
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:9. Using pure water, 1.0 M NaCI, and 1.0 M CaCl,:
a) List the substances in decreasing melting point
b) List the substances in increasing boiling point
East
The
96
5
8
3
T
E
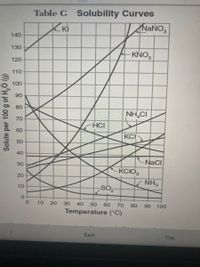
Transcribed Image Text:Table G Solubility Curves
KI
NANO
140
130
KNO,
120
110
100
90
80
NH,CI
70
HCI
60
KCI
50
40
30
NaCI
KCIO,
20
NH3
10
SO2
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Temperature (°C)
East
The
Solute per 100 g of H,0 (g)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A solution is made by mixing 39.0 mL of ethanol, C, H,O, and 61.0 mL of water. Assuming ideal behavior, what is the vapor pressure of the solution at 20 °C? The relevant values at 20 °C are included in the table. Liquid Density (g/mL) Vapor Pressure, P° (Torr) ethanol 0.789 43.9 water 0.998 17.5 vapor pressure: Torrarrow_forwardQuestion 19 Determine the vapour pressure (mmHg) of a solution prepared by dissolving 11.2 g of glucose (C6H1206) in 85.0 g of water at 25°C. The vapour pressure of pure water at 25°C is 23.8 mmHg. «< Question 19 of 20 A Moving to another question will save this response. tv 12 MacBook Air 44 * esc * 23 2$ % %D 2 4 7 8 9. Q W E T Y S F G H. J K Z C V alt alt command option option command .. .. DIarrow_forward25. A solution is made using 28.3 percent by mass CH₂Cl₂ in CHCl₃. At 30 °C, the vapor pressure of pure CH₂Cl₂ is 490 mm Hg, and the vapor pressure of pure CHCl₃ is 260 mm Hg. The normal boiling point of CHCl₃ is 61.7 °C. D) what is the vapor pressure of the solution in mmHg?arrow_forward
- Select the correct statement about cryoscopic constant. O It relates molality to freezing point elevation. O It relates molarity to freezing point elevation. O It relates molarity to freezing point depression. O The other statements are false. O It relates molality to freezing point depression.arrow_forward0.0821 kg of biphenyl (C12H10) is dissolve in benzene (CHo) to create a solution with a total volume of 350.0 mL. (Assume the change in volume is negligible) a) What intermolecular forces are shared between biphenyl and benzene? b) If the boiling point of pure benzene is 80.1 °C, then what would be the boiling point of this solution in °C? (Kb for benzene is 2.53 °C/m and the density of benzene is 0.877 g/mL) c) If the vapor pressure of pure benzene is 24.4 kPa at 40.0 °C, then what will the vapor pressure of the solution be in kPa? (Consider biphenyl to be nonvolatile and the density of benzene is 0.877 g/mL) d) What would be the osmotic pressure (in atm) of this solution at 40.0 °C? Assume the density of the solution is the same as benzene, 0.877 g/mL.arrow_forward18. A solution of 0.640 g of an organic compound (i-1) in 100.0 g of benzene boils at 80.23oC. The boiling point of benzene is 80.10oC; the Kb is 2.53 oC/molal. What is the molar masst of the compound? Group of answer choices 135 g/mol 125 g/mol 115 g/mol 145 g/mol 19. An aqueous solution of 0.864 g of a hormone in 100.0 mL of solution has an osmotic pressure of 0.195 atm at 25oC. What is the molecular weight of the hormone? Group of answer choices 1.08 x 104 1.08 x 103 8.20 x 102 8.20 x 103 0.990 x 103 20. What volume (mL) of 1.25 M AgNO3 should be used to prepare 250.0 mL of a 0.100 M solution? Group of answer choices 30.0 15.0 10.0 20.0 21. The density of a 3.00 M solution of KI is 1.350 g/cm3. What is the molality of the solution? Group of answer choices 5.26 2.56 5.32 3.52arrow_forward
- 25. A solution is made using 28.3 percent by mass CH₂Cl₂ in CHCl₃. At 30 °C, the vapor pressure of pure CH₂Cl₂ is 490 mm Hg, and the vapor pressure of pure CHCl₃ is 260 mm Hg. The normal boiling point of CHCl₃ is 61.7 °C. F) What is the boiling point in °C of the solution? (Kb for CHCl₃ is 3.67 °C/m).arrow_forwardA solution contains 17.83 grams of magnesium chloride and 811.7 grams of water. What is the vapor pressure (in torr) of this solution at 40.00°C? The vapor pressure of water at this temperature is 55.30 torr. You should use the experimental value of the van't Hoff factor for this calculation. (4 significant figures)arrow_forward97. Consider an aqueous solution that freezes at -0.229°C and is composed of 4.00% by mass maltose. a) Calculate the molar mass of maltose. b) Explain what causes a solution to have a lower freezing point than pure solvent. c) Explain why an aqueous solution actually freezes over a broader temperature range than pure water (which freezes sharply at 0.00°C).arrow_forward
- Given the following mixture of two compounds 45.00 mL of X (MW =82.00 g/mol)(density 1.077 g/mL) and 710.00 mL of Y (91.00 g/mol))(density 0.907 g/mL). The boiling point of pure Y is -18.00 degrees C. The molal boiling constant is 2.049 degrees C/m. What is the boiling point of the solution, in degrees C?arrow_forward11. Why is the boiling point of 2 M NaCl solution higher than the boiling point of 1 M of NaCl solution? The 2 M NaCl solution has a higher vapor pressure and requires more energy to reach boiling point. The 2 M NaCl solution has a lower vapor pressure and requires more energy to reach boiling point. The 2 M NaCl solution has a lower vapor pressure and requires less energy to reach boiling point. The 2 M NaCl solution has a higher vapor pressure and requires less energy to reach boiling point.arrow_forwardPredictarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY