
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The beam supports the distributed load shown. Determine the resultant internal loadings on the cross-section at points D and E. Assume the reactions at the supports A and B are vertical.
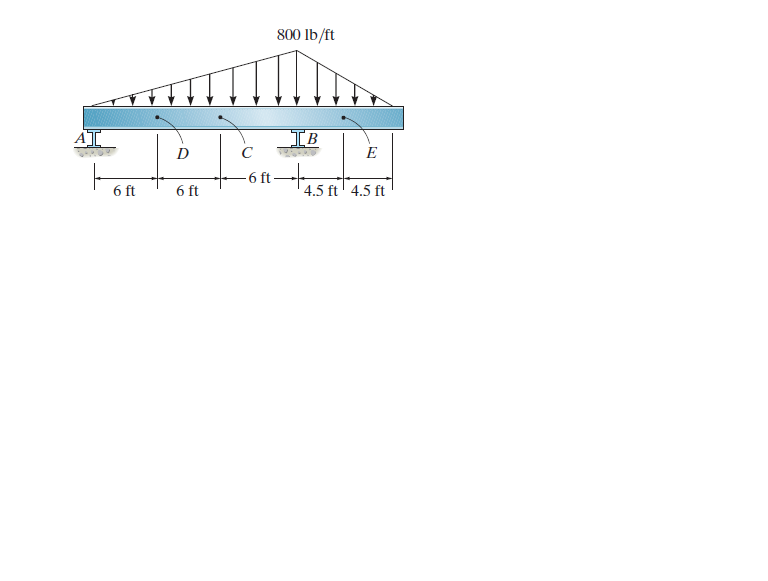
Transcribed Image Text:800 lb/ft
AI
IB
-6 ft
6 ft
6 ft
4.5 ft' 4.5 ft
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 13 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Answer should be R=168 kn and x^- = 6marrow_forwardQ.3) The rod is supported by a roller at A and a smooth collar at B. The collar is fixed to the rod AB but is allowed to slip along rod CD. Determine the support reactions at A and at B, the moment reaction in the collar at B. A 900 N -1.5 m -1.5 m- 800 N-m B 45% 3marrow_forwardThe answer should be correct please use a sheet of paper.arrow_forward
- Problem 1 The compound beam is fixed at E and supported by rollers at A and B. Determine the reaction at these supports. There are pins at C and D. 800 lb 5 ft+ 1200 lb В, C 600 lb 10 ft 5 ft—4 ft—— 6 ft D E -5 ft-arrow_forwardProvide the correct exponents and distances to make the singularity function given valid for the beam shown. V₁ = 8 kN, V2 = 7 kN, V3 = 200 mm, and V4 = 1100 mm. Determine the reaction forces at the supports. ATATV3 -V3- (mm) O The singularity functions are q = R₁(x)ª − v₁(x − P)ª − v₂(x − Q)¹ + R₂(x − R)ª V = R₁ – v₁(x – D)³ − v2(x − E)³ + R2(x – F)³ M = R₁x – v₁(x – G)ª − v₂(x − H)C + R₂(x − 1)C From the given singularity functions the exponents aro (1) (2)arrow_forwardA continuous beam supports loads as shown in the image. Determine the support reactions using the three-moment method. Consider that the stiffness of the beam is constant throughout.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY