
University Physics Volume 1
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781938168277
Author: William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher: OpenStax - Rice University
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
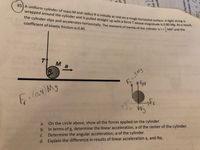
Transcribed Image Text:85. A uniform cylinder of mass M and radius R is initially at rest on a rough horizontal surface. A light strine
wrapped around the cylinder and is pulled straight up with a force T whose magnitude is 0.80 MB- As a reser
the cylinder slips and accelerates horizontally. The moment of inertia of the cylinder is I =MR- and the
coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.40.
%3D
2
a
Fr
(0.4
VFg
On the circle above, show all the forces applied on the cylinder.
b. In terms of g, determine the linear acceleration, a of the center of the cylinder.
Determine the angular acceleration, a of the cylinder.
d. Explain the difference in results of linear acceleration a, and Ra.
20
ar velocityr
velocity ?
gular
ar dis
(2)
lov
of
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Math Review (a) Convert 47.0 to radians, using the appropriate conversion ratio. (b) Convert 2.35 rad to degrees. (c) If a circle has radius 1.70 m, what is the are length subtended by a 47.0 angle? (See Sections 1.5 and 7.1.)arrow_forwardA solid aluminum sphere of radius R has moment of inertia I about an axis through its center. Will the moment of inertia about a central axis of a solid aluminum sphere of radius 2Rbe (a) 2I, (b) 4I, (c) 8I. (d) 16I. or (e) 32I?arrow_forwardThe centrifuge at NASA Ames Research Center has a radius of 8.8 m and can produce farces on its payload of 20 gs or 20 times the force of gravity on Earth. (a) What is the angular momentum of a 20-kg payload that experiences 10 gs in the centrifuge? (b) If the driver motor was turned off in (a) and the payload lost 10 kg, what would be its new spin rate, taking into account there are no frictional forces present?arrow_forward
- A proton is accelerated in a cyclotron to 5.0106m/s in 0.01 s. The proton follows a circular path. If the radius of the cyclotron is 0.5 km, (a) What is the angular momentum of the proton about the center at its maximum speed? (b) What is the torque on the proton about the center as it accelerates to maximum speed?arrow_forwardA particle has mass 0.5 kg and is traveling along the line x=5.0m at 2.0 m/s In the positive y-direction. What is the particle’s angular momentum about the origin?arrow_forwardA thin rod of length 2.65 m and mass 13.7 kg is rotated at anangular speed of 3.89 rad/s around an axis perpendicular to therod and through its center of mass. Find the magnitude of therods angular momentum.arrow_forward
- A 0.2-kg particle is travelling along the line y=2.0m with a velocity 5.0 m/s. What is the angular momentum of the particle about the origin?arrow_forwardAt a particular instant, a 1.0-kg particle’s position is , its velocity is , and the force on it is . (a) What is the angular momentum of the particle about the origin? (b) What is the torque on the particle about the origin? (c) What is the time rate of change of the particle’s angular momentum at this instant?arrow_forwardJeff, running outside to play, pushes on a swinging door, causing its motion to be briefly described by = t2 + 0.800 t + 2.00,where t is in seconds and is in radians. At t = 0 and at t = 1.50s, what are the a. angular position, b. angular speed, and c. angularacceleration of the door?arrow_forward
- A compact disc rotates at 500 rev/min. If the diameter of the disc is 120 mm, (a) what is the tangential speed of a point at the edge of the disc? (b) At a point halfway to the center of the disc?arrow_forwardA diver off the high board imparts an initial rotation with his body fully extended before going into a tuck and executing three back somersaults before hitting the water. If his moment of inertia before the tuck is 16.9kgm2 and after the tuck during the somersaults is 4.2kgm2 , what rotation rate must he impart to his body directly off the board and before the tuck if he takes 1.4 s to execute the somersaults before hitting the water?arrow_forwardA gymnast does cartwheels along the floor and then launches herself into the air and executes several flips in a tuck while she is airborne. If her moment of inertia when executing the cartwheels is 13.5kgm2 and her spin rate is 0.5 rev/s, how many revolutions does she do in the air if her moment of inertia in the tuck is 3.4kgm2 and she has 2.0 s to do the flips in the air?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning