
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
Transcribed Image Text:80
Exercise 2-12
Analyzing and journalizing
expense transactions
A1 P1
Exercise 2-13
Preparing an income
statement
C3 P3
ow
Check Net income, $10,470
Exercise 2-14
Preparing a statement
of owner's equity P3
Check End. Capital, $106,470
D
Exercise 2-15
Preparing a balance sheet P3
Exercise 2-16
Computing net income
A1
Exercise 2-17
Analyzing changes in a
company's equity
P31
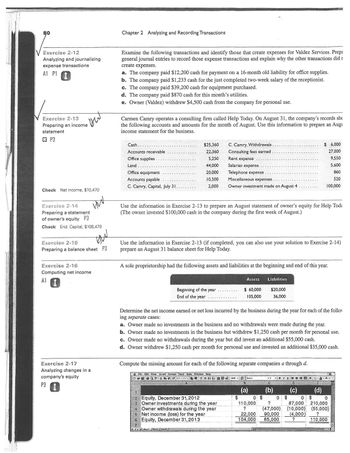
Chapter 2 Analyzing and Recording Transactions
Examine the following transactions and identify those that create expenses for Valdez Services. Prepa
general journal entries to record those expense transactions and explain why the other transactions did r
create expenses.
a. The company paid $12,200 cash for payment on a 16-month old liability for office supplies.
b. The company paid $1,233 cash for the just completed two-week salary of the receptionist.
c. The company paid $39,200 cash for equipment purchased.
d. The company paid $870 cash for this month's utilities.
e. Owner (Valdez) withdrew $4,500 cash from the company for personal use.
Carmen Camry operates a consulting firm called Help Today. On August 31, the company's records sh
the following accounts and amounts for the month of August. Use this information to prepare an Augi
income statement for the business.
B
Cash.
Accounts receivable
Office supplies
Land
Office equipment
Accounts payable
C. Camry, Capital, July 31.
$25,360
22,360
5,250
44,000
20,000
10,500
2,000
C. Camry, Withdrawals
Consulting fees earned.
Use the information in Exercise 2-13 to prepare an August statement of owner's equity for Help Toda
(The owner invested $100,000 cash in the company during the first week of August.)
Beginning of the year
End of the year
Rent expense
Salaries expense.
Telephone expense
Miscellaneous expenses.
Owner investment made on August 4
Use the information in Exercise 2-13 (if completed, you can also use your solution to Exercise 2-14)
prepare an August 31 balance sheet for Help Today.
A sole proprietorship had the following assets and liabilities at the beginning and
Window Help
1
2 Equity, December 31, 2012
3 Owner investments during the year
4 Owner withdrawals during the year
5 Net income (loss) for the year
6 Equity, December 31, 2013
7
KHASheet1 / Sheet2 Sheets/
Σ £ 271 E 100%
Assets
$ 60,000
105,000
$
Determine the net income earned or net loss incurred by the business during the year for each of the follo
ing separate cases:
a. Owner made no investments in the business and no withdrawals were made during the year.
b. Owner made no investments in the business but withdrew $1,250 cash per month for personal use.
c. Owner made no withdrawals during the year but did invest an additional $55,000 cash.
d. Owner withdrew $1,250 cash per month for personal use and invested an additional $35,000 cash.
Compute the missing amount for each of the following separate companies a through d.
File Edit View Insert Format Tools Data
DD
AV
Genev
(a)
Liabilities
$20,000
36,000
0 $
110,000
?
22,000
104,000
$ 6,000
27,000
9,550
5,600
860
520
100,000
C
(b)
of this year.
BYUE
D
E
(c) (d)
0 $ 0
?
87,000 210,000
(47,000) (10,000) (55,000)
90,000 (4,000)
85,000 ?
?
110,000
DU

Transcribed Image Text:Chapter 2 Analyzing and Recording Transactions
Groro Co. bills a client $62,000 for services provided and agrees to accept the following three items in full
payment: (1) $10,000 cash, (2) computer equipment worth $80,000, and (3) to assume responsibility for a
$28,000 note payable related to the computer equipment. The entry Groro makes to record this transaction
includes which one or more of the following?
a. $28,000 increase in a liability account
b. $10,000 increase in the Cash account
c. $10,000 increase in a revenue account
2
5
d. $62,000 increase in an asset account
e. $62,000 increase in a revenue account
f. $62,000 increase in an equity account
Prepare general journal entries for the following transactions of a new company called Pose-for-Pics.
Aug. 1
Madison Harris, the owner, invested $6,500 cash and $33,500 of photography equipment in the
company.
The company paid $2,100 cash for an insurance policy covering the next 24 months.
The company purchased office supplies for $880 cash.
20 The company received $3,331 cash in photography fees earned.
31
The company paid $675 cash for August utilities.
Use the information in Exercise 2-7 to prepare an August 31 trial balance for Pose-for-Pics. Begin by
opening these T-accounts: Cash; Office Supplies; Prepaid Insurance; Photography Equipment; M. Harris,
Capital; Photography Fees Earned; and Utilities Expense. Then, post the general journal entries to these
T-accounts (which will serve as the ledger), and prepare the trial balance.
Prepare general journal entries to record the transactions below for Spade Company by using the fol-
lowing accounts: Cash; Accounts Receivable; Office Supplies; Office Equipment; Accounts Payable;
K. Spade, Capital; K. Spade, Withdrawals; Fees Earned; and Rent Expense. Use the letters beside each
transaction to identify entries. After recording the transactions, post them to T-accounts, which serves
as the general ledger for this assignment. Determine the ending balance of each T-account.
a. Kacy Spade, owner, invested $100,750 cash in the company.
b. The company purchased office supplies for $1,250 cash.
c. The company pur
$10,050 of office equipment on credit.
d. The company received $15,500 cash as fees for services provided to a customer.
e. The company paid $10,050 cash to settle the payable for the office equipment purchased in transaction c.
f. The company billed a customer $2,700 as fees for services provided.
g. The company paid $1,225 cash for the monthly rent.
h. The company collected $1,125 cash as partial payment for the account receivable created in transaction f.
i. Kacy Spade withdrew $10,000 cash from the company for personal use.
After recording the transactions of Exercise 2-9 in T-accounts and calculating the balance of each account,
prepare a trial balance. Use May 31, 2013, as its report date.
Examine the following transactions and identify those that create revenues for Valdez Services, a company
owned by Brina Valdez. Prepare general journal entries to record those revenue transactions and explain
why the other transactions did not create revenues.
a. Brina Valdez invests $39,350 cash in the company.
b. The company provided $2,300 of services on credit.
c. The company provided services to a client and immediately received $875 cash.
d. The company received $10,200 cash from a client in payment for services to be provided next year.
e. The company received $3,500 cash from a client in partial payment of an account receivable.
f. The company borrowed $120,000 cash from the bank by signing a promissory note.
Exercise 2-6
Analyzing effects of
transactions on accounts
A1
review
Exercise 2-7
Preparing general journal
entries
P1-
Exercise 2-8
Preparing T-accounts (ledger)
and a trial balance P2
V
low
Exercise 2-9
Recording effects of transactions
in T-accounts
A1
Check Cash ending balance,
$94,850
79
HW ✓
Exercise 2-10
Preparing a trial balance P2
Exercise 2-11
Analyzing and journalizing
revenue transactions
A1 P1 I
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Connect Homework 11/25/19 I have attached a copy of a homework assignment I just took. Would you please give me the correct answers.arrow_forwardapter 13 Homework 4 2 of 6 Book - rint ences Required information [The following information applies to the questions displayed below.] Simon Company's year-end balance sheets follow. At December 31 Assets Cash Accounts receivable, net Merchandise inventory Prepaid expenses Plant assets, net Total assets Required 1A Liabilities and Equity Accounts payable Long-term notes payable. Common stock, $10 par value Retained earnings Total liabilities and equity For both the current year and one year ago, compute the following ratios: Required 18 Current Year: 1 Year Ago: 2 Years Ago: Required 2A (1-a) Compute the current ratio for each of the three years. (1-b) Did the current ratio improve or worsen over the three-year period? (2-a) Compute the acid-test ratio for each of the three years. (2-b) Did the acid-test ratio improve or worsen over the three-year period? Compute the acid-test ratio for each of the three years. McGraw-Hill Connect Complete this question by entering your answers in the…arrow_forwardCh14arrow_forward
- < Prev Ne Question 1 View Policies Current Attempt in Progress ns Match the following statements to the appropriate terms. The entire group of accounts maintained by a company. On- Transferring journal entries to ledger accounts. The side which increases an account. A list of all the accounts used by a company. An accounting record of increases and decreases in specific assets, liabilities, and stockholders' equity items. Left side of an account. Evidence that a transaction has taken place. Shows the debit and credit effects of specific transactions. A list of accounts and their balances at a given time. Has a credit normal balance eTextbook and Media Attempts: 0 of 3 used Submit Answ Save for Later IIarrow_forwardQ. 6 You are examining a company’s balance sheet and find that it has a total assets of $@0,572, a cash balance of $2,208, inventory of $4,913, current liabilities of $5,829 and accounts receivable of $2,727. What is the company’s net working capital? A. $894 B. $1,811 C. $5,807 D. $14,743 E. $4,019arrow_forwardPlease do not give image formatarrow_forward
- Answer 16arrow_forwardQuestion 10 Cash $ 14,890 Cash withdrawals by owner $ 930 Accounts receivable 12,820 Consulting revenue 12,820 Office supplies 2,290 Rent expense 2,530 Land 45,960 Salaries expense 5,780 Office equipment 16,900 Telephone expense 790 Accounts payable 7,670 Miscellaneous expenses 610 Owner investments 83,010arrow_forwardQuestion 1 of 13 Current Attempt in Progress Suppose the following selected condensed data are taken from a recent balance sheet of Bob Evans Farms (in millions of dollars Cash Accounts receivable Inventory Other current assets Total current assets Total current liabilities Working capital Compute working capital and the current ratio. (For working capital, enter answer in millions of dollars. If answer is negative enter it with a negative sign preceding the number e.g.-15.2 or in parentheses eg. (15.2). Round current ratio to 2 decimal places, e.g. 0.78:1) Current ratio $ $31.2 21.1 28.2 25.9 eTextbook and Media $106.4 $190.0arrow_forward
- QUESTION 10 The cash invested in the busìness by the owner is known as? a. Shares b.Capital c. Loan d. Profitarrow_forwardV SC Chapter 1 Homework Question 10 of 10 Cash 1 ! Accounts receivable Service revenue 0 Z Supplies Advertising expense Equipment Common stock On June 1, 2025, Crane Service Co. was started with an initial investment in the company of $26,000 cash. Here are the a liabilities, and common stock of the company at June 30, 2025, and the revenues and expenses for the month of June, its f operations: Q 2 < W $4,850 J 4,250 7,800 2,329 400 30,200 26,000 JAN 26 180 # 3 During June, the company issued no additional stock but paid dividends of $1,521. E Notes payable Accounts payable Supplies expense Maintenance and repairs expense Utilities expense Salaries and wages expense $ 4 Virtual muesum education.wiley.com 000 000 R DOCX % 5 2 T $12,500 6 750 1,100 690 210 1,500 OneDrive Ⓒ MacBook Pro Y & 7 IMG_4270.jpg tv A & & C U * 00 8 -/5 1 E ( Sarrow_forwardQuestion 2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education