
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780134753119
Author: Sheldon Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
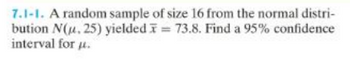
Transcribed Image Text:7.1-1. A random sample of size 16 from the normal distri-
bution N(u. 25) yielded = 73.8. Find a 95% confidence
interval for u.
![7.1-1 [71.35. 76.25].](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/2b62c17d-5c05-48d6-ac2b-a3a7c31907f7/f9a7a48b-d05f-4dcf-aaeb-041522e7c7eb/z8fqvle_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:7.1-1 [71.35. 76.25].
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 10.29 Past experience indicates that the time required for high school seniors to complete a standardized test is a normal random variable with a mean of 35 minutes. If a random sample of 20 high school seniors took an average of 33.1 minutes to complete this test with a standard deviation of 4.3 minutes, test the hypothesis, at the 0.05 level of significance, that μ = 35 minutes against the alternative that μ < 35 minutes.arrow_forwardUse the t-distribution and the given sample results to complete the test of the given hypotheses. Assume the results come from random samples, and if the sample sizes are small, assume the underlying distributions are relatively normal. Test Ho : HA = Ha VS H. : HA # Hg using the fact that Group A has 8 cases with a mean of 125 and a standard deviation of 18 while Group B has 15 cases with a mean of 118 and a standard deviation of 14. (a) Give the test statistic and thep-value. Round your answer for the test statistic to two decimal places and your answer for the p- value to three decimal places. test statistic = p-value = eTextbook and Media (b) What is the conclusion of the test? Test at a 10% level. O Reject Ho. O Do not reject Ho. eTextbook and Mediaarrow_forwardsuppose that 43% of people who enter a store will make a purchase. Random samples of people who walk into a particular store is studied, and the proportion of those who made a purchase is found for each sample. Assume that all the samples were the same size. If 29.46% of all sample proportions are less than 0.3274. What was the z-score for 0.3274? What is σp′?arrow_forward
- A sample of n 4 scores is selected from a population with an unknown mean. The sample has a mean of M= 40 and a variance of s² = 16. Which of the following is the correct 90% confidence interval for u? %3D O H = 40 + 1.638(4) O H = 40 + 2.353(4) OH= 40 + 1.638(2) Ομ= 40+ 2.353(2)arrow_forward7.1-1arrow_forwardSuppose a marketing company randomly surveyed 404 households and found that in 214 of them, the woman made the majority of the purchasing decisions. Construct a 90% confidence interval for the population proportion of households where the women make the majority of the purchasing decisions.p'=α2=zα2=Margin of Error: E=We are 90% confident that the proportion of households in the population where women make the majority of purchasing decisions is between___ and ___.arrow_forward
- Independent samples of size n1 = 25 and n2 = 36 are taken from two normal populations with knownstandard deviations of σ1 = 5.5 and σ2 = 4.2. e sample means are x¯1 = 13.6 and x¯2 = 19.2. Find a95% confidence interval for µ1 − µ2.arrow_forward5.6-4arrow_forward6.02 Consider X1,..., X100 iid. Obtain a 90% confidence interval for the mean response of X having observed ī = 3.5 and s² = 1.44.arrow_forward
- Suppose that we would like to test the following hypotheses on the population correlation coefficient ρ: H0: ρ ≤ 0 and H1: ρ > 0. The sample correlation coefficient (r) for a sample with 7 observations (n = 7) on x and y is 0.35 . Then the test statistic t has a value ofarrow_forwardFind the a/2 ( the area in one tail outside of the confidence interval) and the critical value z a/2 necessary to construct an 80% confidence interval.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)ProbabilityISBN:9780134753119Author:Sheldon RossPublisher:PEARSON

A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
Probability
ISBN:9780134753119
Author:Sheldon Ross
Publisher:PEARSON
