
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
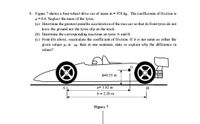
Transcribed Image Text:8. Figure 7 shows a four-wheel drive car of mass m = 970 kg. The coefficients of friction is
H=0.6. Neglect the mass of the tyres.
(a) Determine the greatest possible acceleration of the race car so that its front tyres do not
kave the ground nor the tyres slip on the track.
(b) Determine the corresponding reactions on tyres A and B.
(c) From (b) above, recaleulate the coefficient of friction. If it is not same as either the
given values Hs or k, then in one sentence, state or explain why the difference in
values?
h=0.55 m
a= 1,82 m
b = 2.20 m
Figure 7
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4 10 points A file cabinet weighing 215 lb is being pushed to the right with a horizontal force P applied a distance h from the floor. The width of the file cabinet is w = 15 in., its mass center G is a distance d = 2 ft above the floor, and static friction is insufficient to prevent slipping between the cabinet and the floor. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the cabinet and the floor is Uk = 0.28. Take the value of P to be 70 lb. 01 0!!! 01 Determine the maximum height ʼn at which the cabinet can be pushed so that it does not tip over, and find the corresponding acceleration of the cabinet. The maximum height at which the cabinet can be pushed so that it does not tip over is The acceleration of the cabinet is 1.466 ft/s². 1.7 x ft.arrow_forwardA 10000N weight is to be lowered by a vertical cylinder as shown in Figure . The cylinder hasa 75−mm−diameter piston and a 50−mm− diameter rod. The weight is to decelerate from100m/min to stop in 0.5s. Determine the required pressure in the rod end of the cylinderduring the deceleration motion.arrow_forwardF2 Problem 2. EOM Derivation Derive the equation of motion for the following system: F3 F4 Dry Friction= Fµ m Q Search DII % y(t) F5 ☀ F6 A F7 7 PrtScn F8 * M Home F9 B Earrow_forward
- A uniform, solid cylinder of mass mc=7.42 kg and radius R=.26 m with Icm=1/2MR^2 is attached at its axle to a string. The string is wrapped around a small ideal pulley and is attached to a hanging block of mass mb=2.73 kg as indicated in the figure above. You release the objects from rest and the cylinder rolls without slipping. What is the magnitude of the acceleration of the block?arrow_forwardA block of mass, m = 20 kg, rests on the inclined plane shown. What is the minimum force, P, required to maintain equilibrium of the block? The static coefficient of friction is 0.2 and the kinetic coeficcient of friction is 0.15 M 25° P 80⁰ Solve the problem and answer the questions that follow.arrow_forwardThe uniform blocks A and B weigh 90lb and 60lb, respectively. The coefficients of static friction at the three contacting surfaces are shown in the figure. Find the maximum value for P in the direction shown which maintains static equilibrium. The sliding surfaces are flat and parallel to the applied force P.arrow_forward
- 7. 2) The lawn roller has a mass m = 55 kg and a radius of gyration about its gravitational center G, kG = 196 mm. It has a handle that connects to its center axle, and the handle is pushed forward with a force F = 420 N at a 45° angle. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the roller and the ground are us = 0.11 and Hk = 0.08, respectively. For the sets of parameters listed below, determine the magnitude of the roller's angular acceleration (in rad/s²). Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. Take g = 9.81 m/s?. F 45° 200 mm Aarrow_forwardB6arrow_forwardThe figure shows a graph of force against distance for a locomotive pushing a carriage along a train track. x (m) Note: Please enter all your answers in this question to full precision. For the case where x:= 330 m x,= 750 m x, =1260 m and Fmax 31000 N, calculate the work done by the locomotive in megajoules for: (a) the part of the journey where the force is increasing (i.e. the first stage): MJ (b) the part of the journey where the force is constant (i.e. the second stage): MJ (c) the part of the journey where the force is decreasing (l.e. the third stage): MJ (d) Calculate the total work done by the locomotive: MJarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY