
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Find the pH of the two equivalence points and the volume (mL) of 0.0888 M KOH needed to reach them in the titration of 17.3 mL of 0.130 M H2CO3.

Transcribed Image Text:O Question 10 - Ch 19 HW - Conne X
b Answered: Find the pH of the equ X
b Success Confirmation of Questior X G (a) 0.10 M CH3NH2(Kb = 4.4 × 1 X +
->
i ezto.mheducation.com/ext/map/index.html?_con=con&external_browser=0&launchUrl=https%253A%252F%252Fnewconnect.mheduc. A
C Paused
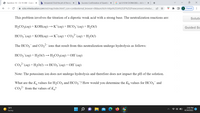
Be sure to answer all parts.
Find the pH of the two equivalence points and the volume (mL) of 0.0888 M KOH needed to reach them
in the titration of 17.3 mL of 0.130 M H2CO3.
First equivalent point
Second equivalent point
mL KOH
mL KOH
pH
pH =
70°F
2:20 PM
Sunny
4/24/2022
II
Transcribed Image Text:O Question 10 - Ch 19 HW - Conne X
b Answered: Find the pH of the equ X
b Success Confirmation of Questior X G (a) 0.10 M CH3NH2(Kb = 4.4 x 10 × +
->
i ezto.mheducation.com/ext/map/index.html?_con=con&external_browser=0&launchUrl=https%253A%252F%252Fnewconnect.mheduc. A
C Paused
This problem involves the titration of a diprotic weak acid with a strong base. The neutralization reactions are:
Soluti
Н-СОЗ(аq) + КОН(аq) — к'"(аq) + НСО; (аq) + Н,0()
Guided So
HCO3 (aq) + KOH(aq) → K"(aq) + CO3² (aq) + H20(1)
The HCO3 and CO3 ions that result from this neutralization undergo hydrolysis as follows:
НСОЗ (ад) + Hә0() — Н-СО3(аq) + ОН (аq)
СОз (аq) + H20() — НСО; (аq) + ОН (аq)
Note: The potassium ion does not undergo hydrolysis and therefore does not impact the pH of the solution.
What are the K, values for H2CO3 and HCO3 ? How would you determine the K, values for HCO3 and
CO3?- from the values of Ka?
70°F
2:18 PM
Sunny
4/24/2022
|D
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A volume of 10.0 mL of a 0.780 MHNO3 solution is titrated with 0.760 M KOH. Calculate the volume of KOH required to reach the equivalence point.arrow_forwardFind the pH of the two equivalence points and the volume (mL) of 0.0400 M KOH needed to reach them in the titration of 17.3 mL of 0.130 M H2CO3.arrow_forwardWhat is the pH at the equivalence point in the titration of 100.0 mL of 0.0500 M HOCl (Ka=3.5e−8) with 0.100 M NaOH?arrow_forward
- Find the pH during the titration of 20.00 mL of 0.1000 M triethylamine, (CH3CH2)3N, with 0.1000 M HCl solution after the following additions of titrant. 10.00 mL: 21.00 mL: 28.00 mL:arrow_forwardCalculate the pH for each of the cases in the titration of 25.0 mL of 0.110 M pyridine, C₁H₁N(aq) with 0.110 M HBr(aq). The Kb of pyridine is 1.7 x 10-⁹. before addition of any HBr pH = after addition of 12.5 mL of HBr after addition of 16.0 mL of HBr after addition of 25.0 mL of HBr after addition of 35.0 mL of HBr 9.31 pH = pH = pH = pH = 5.23 4.63 Incorrect 11.65 Incorrect 1.33 Incorrectarrow_forwardDetermine the pH at the equivalence point in the titration of 50.0 mL of 0.300 M CH₃COOH with 0.300 M NaOH. The value of Ka for CH₃COOH is 1.8 × 10⁻⁵. Use a BCA table to detrmine the moles of reactant and product after the reaction of the acid and base. Ignore the amount of liquid water. Then, set up an ICE table to identify the unknown. Then figure the pH.arrow_forward
- 19) What is the solution pH when 0.10 mol of H+ is added to a 2.0-liter buffered solution created from 0.31 M NH3 (Kb = 1.8 × 10–5) and 0.26 M NH4F.arrow_forwardCalculate the equivalence point volume in the titration of 15.00 mL of 0.2654 M HBr with 0.5678 M Ba(OH)2.arrow_forwardConsider the titration of 20.00 mL of 0.1145 M sodium azide (NaN3) with 0.1250 M HCl. The Ka of HN3 is 2.2 x 10–5. What is the pH at the equivalence point?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY