
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:A ng.cengage.com/static/nb/ui/evo/index.html?deploymentld%3598281247957E
1Gmail
E eAccount Quick Car..
B Calendar | Navigate
Main Street Comm.
劉 Ta
«
CENGAGE MINDTAP
Homework (Ch 10)
Back to Assignment
Atempts
Keep the Highest/3
Tools
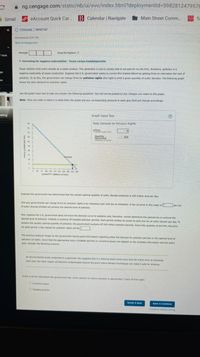
7. Correcting for negative externalities - Taxes versus tradablepermits
Power stations emit sultur dioxide as a waste product. This generates a cost to society that is not paid for by the firm; therefore, pollution is a
ps
negative externality of power production. Suppose the u.S. government wants to correct this market failure by getting firms to internalize the cost of
pollution. To da this, the government can charge firms for pollution rights (the right ta emit a given quandity of sulfur dioxide). The following graph
ps
shows the daly demand for polution rights.
Lise the graph input tool to hel you answer the fallowing questions. You wit not be praded on any changes you make to this graph.
Note: Once you enter a value in a white feld, the graph and any coresponding amounts in each grey field will change accordingly.
aking
Graph Input Tool
Daily Dernand for Polution Rights
Price
(Delarsper tan)
12
Quantity
Demanded
TMons of tan
315
54
27
bemand
25N s 140 17s a0 245 2ac s 0
QUANTITY Mons of sons)
Suppose the govemment has determined that the socaly optimal quantity of sultur diaxide emissions is 245 milion tons per day.
One way govermments can charge firms for poltion rights is by imposing a per unit tax on emissions. A tax for price in this case) of per ton
of sulfur dicide emitted will achieve the desired level of pollution.
Now suppose the U.S. government does not know the demand curve for pollution and, therefore, cannot determine the optimal tax to achieve the
desired level of pollution. Instead, it auctions off tradable potution permits. Each permit entities its owner to emit one ton of sufur dexide per day. To
achieve the socially optimal quantity of polution, the government auctions off 24S million polution permits. Given this quantity of permts, the price
for each permit in the market for polution rights will bes
The previous analysis hinges on the government having good information regarding ether the demand for polution permits or the optimal level of
polution (or bath). Given that the approprate policy (tradatie permits or comective taxes) can depend on the avalable infomatian and the policy
goal, consider the folowing sconario
An environmental study conducted in a particular city suggests that if a chemical plart emits more than 90 milion tons of chemicals
each year, the water suppy will become contaminated beyond the point where naration techniques can make it sate for drinking
ar this is al the information the government has, which solution to reduce poluton is appropriate? Check al that apply
O Comective taxes
O tradable perits
Grade Now
Save & Continue
Corsnue withol saving
ad seonia
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1arrow_forwardfirms matter for efficiency? Explain. 9. There are three industrial firms in Happy Valley. Initial Pollution Cost of Reducing Firm Level Pollution by 1 Unit A 30 units $20 В 40 units $30 C 20 units $10 The government wants to reduce pollution to 60 units, so it gives each firm 20 tradable pollution permits. a. Who sells permits and how many do they sell? Who buys permits and how many do they buy? Briefly explain why the sellers and buyers are each willing to do so. What is the total cost of pollution reduction in this situation? b. How much higher would the costs of pollution reduction be if the permits could not be traded? Answersarrow_forward3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantityof consumption Consider the market for paper. Suppose that a paper factory dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the factory. Producing an additional ton of paper imposes a constant external cost of $385 per ton. The following graph shows the demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for paper. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $385 per ton. PRICE (Dollars per ton of paper) 1100 990 880 770 660 550 440 330 220 110 0 0 ☐ 1 ☐ 2 3 4 5 QUANTITY (Tons of paper) O n Supply 8 (Private Cost) Demand (Private Value) 7 Social Cost (?) The market equilibrium quantity is tons of paper, but the socially optimal quantity of paper production is To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal quantity of paper, the government could impose a of paper. tons. of $ per tonarrow_forward
- 3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantityof consumption Consider the market for paper. Suppose that a paper factory dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the factory. Producing an additional ton of paper imposes a constant external cost of $450 per ton. The following graph shows the demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for paper. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $450 per ton, 1500 PRICE (Dollars per ton of paper) 1350 1200 1050 900 750 600 450 300 150 0 D O QUANTITY (Tons of paper) Supply (Private Cost) The market equilibrium quantity is Demand (Private Value) Social Cost tons of paper, but the socially optimal quantity of paper production is To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal quantity of paper, the government could impose a of paper. tons. per tonarrow_forwardSuppose that a mayor of a large city believes strongly that education provides great benefits to the community andurges the state government to provide the district with more money. An economist would say that this reflects theMayor's belief that:Asince teachers are overpaid, the district needs more money to hire enough teachers for its classrooms.Bthere are positive external benefits associated with education.Cthere are nontrivial external costs associated with education.Dpublic schools provide a higher quality education than private schools.arrow_forwardGive proper exact answer to every part step by step and take a likearrow_forward
- 2. Efficiency in the presence of externalities Vaping imposes many external costs on society secondhand smoke, the adverse health burdens imposed on society, and so on. Therefore, the market equilibrium quiantity of vapes does not equal the socially optimal quantity. The following graph plots the demand for vapes (their private value), the supply of vapes (the private cost of producing them), and the social cost of vapes, including both the private cost and external costs. Use the block point (plus symbol) to indicate the market equilibrium quaneity Next, use the purple point (diamond symbol) to indicate the socially opamal quantity ? PRICE OF VAPES Demand (Private Value) QUANTITY OF VAPES Social Cost Supply (Private Cost) + Market Equilibrium Socially Optimal Levelarrow_forwardThere are two factories in a small town. Both of them emit carbon dioxide into the air. Their current monthly emissions, as well as their total costs for reducing emissions in 20-ton increments, are listed in the tables below. Factory 1 Current emissions (tons/month) 120 Total cost of reducing emissions by 20 tons/month $50 Total cost of reducing emissions by 40 tons/month Total cost of reducing emissions by 60 tons/month Total cost of reducing emissions by 80 tons/month Total cost of reducing emissions by 100 tons/month $150 $270 $410 $570 Factory 2 Current emissions (tons/month) 160 Total cost of reducing emissions by 20 tons/month $20 Total cost of reducing emissions by 40 tons/month $60 Total cost of reducing emissions by 60 tons/month $110 Total cost of reducing emissions by 80 tons/month $200 Total cost of reducing emissions by 100 tons/month $300arrow_forwardAccording to economists what is the optimal amount of pollution? O a. The optimal amount of pollution is where private costs equal social costs O b. Pollution should be reduced to a level as determined by government regulation O c. None, the goal is to completely eliminate pollution d. The point where the marginal benefit from further pollution reduction equals the marginal cost of further reductionarrow_forward
- 4arrow_forward3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantityof consumption Consider the market for pharmaceuticals. Suppose that a pharmaceutical factory dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the factory. Producing additional pharmaceuticals imposes a constant per-unit external cost of $280. The following graph shows the demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for pharmaceuticals. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $280 per unit. PRICE (Dollars per unit of pharmaceuticals) 800 720 640 560 480 400 320 240 160 80 O 1 2 3 □ O O ㅁ 4 Supply (Private Cost) Demand (Private Value) 5 6 7 QUANTITY (Units of pharmaceuticals) Social Cost ? The market equilibrium quantity is units of pharmaceuticals, but the socially optimal quantity of pharmaceuticals production is units. To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal…arrow_forwardQu 2 This question is chang before solution So plz do not copy past this answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education