of 380 units from the April 16 purchase, 80 units from the April 7 purchase, and 100 units from beginning inventory. Multiple Choicearrow_forwardFIFO Perpetual Inventory The beginning inventory at Dunne Co. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending June 30 are as follows: Number of Units Date Apr. 3 8 11 30 May 8. 10 19 28 June 5 16 2 29 Transaction Inventory Purchase Sale Sale Purchase Sale Sale Purchase Sale Sale Purchase 28 Sale 42 84 56 35 70 42 21 70 42 56 126 63 Per Unit $450 540 1,500 1,500 600 1,500 1,500 660 1,575 1,575 720 1,575 Total $18,900 45,360 84,000 52,500 42,000 63,000 31,500 46,200 66,150 88,200 90,720 99,225arrow_forwardPeriodic Inventory Using FIFO, LIFO, and Weighted Average Cost Methods The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Jan. 1 Inventory 15 units at $5,000 $75,000 Aug. 7 Purchase 16 units at $5,100 81,600 Dec. 11 Purchase 11 units at $5,300 58,300 42 units $214,900 There are 17 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic inventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost using (a) the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method; (b) the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method; and (c) the weighted average cost method (Round per unit cost to two decimal places and your final answer to the nearest whole dollar). а. First-in, first-out (FIFO) $4 b. Last-in, first-out (LIFO) С. Weighted average costarrow_forward
- Compute the correct December 31 Inventory The accounting records of Larkspur Electronics show the following data Beginning inventory3,120 units at $3 Purchases7,280 units at $5 Sales 8,760 units at $8 Determine cost of goods sold during the period under a periodic inventory system using (a) the FIFO method, (b) the LIFO method, and () the average cost methodarrow_forwardInventory by Three Methods The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Jan.1 Inventory 27 units at $400 per unit Feb. 19 Purchase 55 units at $460 per unit June 8 Purchase 62 units at $540 per unit Oct. 7 Purchase 57 units at $550 per unit There are 46 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic inventory system is used. Determine the inventory cost under each of the following methods. a. Determine the inventory cost by the first-in, first-out method.$ b. Determine the inventory cost by the last-in, first-out method.$ c. Determine the inventory cost by the average cost method. Do not round intermediate calculation and round final answer to the nearest whole value.$arrow_forwardPeriodic Inventory by Three Methods The units of an item available for sale during the year were as follows: Jan. 1 Inventory 1,045 units @ $130 Feb. 17 Purchase 1,380 units @ $132 July 21 Purchase 1,660 units @ $135 Nov. 23 Purchase 1,130 units @ $137 There are 1,205 units of the item in the physical inventory at December 31. The periodic inventory system is used. a. Determine the inventory cost by the first-in, first-out method. b. Determine the inventory cost by the last-in, first-out method. C. Determine the inventory cost by the weighted average cost method. Do not round intermediate calculation and round final answer to the nearest whole dollar. 11:52 PM 5/20/2021 DI %24 %24 %24arrow_forward
- Waterway Company had a beginning inventory on January 1 of 180 units of Product 4-18-15 at a cost of $20 per unit. During the year, purchases were as follows. Mar. 15 July 20 450 units 320 units (a) at $23 at $25 Sept. 4 Dec. 2 Determine the cost of goods available for sale. The cost of goods available for sale Waterway Company uses a periodic inventory system. Sales totaled 1,180 units. $ 350 units $27 100 units at $29 atarrow_forward97) A company had the following purchases and sales during its first month of operations: Date January 1 January 9 January 17 January 27 A) $84.00. B) $60.71. Activities C) $23.35. D) $46.70. E) $37.36. Purchase Sales Purchase Sales Units Acquired at Cost 10 units @ $4.00 = $40.00 8 units @ $5.50 = $44.00 Units Sold at Retail 6 units @ $12.00 Using the Periodic weighted average method, what is the value of cost of goods sold? (Round weighted average cost per unit to 2 decimal places.) 7 units @ $12.00arrow_forward12 Hazards company had the following data Beginning inventory (on May 1) Purchases during May $300 $5,400 $5,740 Cost of goods sold during May Based on the above data, calculate ending inventory as of May 30 O $380 $5,740 $340 O $40arrow_forward
- LIFO Perpetual Inventory The beginning inventory of merchandise at Dunne Co. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period ending June 30 are as follows: Number Date Transaction Per Unit Total of Units Apr. 3 Inventory 42 $225 $9,450 Purchase 84 270 22,680 11 Sale 56 750 42,000 30 Sale 35 750 26,250 May 8 Purchase 70 300 21,000 10 Sale 42 750 31,500 19 Sale 21 750 15.750 28 Purchase 70 330 23,100 June 5 Sale 42 790 33.180 16 Sale 56 790 44,240 21 Purchase 126 360 45,360 28 Sale 63 790 49,770 Required: 1. Record the inventory, purchases, and cost of merchandise sold data in a perpetual inventory record similar to the one illustrated in Exhibit 4, using the last-in, first-out method. Under LIFO, if units are in inventory at two different costs, enter the units with the HIGHER unit cost first in the Cost of Merchandise Sold Unit Cost column and LOWER unit cost first in the Inventory Unit Cost column. Dunne Co. Schedule of Cost of Merchandise Sold LIFO Method For the…arrow_forwardInventory - Perpetual Moving Weighted Average The following information was available from the inventory records of the Bean Company for January: Balance at January 1 Purchases: January 6 January 26 Sales (at $15/unit): January 7 January 31 Balance at January 31 Units 2,000 3,000 2,700 (2,500) (3,500) 1,700 Unit Cost $9.77 10.30 10.71 Total Cost $19,540 30,900 28,917 Assuming that Bean uses a perpetual moving weighted average system, record the entry/entries needed on January 31. Keep unit costs to 3 decimals.arrow_forwardThe beginning inventory for Dunne Co. and data on purchases and sales for a three-month period are shown in Problem 7-1B. Date Transaction Number of units Per unit ($) Total ($) April 3 Inventory 25 1.200 30.000 8 Purchase 75 1.240 93.000 11 Sale 40 2.000 80.000 30 Sale 30 2.000 60.000 May 8 Purchase 60 1.260 76.500 10 Sale 50 2.000 100.000 19 Sale 20 2.000 40.000 28 Purchase 80 1.260 100.800 June 5 Sale 40 2.250 90.000 16 Sale 25 2.250 56.250 21 Purchase 35 1.264 44.240 28 Sale 44 2.250 99.000 Instructions1. Determine the inventory on June 30, 2014, and the cost of goods sold for the threemonth period, using the first-in, first-out method and the periodic inventory system.2. Determine the inventory on June 30, 2014, and the cost of goods sold for the threemonth period, using the last-in, first-out method and the periodic inventory system.3. Determine the inventory on June 30, 2014, and the cost of goods sold for the threemonth period,…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education