
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:e.co
CU
ct
sona-
n
ect Pool
artment...
W
24,919
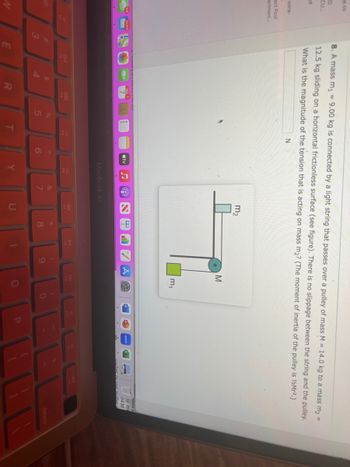
8. A mass m₁ = 9.00 kg is connected by a light string that passes over a pulley of mass M = 14.0 kg to a mass m₂ =
12.5 kg sliding on a horizontal frictionless surface (see figure). There is no slippage between the string and the pulley.
What is the magnitude of the tension that is acting on mass m₂? (The moment of inertia of the pulley is ½/Mr².)
N
#
3
20
$
4
R
999
F4
%
5
FS
^
6
tv
©
MacBook Air
Y
&
7
m₂
F7
*
8
Dall
1
(
9
M
m₁
A 02
DD
)
0
P
ISULI H
by mi
04 M
vauies or roe puffer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two weights attached to a uniform beam of mass 38 kg are supported in a horizontal position by a pin and cable as shown in the figure. 2.4 m kN. 38 kg 11 kg 5.9 m 43° 34 kg What is the tension in the cable which sup- ports the beam? The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s². Answer in units of kN. Answer in units of Your response... i Previous Responses X #1.0.6495 PALETTEarrow_forwardA weight with mass mw = 250 g is tied to a piece of thread wrapped around a spool, which is suspended in such a way that it can rotate freely. When the weight is released, it accelerates toward the floor as the thread unwinds. Assume that the spool can be treated as a uniform solid cylinder of radius R = 3.00 cm and mass Ms 100 g . M, Find the magnitude a of the acceleration of the weight as it descends. Assume the thread has negligible mass and does not slip or stretch as it unwinds. Use g = 9.81 m/s?. m a = mw Find the tension T in the thread.arrow_forwardThe figure shows an arrangement in which four disks are suspended by cords. The longer, top cord loops over a frictionless pulley and pulls with a force of magnitude 86.2 N on the wall to which it is attached. The tensions in the shorter cords are T₁ = 60.1 N, T₂ = 33.1 N, and T3 = 8.21 N. What are the masses of (a) disk A, (b) disk B, (c) disk C, and (d) disk D? (a) Number (b) Number (c) Number (d) Number Units Units Units Units A B D Ti T₂ T3 SUPPORarrow_forward
- 1.0m 3.0m 0.5m mi m, PA N, 5. The drawing above shows two objects on a board supported at two locations. The m; = 40 kg (centered over P), m2=20 kg and m3=10 kg. a. Show the forces acting on the board below with arrows with labels beginning at their approximate point of application (see example for the force exerted by m;). (Don't forget the gravitational forces acting on the board.) P F1arrow_forwarda 4kg block is attached to the vertical pole by two strings. when the system rotates about the axis of the pole the two strings are extended as shown in the diagram, the tension in the upper string is 88N. find the tension in the lower string, the rev/min the system makes normally and when the lower cord just goes slack.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows two blocks connected by a string of negligible mass passing over a frictionless pulley. m₁ = 4.8 kg and 8 = 12.0°. Assume that the incline is smooth. m, m₁ For what value of m₂ (in kg) will the system be in equilibrium? m₂ 23.1 kg = If the block has to slide down the incline with an acceleration of 1.1 m/s², what should be the value of m₂ (in kg)? m₂ kgarrow_forward
- Children playing pirates have suspended a uniform wooden plank with mass M = 13.4 kg, length ℓ = 2.40 m, and angle θ = 35.0°, as shown in the figure. Sophia, with a mass of m = 21.6 kg, is made to "walk the plank" and is d = 1.5 m from reaching the end of the plank. What is the tension acting on the rope at the end (i.e value of F3)?arrow_forwardIn the Atwood machine shown below, ml = 2.00-kg and m2 = 5.60-kg. The masses of the pulley and string are negligible by comparison. The pulley turns without friction and the string does not stretch. The lighter object is released with a sharp push that sets it into motion at vi = 2.15 m/s downward. How long will it take for mị to reach the lowest level? m1 m2arrow_forwardIn a “Giant Swing” shown in figure, the seat is connected to two cables. One is from the top of the central shaft which makes an angle of 40.0° with the vertical and the other cable of 7.50 m is horizontal. The seat swings in a horizontal circle at a rate of 25.1 m/s. If the seat weighs 245 N and a 540 N person is sitting in it, find the tension in each cable.arrow_forward
- In the figure shown below, the 4 forces are being supported by an eyebolt. Determine the force F2 (in kN, roundoff to 2 decimal places) that would produce a net effect on the bolt of R direct pull along the horizontal. F1=2KN R=3KN F3=1.2kN a=30° F4=1.8KN B=30° F1 y -F2 F3 F4 α В Ꮎarrow_forwardObjects of masses m1 = 4.00 kg and m2 = 9.00 kg are connected by a light string that passes over a frictionless pulley as in the figure below. The object m1 is held at rest on the floor, and m2 rests on a fixed incline of θ = 39.5°. The objects are released from rest, and m2 slides 1.25 m down the slope of the incline in 3.85 s. A triangular structure is oriented such that its base rests upon a horizontal surface, its left side is perpendicular to its base, and its right side forms an incline of angle θ. A pulley is attached to the structure's apex. Two objects are connected by a cord that passes over the pulley. An object labeled m1 is attached to the left end of the cord and hangs such that it is very close to the horizontal surface. A rectangular object labeled m2 is attached to the end of the cord and rests upon the incline. A pale image of m1 is above m1, and a pale image of m2 is farther down the incline than m2. (a) Determine the acceleration of each object. (Enter…arrow_forward4arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON