
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
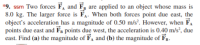
Transcribed Image Text:*9. ssm Two forces F, and F, are applied to an object whose mass is
8.0 kg. The larger force is FA. When both forces point due east, the
object's acceleration has a magnitude of 0.50 m/s². However, when F.
points due east and FB points due west, the acceleration is 0.40 m/s², due
east. Find (a) the magnitude of F, and (b) the magnitude of Fp.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- When Two forces FA and FB are applied to an object whose mass is 9.15 kg. The larger force is FA. both forces point due east, the object's acceleration has a magnitude of 0.784 m/s². However, when FA points due east and FB points due west, the acceleration is 0.420 m/s², due east. Find (a) the magnitude of FA and (b) the magnitude of FB. (a) Number i (b) Number i Units Unitsarrow_forwardTwo forces É, = (81.24i – 26.83j) N and É, = (27.41i - 80.52j) N are exerted on a particle. The particle's mass is 23.21 kg. (a) Find the particle's acceleration in component form. (Express your answer in vector form.) a = m/s? (b) What are the magnitude and direction of the acceleration? magnitude |m/s2 direction counterclockwise from the +x axisarrow_forwardThree forces acting on an object are given by F₁ = (−2.2î + 6.85ĵ) N, F₂ = (4.75î – 1.25ĵ) N, and F3 = (-401) N. The object experiences an acceleration of magnitude 3.80 m/s². (a) What is the direction of the acceleration? 98.50 X Note that the direction of the acceleration is the same as the direction of the net force.° (counterclockwise from the +x-axis) (b) What is the mass of the object? 9.964 kg (c) If the object is initially at rest, what is its speed after 11.0 s? 41.8 m/s (d) What are the velocity components of the object after 11.0 s? (Let the velocity be denoted by v.) ✓ = -41.34 m/s +6.18arrow_forward
- The 1 kg standard body has an acceleration of 2.00 m/s2 at 41° to the positive direction of the x axis. (a) What are the x and y components of the net force on it? x component N y component N (b) What is the net force in unit-vector notation? = Narrow_forwardA box of mass m, = 5 kg and a box of mass m,=2.5 kg are connected with a cord of negligible mass over a frictionless and massless pulley. The two objects are released from rest. The box is placed on a frictionless incline of angle 0 = 23°. (please use g = 9.8 m. m. 1. Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the masses with its unit: a = 4.6025 X m s^(-2) v 2. Calculate the magnitude of the tension in the cord with its unit: T= 25 X N 3. The box is sliding upward sliding downwardx not slidingarrow_forwardTwo teams of nine members each engage in a tug of war. Each of the first team's members has an average mass of 72 kg and exerts an average force of 1350 N horizontally. Each of the second team's members has an average mass of 77 kg and exerts an average force of 1373 N horizontally. (a) What is the acceleration (in m/s2 in the direction the heavy team is pulling) of the two teams?arrow_forward
- Three forces acting on an object are given by F₁ = (-1.95î + 6.60ĵ) N, F₂ = (4.651 – 1.85ĵ) N, and F3 = (-43.51) N. The object experiences an acceleration of magnitude 3.65 m/s². (a) What is the direction of the acceleration? O (counterclockwise from the +x-axis) (b) What is the mass of the object? kg (c) If the object is initially at rest, what is its speed after 18.0 s? m/s (d) What are the velocity components of the object after 18.0 s? (Let the velocity be denoted by v.) î+ î) m/sarrow_forwardA 1.20 kg object is subjected to three forces that give it an acceleration à = (4.80 m/s² )î + (5.00 m/s²). If two of the three forces are F₁ = (28.0 N )i + (11.0 N ) and F₂ = (15.0 N )i + (8.00 N )ĵ, find (a) the x component and (b) the y component of the the third force.arrow_forwardA 3.45-kg object is moving in a plane, with its x and y coordinates given by x = 3t2 - 3 and y = 2t3 + 4, where x and y are in meters and t is in seconds. Find the magnitude of the net force acting on this object at t = 2.50 s.arrow_forward
- Two forces FA and FB are applied to an object whose mass is 15.1 kg. The larger force is FA. When both forces point due east, the object's acceleration has a magnitude of 0.561 m/s². However, when FA points due east and FB points due west, the acceleration is 0.328 m/s², due east. Find (a) the magnitude of FA and (b) the magnitude of Fg. (a) Number i (b) Number i Units Units + ➜arrow_forwardThe nucleus of 8Be, which consists of 4 protons and 4 neutrons, is very unstable and spontaneously breaks into two alpha particles (helium nuclei, each consisting of 2 protons and 2 neutrons). (a) What is the force between the two alpha particles when they are 3.00 x10-15 m apart? N(b) What is the initial magnitude of the acceleration of the alpha particles due to this force? Note that the mass of an alpha particle is 4.0026 u. m/s2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON