
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
An axial member consisting of two polymer bars is supported at C as shown. Bar (1) has a cross-sectional area of 760 mm2 and an elastic modulus of 28 GPa. Bar (2) has a cross-sectional area of 1500 mm2 and an elastic modulus of 16.6 GPa. Determine the deflection of point A relative to support C.
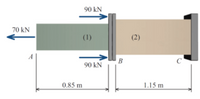
Transcribed Image Text:90 kN
70 kN
(1)
(2)
A
C
90 kN
0.85 m
1.15 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the minimum diameter of a 10-meter-long aluminum cantilever rod that can support the following loading and a maximum deflection of 0.01 meters: 1. Fixed from the left end 2. Concentrated downward force of 100 N at its right free end 3. Distributed load of 19.86 N/m throughout the entire length of the rod 4. Clockwise moment of 1000 N.m at its free end 5. A intermediate downward force of 200 N placed at the center of the rodarrow_forwardPravinbhaiarrow_forwardDetermine the horizontal and vertical components of reaction at the pin A and the reaction on the beam at C. ( Figure 1) Figure 1.5 m y -1.5 m- Part C FCD 1.5 m- = 1 of 1 4 kN B μà Part A Value Determine the horizontal component of reaction at the pin A. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Az = Submit Part B A₁ = μÁ Value Submit Request Answer Request Answer 4 Determine the vertical component of reaction at the pin A. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. μA Value Submit Request Answer Units Determine the magnitude of the force of reaction on the beam at point C. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. C Units ? Units ?arrow_forward
- A uniformly-distributed load w is supported by a structure consisting of rigid bar BDF and three rods. Rods (1) and (2) are 15-mm- diameter stainless steel rods that have an elastic modulus of E= 191 GPa. Rod (3) is a 21-mm-diameter bronze rod that has an elastic modulus of E= 100 GPa. Use a = 1.6 m and L = 3.2 m. For a load magnitude of w= 32 kN/m, calculate (a) the normal stress in each rod. (b) the vertical deflection of the rigid bar at F. (1) B Answers: (a) σ₁ = i (b) VF= i D Save for Later (2) eTextbook and Media 2a W E MPa, σ₂ = i mm MPa, and σ3 = i Attempts: 0 of 5 used MPa Submit Answerarrow_forward2. Link BD is made of brass ( E = 103 GPa ) and has a cross-sectional area of 258 mm?. Link CE is made of aluminum ( E = 72 GPa ) and has a cross sectional area of 332 mm? . Determine the maximum force P that can be applied vertically at point A if the deflection of A is not to exceed 0.30 mm. 225 mm 150 mm -225 mm 125 mmarrow_forwardThe deck is supported by the two 35-mm-square columns which are h = 3.7 m long. Column AB is pinned at A and fixed at B, whereas CD is pinned at C and The center of gravity of the load is located at d = 2 m. Both columns are made from Douglas Fir. Part A If the deck is prevented from sidesway, determine the greatest weight of the load that can be applied without causing the deck to collapse. Use E 13.1 GPa. Express your answer to three significant figures and include appropriate units. W = ON μà Value → Narrow_forward
- A steel bar with a rectangular cross section is used to transmit four axial loads as shown in Fig. Determine the axial forces transmitted by transverse cross sections in intervals AB, BC, and CD of the bar. 35 kip 20 kip 18 kiparrow_forwardQ1 / Two solid cylindrical rods are joined at B and loaded as shown. Rod AB is made GPa) and rod BC of brass (E = 105 GPa). Determine (a) the total deformation of the composite rod ABC, (b) the deflection of point B.arrow_forwardQuestion 6* Each member of the truss shown is made of steel and has the cross-sectional area of 400mm². Use Castigliano's theorem to determine the vertical and horizontal deflections of joint A. P = 3 KN E = 200 GPa A VP m F 2.5 kN 1 m. E B -1 m. D 1 marrow_forward
- Q1. For the beam given below, find the equation for deflection along the beam. L P EI = GIVEN USE SYMBOL SOLUTION.arrow_forwardi need answer on this asap. thank you! Each of the links AB and CD is made of aluminum and has a cross-sectional area of 0.2 sq.in. Knowing that they support the rigid member BC, determine the downward deflection (in inches) of point B. if x = 13.7 in, y = 28.1 in, z = 20 in, E = 10754407 psi, and P = 26 kips. Round off the final answer to five decimal places.arrow_forwardThe wing spar ABD of a light plane is made from 2014-T6 aluminum and has a cross- sectional area of 800 mm², a height of 79 mm, and a moment of inertia about its neutral axis of 1.07(106) mª. Assume A, B, and C' are pins. The neutral axis passes through the cross-section at half of its height. Connection is made along the central longitudinal axis of the spar. The anticipated loading is to be as shown. (Figure 1) Determine the absolute maximum bending stress in the spar. 0.6 m 14.4 kN/m 0.9 m B -1.8 m-arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY